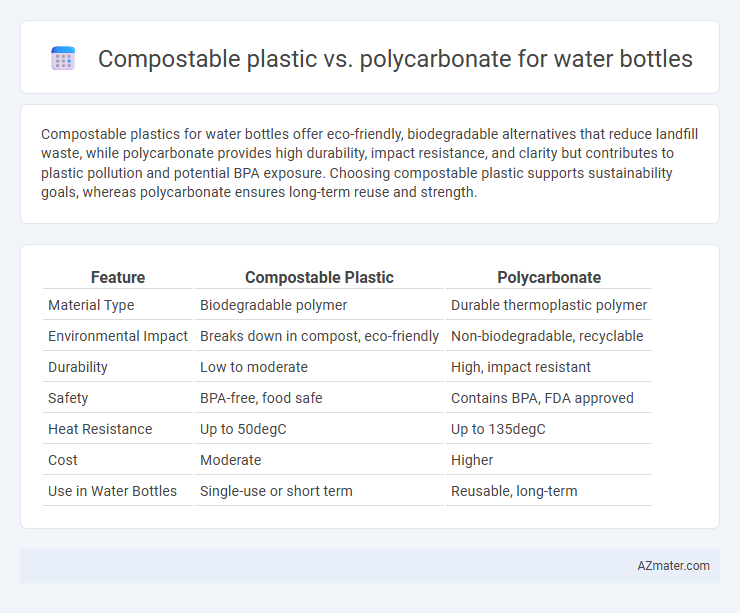
Compostable plastics for water bottles offer eco-friendly, biodegradable alternatives that reduce landfill waste, while polycarbonate provides high durability, impact resistance, and clarity but contributes to plastic pollution and potential BPA exposure. Choosing compostable plastic supports sustainability goals, whereas polycarbonate ensures long-term reuse and strength.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Compostable Plastic | Polycarbonate |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Biodegradable polymer | Durable thermoplastic polymer |
| Environmental Impact | Breaks down in compost, eco-friendly | Non-biodegradable, recyclable |
| Durability | Low to moderate | High, impact resistant |
| Safety | BPA-free, food safe | Contains BPA, FDA approved |
| Heat Resistance | Up to 50degC | Up to 135degC |
| Cost | Moderate | Higher |
| Use in Water Bottles | Single-use or short term | Reusable, long-term |
Introduction: The Rise of Sustainable Water Bottles
Compostable plastics are gaining momentum as eco-friendly alternatives to traditional polycarbonate water bottles, which rely on petroleum-based materials and pose environmental concerns. Compostable plastics, derived from renewable resources such as cornstarch or sugarcane, break down into natural elements within a few months under industrial composting conditions, significantly reducing landfill waste. Polycarbonate bottles, known for durability and clarity, often contain bisphenol A (BPA), raising health and ecological issues that drive the demand for sustainable, biodegradable options in the water bottle industry.
What Are Compostable Plastics?
Compostable plastics are derived from renewable plant-based materials such as cornstarch or sugarcane and are designed to break down into natural elements within a compost environment, reducing environmental impact compared to traditional plastics. Unlike polycarbonate, a durable and clear petroleum-based plastic known for its strength and heat resistance in water bottles, compostable plastics prioritize eco-friendly disposal by decomposing within weeks to months under industrial composting conditions. Using compostable plastics in water bottles supports sustainability goals by minimizing plastic pollution, although they often lack the mechanical robustness and longevity of polycarbonate materials.
Polycarbonate: Features and Common Uses
Polycarbonate is a durable, impact-resistant thermoplastic known for its high transparency and heat resistance, making it ideal for reusable water bottles. Its lightweight nature and excellent clarity allow for aesthetic designs while maintaining safety and longevity in everyday use. Common uses extend beyond water bottles to eyewear lenses, electronic components, and automotive parts due to its strength and versatility.
Environmental Impact Comparison
Compostable plastic water bottles significantly reduce environmental impact by biodegrading within months under industrial composting conditions, minimizing plastic pollution and landfill accumulation. Polycarbonate bottles, derived from petroleum, persist in the environment for centuries and can release bisphenol A (BPA), a harmful chemical that affects ecosystems and human health. Lifecycle assessments highlight compostable plastics' lower carbon footprint and enhanced sustainability compared to polycarbonate's resource-intensive production and long-term ecological risks.
Safety and Health Considerations
Compostable plastics for water bottles are designed to break down naturally, reducing environmental impact but may leach fewer chemicals compared to polycarbonate, which often contains bisphenol A (BPA), a compound linked to potential health risks. Safety concerns for polycarbonate bottles include BPA exposure, which can disrupt endocrine functions and pose reproductive and developmental risks. Compostable plastics typically avoid such harmful additives, making them a safer choice for long-term health, although their durability and chemical resistance under various conditions require careful evaluation.
Durability and Lifespan
Compostable plastic water bottles typically have a shorter lifespan and lower durability compared to polycarbonate bottles, as they are designed to break down under composting conditions. Polycarbonate bottles offer superior impact resistance, longevity, and the ability to withstand repeated use and cleaning without degrading. The durability of polycarbonate makes it a preferred choice for long-term water bottle use, while compostable plastics are better suited for single-use or short-term applications.
Performance in Everyday Use
Compostable plastic water bottles offer moderate durability and biodegradability, making them suitable for short-term use but less resistant to impacts and temperature fluctuations compared to polycarbonate. Polycarbonate water bottles excel in strength, clarity, and heat resistance, providing long-lasting performance and maintaining structural integrity under daily wear and tear. For everyday use where durability and repeated cleaning are essential, polycarbonate outperforms compostable plastics in maintaining functionality and safety.
End-of-Life: Composting vs Recycling
Compostable plastic water bottles break down through industrial composting processes, converting into organic matter within months, reducing landfill waste significantly. Polycarbonate water bottles rely on recycling programs that recover and repurpose the plastic, but face challenges such as limited recycling facilities and potential chemical leaching if not processed correctly. End-of-life for compostable plastics emphasizes biodegradability when composted properly, whereas polycarbonate depends on established recycling infrastructure to minimize environmental impact.
Cost and Accessibility
Compostable plastic water bottles generally cost more upfront due to specialized materials and limited production scale, making them less accessible in mainstream markets compared to polycarbonate bottles. Polycarbonate bottles offer greater affordability and widespread availability, benefiting from mass manufacturing and established supply chains. Consumers seeking eco-friendly options may face higher prices and limited distribution with compostable plastics, while polycarbonate remains a cost-effective, easily accessible choice.
Which Material Is the Better Choice?
Compostable plastic water bottles offer eco-friendly benefits by breaking down in industrial composting facilities, reducing plastic waste and environmental impact, while polycarbonate bottles provide superior durability, clarity, and resistance to heat, making them ideal for long-term use. Polycarbonate's BPA-free variants ensure safety, but concerns remain over potential chemical leaching, whereas compostable plastics avoid these risks but often lack the same strength and lifespan. Choosing between the two depends on prioritizing environmental sustainability versus product longevity and robustness.
Infographic: Compostable plastic vs Polycarbonate for Water bottle
 azmater.com
azmater.com