Polycarbonate offers superior impact resistance and durability for glue applications, while polyvinyl acetate provides strong adhesion with flexibility and quick drying time. Selecting between them depends on whether durability or ease of use is the priority in bonding materials.
Table of Comparison
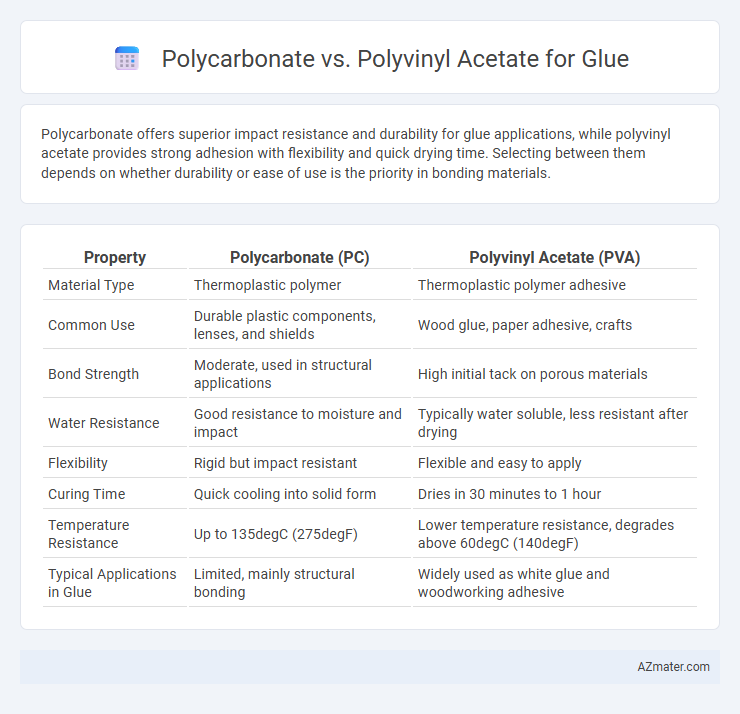
| Property | Polycarbonate (PC) | Polyvinyl Acetate (PVA) |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Thermoplastic polymer | Thermoplastic polymer adhesive |
| Common Use | Durable plastic components, lenses, and shields | Wood glue, paper adhesive, crafts |
| Bond Strength | Moderate, used in structural applications | High initial tack on porous materials |
| Water Resistance | Good resistance to moisture and impact | Typically water soluble, less resistant after drying |
| Flexibility | Rigid but impact resistant | Flexible and easy to apply |
| Curing Time | Quick cooling into solid form | Dries in 30 minutes to 1 hour |
| Temperature Resistance | Up to 135degC (275degF) | Lower temperature resistance, degrades above 60degC (140degF) |
| Typical Applications in Glue | Limited, mainly structural bonding | Widely used as white glue and woodworking adhesive |
Introduction to Polycarbonate and Polyvinyl Acetate
Polycarbonate, a durable thermoplastic known for its high impact resistance and transparency, is less commonly used as an adhesive but serves as a strong bonding agent when applied as a polymer resin. Polyvinyl acetate (PVA), a widely used adhesive in woodworking and paper products, is a water-based polymer renowned for its strong initial tack, flexibility, and ease of cleanup. Understanding the chemical composition and bonding properties of polycarbonate and polyvinyl acetate helps in selecting the right glue for specific applications requiring strength, flexibility, or clarity.
Chemical Structure and Properties Comparison
Polycarbonate features a carbonate group (-O-(C=O)-O-) in its backbone, providing high impact resistance and thermal stability, making it ideal for durable adhesive applications. Polyvinyl acetate (PVAc), composed of repeating vinyl acetate units with ester functional groups, offers excellent flexibility and strong adhesion to porous surfaces but lower mechanical strength and thermal resistance compared to polycarbonate. The chemical structure of polycarbonate contributes to its superior toughness and solvent resistance, whereas PVAc's ester groups enable easier polymerization and stronger bonding with wood and paper substrates.
