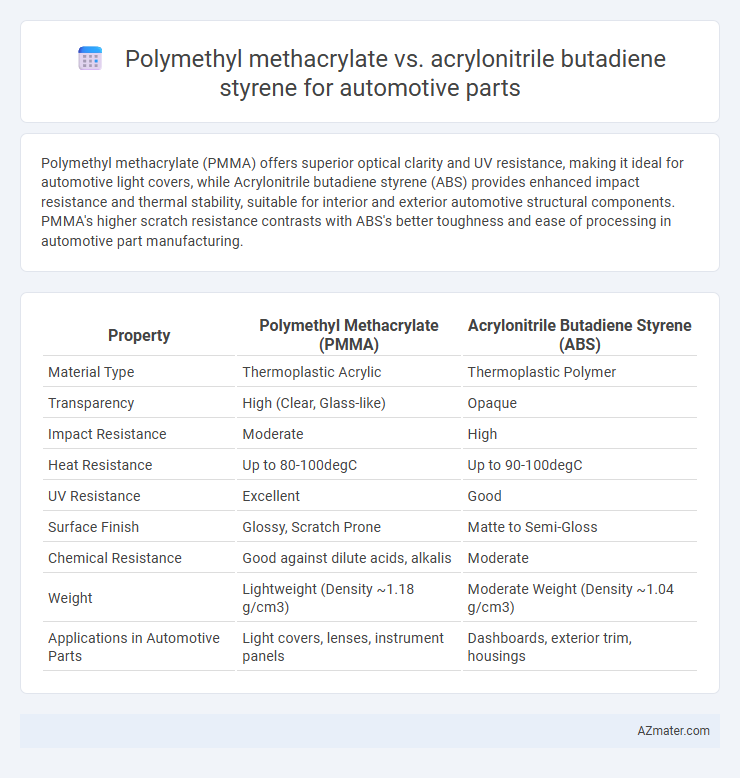
Polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA) offers superior optical clarity and UV resistance, making it ideal for automotive light covers, while Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS) provides enhanced impact resistance and thermal stability, suitable for interior and exterior automotive structural components. PMMA's higher scratch resistance contrasts with ABS's better toughness and ease of processing in automotive part manufacturing.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Polymethyl Methacrylate (PMMA) | Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS) |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Thermoplastic Acrylic | Thermoplastic Polymer |
| Transparency | High (Clear, Glass-like) | Opaque |
| Impact Resistance | Moderate | High |
| Heat Resistance | Up to 80-100degC | Up to 90-100degC |
| UV Resistance | Excellent | Good |
| Surface Finish | Glossy, Scratch Prone | Matte to Semi-Gloss |
| Chemical Resistance | Good against dilute acids, alkalis | Moderate |
| Weight | Lightweight (Density ~1.18 g/cm3) | Moderate Weight (Density ~1.04 g/cm3) |
| Applications in Automotive Parts | Light covers, lenses, instrument panels | Dashboards, exterior trim, housings |
Introduction to PMMA and ABS in Automotive Applications
Polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA) is widely used in automotive applications for its excellent optical clarity, weather resistance, and UV stability, making it ideal for headlight lenses and exterior trim components. Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS) offers high impact resistance, toughness, and good mechanical properties, which are essential for interior parts, dashboards, and bumpers. Both PMMA and ABS contribute to lightweight vehicle design and durability, but PMMA excels in aesthetic applications while ABS is preferred for structural and impact-heavy components.
Chemical Composition and Material Properties
Polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA) consists mainly of methyl methacrylate monomers, offering excellent transparency, UV resistance, and weatherability ideal for automotive light covers and display panels. Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS) is a terpolymer composed of acrylonitrile, butadiene, and styrene, providing superior impact resistance, toughness, and heat tolerance suited for interior trims and structural components. The chemical composition of PMMA results in a rigid, brittle material with high clarity, while ABS delivers a more flexible, impact-resistant polymer with better chemical and thermal resistance for durable automotive applications.
