Polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF) offers superior chemical resistance and thermal stability compared to Polystyrene, making it ideal for high-performance insulation applications. Polystyrene provides cost-effective insulation with good moisture resistance but lacks the durability and temperature tolerance of PVDF.
Table of Comparison
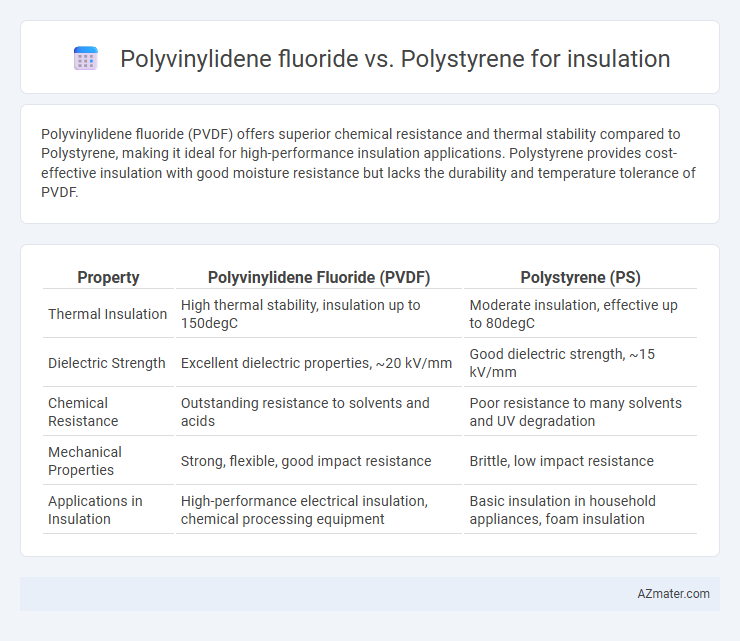
| Property | Polyvinylidene Fluoride (PVDF) | Polystyrene (PS) |
|---|---|---|
| Thermal Insulation | High thermal stability, insulation up to 150degC | Moderate insulation, effective up to 80degC |
| Dielectric Strength | Excellent dielectric properties, ~20 kV/mm | Good dielectric strength, ~15 kV/mm |
| Chemical Resistance | Outstanding resistance to solvents and acids | Poor resistance to many solvents and UV degradation |
| Mechanical Properties | Strong, flexible, good impact resistance | Brittle, low impact resistance |
| Applications in Insulation | High-performance electrical insulation, chemical processing equipment | Basic insulation in household appliances, foam insulation |
Overview of Polyvinylidene Fluoride (PVDF) and Polystyrene
Polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF) is a highly non-reactive and pure thermoplastic fluoropolymer known for its strong chemical resistance, excellent thermal stability up to 150degC, and outstanding mechanical properties, making it suitable for high-performance insulation applications. Polystyrene, a widely used aromatic polymer, offers good electrical insulation, low moisture absorption, and excellent dimensional stability but has lower thermal resistance, typically up to 70-90degC, limiting its use in high-heat environments. PVDF's superior durability and resistance to UV radiation contrast with polystyrene's cost-effectiveness and ease of fabrication, influencing the selection based on specific insulation requirements.
Chemical Structure and Composition Comparison
Polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF) consists of repeating units of -CH2-CF2-, giving it strong carbon-fluorine bonds that contribute to exceptional chemical resistance, thermal stability, and dielectric properties ideal for insulation. Polystyrene is composed of styrene monomers featuring a phenyl group attached to a carbon chain, providing good dielectric strength but lower temperature resistance and chemical stability compared to PVDF. The fluorinated backbone of PVDF offers superior durability and performance in harsh environments, while polystyrene's hydrocarbon structure makes it more susceptible to degradation under thermal and chemical stress.
Insulation Performance: Thermal Conductivity Analysis
Polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF) exhibits superior insulation performance compared to polystyrene, with a lower thermal conductivity typically around 0.12 W/m*K, enhancing its efficiency in thermal insulation applications. Polystyrene, while widely used, has a thermal conductivity ranging from 0.03 to 0.04 W/m*K in expanded form but generally performs less effectively in harsh environments due to lower chemical resistance. The reduced thermal conductivity and higher durability of PVDF make it a preferred material for demanding insulation requirements in industries like electronics and aerospace.
Moisture Resistance Capabilities
Polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF) exhibits superior moisture resistance compared to polystyrene, making it ideal for insulation in humid or wet environments. PVDF's low water absorption rate and excellent chemical stability prevent degradation and maintain insulating properties under moisture exposure. Polystyrene, while a common insulation material, tends to absorb more water leading to reduced thermal efficiency and potential material breakdown over time.
Mechanical Strength and Durability
Polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF) exhibits superior mechanical strength and durability compared to polystyrene (PS), making it highly suitable for insulation in demanding environments. PVDF offers excellent impact resistance, chemical stability, and UV resistance, ensuring long-term performance under mechanical stress and harsh weather conditions. In contrast, polystyrene, while cost-effective and lightweight, tends to be more brittle and susceptible to cracking over time, limiting its durability in structural insulation applications.
Fire Safety and Flammability Ratings
Polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF) exhibits superior fire safety characteristics with high flame retardancy and a UL94 V-0 flammability rating, making it highly resistant to ignition and self-extinguishing. Polystyrene, while commonly used for insulation, has a lower fire resistance and typically carries a UL94 HB rating, indicating a higher flammability and greater risk of sustained burning. PVDF's chemical structure offers enhanced thermal stability and reduced smoke emission compared to polystyrene, making it a safer choice for applications requiring stringent fire safety standards.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF) offers superior chemical resistance and longer lifecycle stability compared to polystyrene (PS), resulting in less frequent replacement and reduced environmental waste. Polystyrene is derived from non-renewable petroleum sources and presents significant challenges in biodegradability, contributing to persistent landfill accumulation and microplastic pollution. PVDF's recyclability and lower volatile organic compound emissions enhance its sustainability profile in insulation applications, making it a more environmentally responsible choice.
Installation Process and Practical Considerations
Polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF) offers superior chemical resistance and flexibility, requiring specialized adhesives and careful handling during installation to maintain its durability and performance in insulation applications. Polystyrene, commonly used in foam board insulation, is easier to cut and install with standard fasteners but is susceptible to moisture absorption and flammability concerns, necessitating protective barriers or coatings. Practical considerations include PVDF's higher cost and installation complexity balanced against long-term resilience, while polystyrene provides cost-effective, quick installation suitable for less demanding environmental conditions.
Cost Comparison: PVDF vs Polystyrene
Polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF) insulation typically incurs higher material and manufacturing costs compared to polystyrene due to its superior chemical resistance and thermal stability. Polystyrene insulation offers a more budget-friendly option, favored for its lower production expenses and widespread availability, making it popular in large-scale applications. Cost efficiency in insulation projects often favors polystyrene unless the enhanced durability and performance of PVDF justify the additional investment.
Application Suitability and Industry Recommendations
Polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF) offers superior chemical resistance, thermal stability, and UV durability, making it ideal for harsh industrial insulation applications such as chemical processing plants and outdoor electrical insulation. Polystyrene, known for its excellent electrical insulating properties and cost-effectiveness, is preferred in residential and low-temperature applications like packaging insulation and electronic housings. Industry recommendations favor PVDF for long-term, high-performance insulation needs due to its robustness, while polystyrene remains a practical choice for budget-sensitive, less demanding insulation environments.
Infographic: Polyvinylidene fluoride vs Polystyrene for Insulation
 azmater.com
azmater.com