Adhesive Strength and Bonding Capabilities
Polycarbonate adhesives demonstrate superior adhesive strength and excellent bonding capabilities on a wide range of substrates, including metals, plastics, and glass, making them ideal for structural and durable applications. Polyvinyl acetate (PVA) glues provide strong bonds primarily with porous materials like wood and paper but lack the high tensile strength and resistance to moisture that polycarbonate adhesives offer. For high-performance bonding requiring durability and resistance to environmental factors, polycarbonate adhesives outperform polyvinyl acetate in maintaining long-term adhesion.
Applications in Various Industries
Polycarbonate adhesives excel in automotive and electronics industries due to their high impact resistance and thermal stability, making them ideal for bonding transparent components and circuit boards. Polyvinyl acetate (PVA) glue is widely used in woodworking, paper, and textiles industries because of its strong adhesion to porous materials and easy cleanup properties. Both adhesives serve crucial roles across sectors, with polycarbonate favored for durable, high-performance applications and PVA suited for general-purpose bonding of organic substrates.
Durability and Longevity of Bonds
Polycarbonate adhesives exhibit superior durability and longevity compared to polyvinyl acetate (PVA) glues, maintaining strong bonds under stress, moisture, and temperature fluctuations. PVA glue is suitable for light-duty applications with moderate resistance but tends to weaken over time due to water exposure and shear forces. For structural integrity and long-lasting adhesion, polycarbonate-based glues are preferred in demanding environments requiring robust performance.
Environmental Impact and Safety Considerations
Polycarbonate adhesives offer high durability and resistance but pose environmental concerns due to their non-biodegradable nature and potential release of harmful chemicals during production and disposal. Polyvinyl acetate (PVA) glue is water-based, biodegradable, and considered safer for indoor air quality, making it a more eco-friendly choice with lower toxicity risks. Evaluating the trade-offs between durability and ecological footprint is essential when selecting adhesives for sustainable applications.
Performance Under Different Conditions
Polycarbonate adhesives exhibit superior resistance to UV radiation, impact, and temperature fluctuations, making them ideal for outdoor and high-stress applications. Polyvinyl acetate (PVA) glue performs well in indoor environments with moderate humidity but loses strength when exposed to water or extreme temperatures. Manufacturers often recommend polycarbonate-based adhesives for industrial use due to their durability, while PVA glues are preferred for woodworking and lightweight bonding tasks.
Ease of Use and Application Techniques
Polycarbonate adhesives offer strong bonding with excellent impact resistance, but require precise surface preparation and curing conditions, making them less user-friendly for casual applications. Polyvinyl acetate (PVA) glue is widely favored for its ease of use, quick drying time, and simple water-based cleanup, particularly suited for porous materials like wood and paper. Application techniques vary as polycarbonate glues often need specialized dispensers and clamping, while PVA glues can be applied with brushes or rollers without extensive equipment.
Cost and Availability Analysis
Polycarbonate adhesives generally incur higher costs due to their superior durability and thermal resistance, making them suitable for demanding applications, whereas polyvinyl acetate (PVA) adhesives offer a more budget-friendly option with widespread availability in retail and industrial markets. PVA glue is readily accessible, commonly used in woodworking and paper crafts, and benefits from a strong supply chain that keeps prices competitive. In contrast, polycarbonate-based adhesives are less prevalent, often requiring specialized suppliers, which can limit their availability and drive up procurement expenses.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Glue for Your Needs
Polycarbonate offers superior durability and impact resistance, making it ideal for applications requiring strong, long-lasting bonds. Polyvinyl acetate (PVA) glue excels in woodworking and paper projects due to its fast drying time and ease of use with porous materials. Selecting the right glue depends on the materials involved and the desired strength, with polycarbonate adhesives suited for heavy-duty tasks and PVA preferred for lighter, craft-oriented bonding.
Infographic: Polycarbonate vs Polyvinyl Acetate for Glue
 azmater.com
azmater.com