Mechanical Strength and Durability Comparison
Polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA) offers excellent optical clarity and moderate mechanical strength, making it suitable for automotive parts requiring good impact resistance and surface hardness but lower flexibility. Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS) exhibits superior toughness, impact resistance, and higher durability under mechanical stress, ideal for structural automotive components exposed to vibrations and variable loads. Comparatively, ABS outperforms PMMA in mechanical strength and long-term durability, especially in applications demanding resistance to impact, fatigue, and environmental stress cracking.
Impact Resistance: PMMA vs ABS
Polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA) offers excellent optical clarity but has lower impact resistance compared to Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS), which provides superior toughness and impact strength essential for automotive parts subjected to mechanical stress. ABS combines rigidity with remarkable impact absorption, making it preferable for components requiring durability under sudden shocks or collisions. In contrast, PMMA's brittle nature limits its use to applications where aesthetics prevail over mechanical performance.
Optical Clarity and Aesthetic Qualities
Polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA) offers superior optical clarity with a light transmittance of up to 92%, making it ideal for automotive parts where transparency and visual appeal are critical. Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS), while providing excellent impact resistance and toughness, lacks the high clarity of PMMA and typically appears opaque with a matte or glossy finish. For aesthetic qualities, PMMA delivers a glass-like finish and excellent weatherability, whereas ABS is favored for versatile colorability and a more durable, scratch-resistant surface.
Weatherability and UV Resistance
Polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA) offers superior weatherability and UV resistance compared to Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS), making it ideal for automotive parts exposed to harsh sunlight and outdoor conditions. PMMA maintains optical clarity and mechanical integrity under prolonged UV exposure, preventing yellowing and degradation that ABS often experiences. ABS typically requires UV stabilizers or coatings to enhance durability, whereas PMMA provides inherent resistance, ensuring longer-lasting performance in automotive exterior components.
Ease of Processing and Manufacturing Methods
Polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA) offers excellent ease of processing with its low melting point and good flow characteristics, making it suitable for injection molding and extrusion in automotive parts manufacturing. Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS) exhibits higher impact resistance and dimensional stability but requires slightly more complex processing conditions, including controlled temperature settings during injection molding. Both materials support rapid prototyping and mass production, yet PMMA excels in applications demanding optical clarity, while ABS is preferred for parts needing superior toughness and heat resistance.
Cost Factors and Economic Considerations
Polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA) offers superior clarity and weather resistance but comes at a higher raw material and processing cost compared to Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS), which is favored for its lower price and ease of manufacturing. ABS provides cost advantages due to faster cycle times and better impact resistance, reducing potential part failures and warranty expenses in automotive applications. Economic considerations also include lifecycle costs where PMMA's durability can lower replacement frequency, yet ABS remains dominant for budget-sensitive automotive interior components.
Typical Automotive Parts Using PMMA and ABS
Polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA) is commonly used in automotive applications such as headlamp lenses, instrument panels, and exterior trims due to its excellent light transmittance and weather resistance. Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS) is frequently selected for interior components like dashboards, door panels, and bumper covers because of its impact resistance, toughness, and ease of molding. Both materials contribute to vehicle durability and aesthetics, with PMMA preferred for optical clarity and ABS favored for structural strength.
Choosing the Right Material: Key Considerations for Automakers
Polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA) offers superior clarity, UV resistance, and scratch resistance, making it ideal for automotive parts like light covers and interior trim where aesthetics and durability are critical. Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS) provides excellent impact resistance, toughness, and ease of processing, making it suitable for structural components, dashboard housings, and exterior panels requiring high mechanical strength. Automakers must consider factors such as environmental exposure, mechanical properties, weight, cost, and manufacturability to choose between PMMA's optical advantages and ABS's robust performance for specific automotive applications.
Infographic: Polymethyl methacrylate vs Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene for Automotive part
 azmater.com
azmater.com