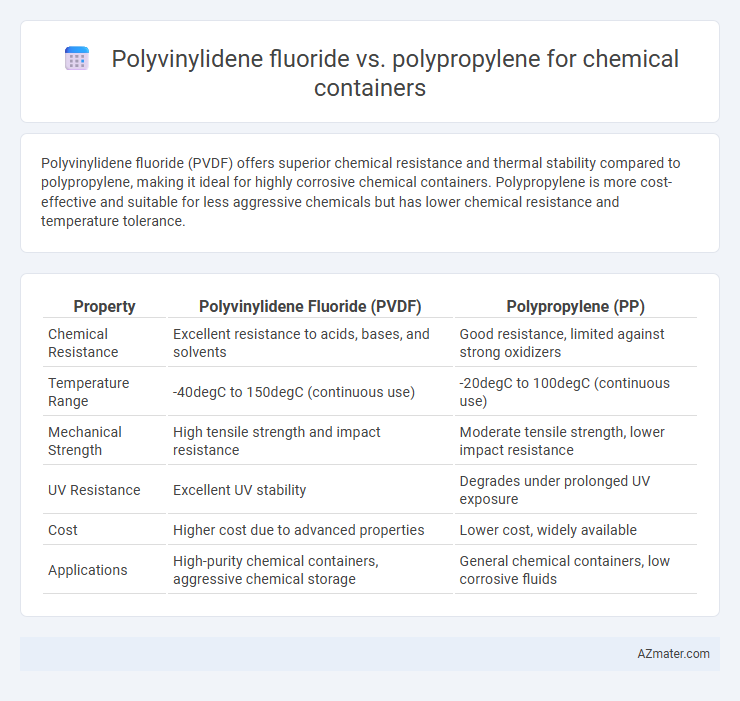
Polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF) offers superior chemical resistance and thermal stability compared to polypropylene, making it ideal for highly corrosive chemical containers. Polypropylene is more cost-effective and suitable for less aggressive chemicals but has lower chemical resistance and temperature tolerance.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Polyvinylidene Fluoride (PVDF) | Polypropylene (PP) |
|---|---|---|
| Chemical Resistance | Excellent resistance to acids, bases, and solvents | Good resistance, limited against strong oxidizers |
| Temperature Range | -40degC to 150degC (continuous use) | -20degC to 100degC (continuous use) |
| Mechanical Strength | High tensile strength and impact resistance | Moderate tensile strength, lower impact resistance |
| UV Resistance | Excellent UV stability | Degrades under prolonged UV exposure |
| Cost | Higher cost due to advanced properties | Lower cost, widely available |
| Applications | High-purity chemical containers, aggressive chemical storage | General chemical containers, low corrosive fluids |
Introduction to Chemical Container Materials
Polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF) offers exceptional chemical resistance, high purity, and thermal stability, making it ideal for containers used in aggressive chemical environments. Polypropylene (PP) is valued for its cost-effectiveness, good chemical resistance, and flexibility but has lower thermal resistance and durability compared to PVDF. Selection between PVDF and PP depends on the specific chemical compatibility, temperature requirements, and mechanical stress expected in storage applications.
Overview of Polyvinylidene Fluoride (PVDF)
Polyvinylidene Fluoride (PVDF) is a high-performance fluoropolymer known for its exceptional chemical resistance, high purity, and excellent mechanical strength, making it ideal for chemical container applications. PVDF exhibits superior resistance to a wide range of acids, bases, and solvents compared to Polypropylene, which is more prone to chemical degradation over time. Its high thermal stability and low permeability further enhance its suitability for storing aggressive chemicals, ensuring long-term durability and safety in industrial environments.
Overview of Polypropylene (PP)
Polypropylene (PP) is a thermoplastic polymer widely used for chemical containers due to its excellent chemical resistance, especially against acids, bases, and solvents. It offers high impact strength, good fatigue resistance, and maintains structural integrity over a broad temperature range from -20degC to 120degC. PP is lightweight, cost-effective, and resistant to stress cracking, making it a preferred choice for many industrial chemical storage applications.
Chemical Resistance Comparison: PVDF vs PP
Polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF) exhibits superior chemical resistance compared to polypropylene (PP), especially against strong acids, bases, and organic solvents, making it ideal for harsh chemical environments. PVDF maintains structural integrity and resists degradation at higher temperatures and prolonged exposure to aggressive chemicals, whereas PP may degrade or swell under similar conditions. This elevated chemical durability of PVDF ensures longer service life and reliability in chemical container applications requiring exposure to highly corrosive substances.
Mechanical Strength and Durability
Polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF) offers superior mechanical strength and chemical resistance compared to polypropylene, making it ideal for chemical containers that require long-term durability under harsh conditions. PVDF exhibits high tensile strength and excellent resistance to impact, UV radiation, and chemical corrosion, ensuring structural integrity over extended use. In contrast, polypropylene is less resistant to chemicals and mechanical stress, which can lead to faster degradation and reduced container lifespan in aggressive chemical environments.
Temperature Resistance and Thermal Stability
Polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF) offers superior temperature resistance, maintaining stability up to 150degC, compared to polypropylene (PP), which typically withstands temperatures only up to 100degC. PVDF's high thermal stability makes it ideal for chemical containers exposed to elevated temperatures and aggressive solvents. Polypropylene, while cost-effective and chemically resistant, is better suited for applications involving lower temperature ranges and less demanding thermal conditions.
Cost Analysis: PVDF vs Polypropylene
Polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF) exhibits higher initial costs compared to polypropylene due to its superior chemical resistance and thermal stability, making it ideal for aggressive chemical storage. Polypropylene offers a more budget-friendly option with acceptable chemical compatibility for less demanding environments, resulting in lower upfront investment but potentially higher long-term maintenance. Cost analysis must consider the balance between PVDF's durability and longevity versus polypropylene's affordability and frequent replacement needs.
Common Applications in Chemical Storage
Polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF) and polypropylene (PP) are widely used in chemical storage containers due to their exceptional chemical resistance. PVDF excels in storing aggressive acids, bases, and solvents, often utilized in pharmaceutical, chemical processing, and semiconductor industries requiring high purity and durability. Polypropylene is favored for general-purpose chemical containers handling alkalis, acids, and aqueous solutions in agricultural, food processing, and industrial sectors, offering cost-effective and versatile storage solutions.
Environmental and Safety Considerations
Polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF) offers superior chemical resistance and UV stability compared to polypropylene, making it a more durable choice for long-term chemical storage with lower risk of degradation and leaching. PVDF is inherently flame retardant and has a higher melting point, enhancing safety in high-temperature or fire-prone environments, while polypropylene is more prone to deformation under heat and less resistant to some aggressive chemicals. From an environmental perspective, polypropylene is more widely recyclable and has a lower production carbon footprint, but PVDF's longevity can reduce the frequency of container replacement, potentially lowering overall environmental impact in chemical containment applications.
Choosing the Right Material for Chemical Containers
Polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF) offers superior chemical resistance and thermal stability compared to polypropylene (PP), making it ideal for containers exposed to aggressive solvents and high temperatures. PP provides excellent impact resistance and cost efficiency but is less resistant to strong acids and solvents, limiting its use in highly corrosive environments. Selecting PVDF or PP depends on the specific chemical compatibility requirements, operating temperature, and budget constraints to ensure safe and durable chemical storage.
Infographic: Polyvinylidene fluoride vs Polypropylene for Chemical Container
 azmater.com
azmater.com