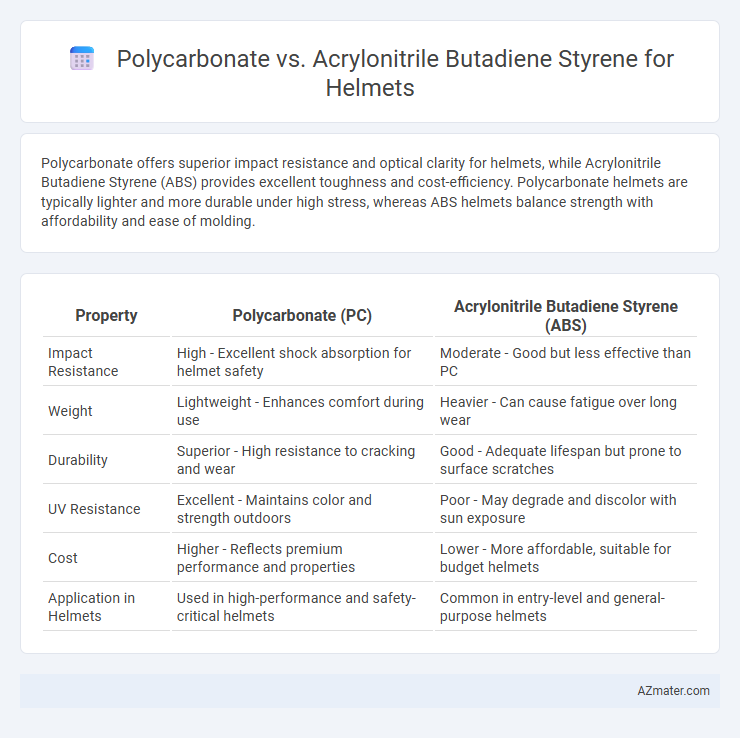
Polycarbonate offers superior impact resistance and optical clarity for helmets, while Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS) provides excellent toughness and cost-efficiency. Polycarbonate helmets are typically lighter and more durable under high stress, whereas ABS helmets balance strength with affordability and ease of molding.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Polycarbonate (PC) | Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS) |
|---|---|---|
| Impact Resistance | High - Excellent shock absorption for helmet safety | Moderate - Good but less effective than PC |
| Weight | Lightweight - Enhances comfort during use | Heavier - Can cause fatigue over long wear |
| Durability | Superior - High resistance to cracking and wear | Good - Adequate lifespan but prone to surface scratches |
| UV Resistance | Excellent - Maintains color and strength outdoors | Poor - May degrade and discolor with sun exposure |
| Cost | Higher - Reflects premium performance and properties | Lower - More affordable, suitable for budget helmets |
| Application in Helmets | Used in high-performance and safety-critical helmets | Common in entry-level and general-purpose helmets |
Introduction: Polycarbonate vs Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene for Helmet Manufacturing
Polycarbonate offers superior impact resistance and clarity, making it ideal for high-performance helmet manufacturing, while Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS) provides excellent toughness and cost-effectiveness. ABS helmets are lighter and easier to mold, which benefits mass production and design flexibility. The choice between Polycarbonate and ABS depends on factors like durability, weight, and budget constraints in helmet manufacturing.
Material Composition and Structural Properties
Polycarbonate helmets feature a polymer composed of bisphenol A and phosgene, offering high impact resistance and excellent optical clarity due to its amorphous, glass-like structure. Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS) helmets consist of three distinct monomers--acrylonitrile, butadiene, and styrene--providing a balance of toughness, flexibility, and thermal stability from its heterogeneous, rubber-reinforced matrix. The molecular arrangement in polycarbonate lends greater stiffness and resistance to cracking under high-impact conditions, whereas ABS combines rigidity with better resistance to abrasion and chemical exposure, making material selection crucial based on helmet application requirements.
Impact Resistance and Safety Standards
Polycarbonate helmets offer superior impact resistance due to their high energy absorption and shatterproof properties, making them ideal for high-performance safety applications. Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS) helmets provide good impact resistance but are generally less durable under extreme impacts compared to polycarbonate. Both materials meet key safety standards such as DOT, ECE, and Snell, but polycarbonate is often preferred for its enhanced ability to withstand multiple impacts without compromising structural integrity.
Weight and Comfort Considerations
Polycarbonate helmets offer a lightweight design, averaging 1000 grams, enhancing comfort for extended wear compared to Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS) helmets, which typically weigh around 1200 grams. The superior impact resistance and flexibility of polycarbonate contribute to a better fit and reduced pressure points, making it ideal for long-duration use. ABS helmets, while durable and cost-effective, often sacrifice some comfort due to their heavier weight and less adaptable shell structure.
Durability: Weather and UV Resistance
Polycarbonate helmets exhibit superior durability with excellent weather and UV resistance, maintaining structural integrity and clarity under prolonged sunlight exposure and extreme temperature variations. Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS) helmets offer moderate weather resistance but tend to degrade faster under UV exposure, leading to brittleness and color fading over time. Selecting polycarbonate enhances helmet longevity by providing better protection against environmental factors and maintaining impact resistance.
Heat and Chemical Resistance Comparison
Polycarbonate offers superior heat resistance with a glass transition temperature around 147degC, making it more effective in maintaining structural integrity under high temperatures than Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS), which has a lower heat resistance threshold near 105degC. Chemically, polycarbonate exhibits better resistance to oils, greases, and many solvents, whereas ABS is more vulnerable to degradation when exposed to harsh chemicals such as acetone and aromatic hydrocarbons. These properties make polycarbonate helmets more durable in high-heat and chemically aggressive environments compared to ABS helmets.
Cost and Manufacturing Efficiency
Polycarbonate helmets generally have higher material costs but offer superior impact resistance and clarity, making them ideal for premium safety gear. Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS) is more cost-effective and easier to mold, allowing for faster production cycles and lower manufacturing expenses. Manufacturers often choose ABS helmets for budget-conscious markets due to its balance of durability and affordability.
Design Flexibility and Aesthetics
Polycarbonate offers superior design flexibility for helmets due to its high impact resistance and ability to be molded into complex shapes, allowing for sleek, aerodynamic designs with vibrant color options. Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS) provides a more rigid structure, enabling sharp edges and varied textures but with limited color vibrancy compared to polycarbonate. Both materials deliver durable aesthetics, but polycarbonate's transparency and gloss finish often result in a more premium, visually appealing helmet design.
Environmental Impact and Recyclability
Polycarbonate helmets offer durability but pose environmental challenges due to their energy-intensive production and limited recyclability compared to Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS), which is easier to recycle and has a lower carbon footprint during manufacturing. ABS helmets can be reprocessed into new products more efficiently, reducing landfill waste and promoting circular economy practices. Choosing ABS over polycarbonate supports better environmental sustainability by minimizing ecological damage and facilitating material reuse.
Which Material is Best for Helmets?
Polycarbonate offers superior impact resistance and greater shatterproof qualities, making it ideal for helmets requiring high durability and safety in crash scenarios. Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS) is lighter and more cost-effective, providing good toughness and flexibility but with slightly less impact absorption compared to polycarbonate. For helmet safety standards, polycarbonate is generally considered the best material due to its enhanced strength and ability to withstand high-impact collisions.
Infographic: Polycarbonate vs Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene for Helmet
 azmater.com
azmater.com