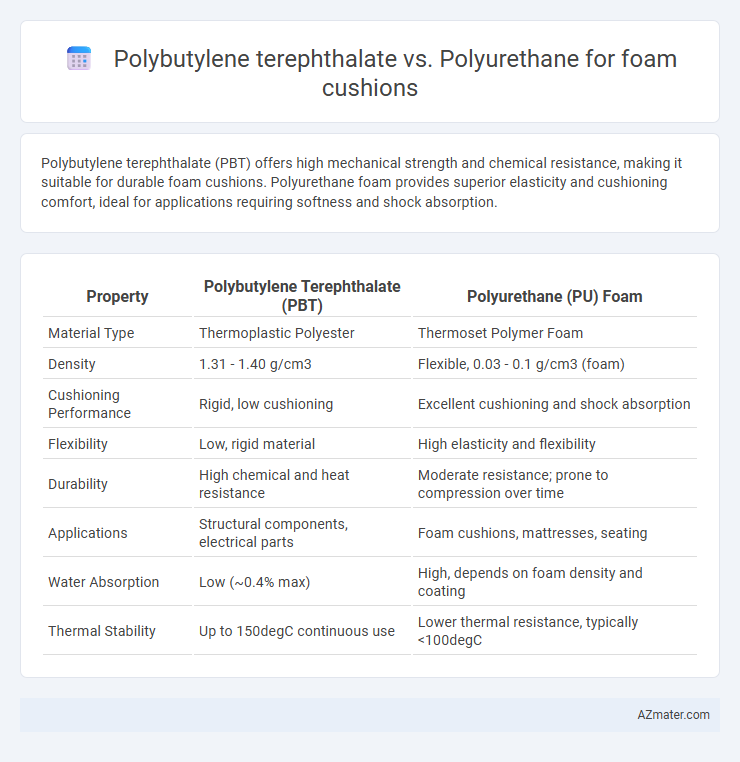
Polybutylene terephthalate (PBT) offers high mechanical strength and chemical resistance, making it suitable for durable foam cushions. Polyurethane foam provides superior elasticity and cushioning comfort, ideal for applications requiring softness and shock absorption.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Polybutylene Terephthalate (PBT) | Polyurethane (PU) Foam |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Thermoplastic Polyester | Thermoset Polymer Foam |
| Density | 1.31 - 1.40 g/cm3 | Flexible, 0.03 - 0.1 g/cm3 (foam) |
| Cushioning Performance | Rigid, low cushioning | Excellent cushioning and shock absorption |
| Flexibility | Low, rigid material | High elasticity and flexibility |
| Durability | High chemical and heat resistance | Moderate resistance; prone to compression over time |
| Applications | Structural components, electrical parts | Foam cushions, mattresses, seating |
| Water Absorption | Low (~0.4% max) | High, depends on foam density and coating |
| Thermal Stability | Up to 150degC continuous use | Lower thermal resistance, typically <100degC |
Introduction to Polybutylene Terephthalate and Polyurethane
Polybutylene terephthalate (PBT) is a thermoplastic polyester known for its excellent mechanical strength, chemical resistance, and dimensional stability, making it suitable for durable foam cushions requiring high resilience. Polyurethane, a versatile polymer formed by reacting polyols and diisocyanates, offers superior flexibility, cushioning properties, and energy absorption, which are essential for comfort-driven foam applications. Choosing between PBT and polyurethane for foam cushions depends on factors such as durability needs, flexibility requirements, and environmental resistance.
Chemical Structure and Composition
Polybutylene terephthalate (PBT) is a semicrystalline polyester composed of repeating units of terephthalic acid and 1,4-butanediol, providing high dimensional stability and chemical resistance ideal for foam cushions. Polyurethane (PU) consists of chains of organic units joined by carbamate (urethane) links, resulting from the reaction between polyols and diisocyanates, offering superior flexibility and cushioning properties. The chemical composition of PBT imparts rigidity and thermal resistance, whereas PU's urethane linkages contribute to elasticity and impact absorption in foam cushion applications.
Manufacturing Processes
Polybutylene terephthalate (PBT) foam cushions are produced through melt extrusion or injection molding, which allows precise control over foam density and cell structure, offering excellent mechanical strength and thermal stability. Polyurethane foam cushions utilize a chemical reaction between polyols and isocyanates, typically via a reaction injection molding (RIM) or slabstock process, enabling versatile customization of firmness and elasticity. Manufacturing PBT foam involves higher processing temperatures and crystallization control, whereas polyurethane foam benefits from faster curing times and greater adaptability for complex shapes and rapid prototyping.
Physical and Mechanical Properties
Polybutylene terephthalate (PBT) foam cushion exhibits excellent dimensional stability, high tensile strength, and superior resistance to impact and abrasion, making it ideal for durable applications. Polyurethane (PU) foam distinguishes itself with remarkable flexibility, superior cushioning ability, and excellent compression set resistance, providing enhanced comfort and shock absorption. While PBT provides rigidity and toughness, polyurethane foam offers a softer, more elastic material suited for cushioning and ergonomic support.
Comfort and Support Performance
Polybutylene terephthalate (PBT) foam cushions offer superior dimensional stability and moderate cushioning, providing consistent support with resistance to compression set, making them ideal for firm seating applications. Polyurethane foam cushions excel in comfort through high resilience and energy absorption, delivering soft, flexible support that contours to body shape for enhanced pressure distribution. The choice depends on desired balance: PBT prioritizes long-term structural support, while polyurethane maximizes immediate comfort and flexibility in foam cushioning.
Durability and Lifespan
Polybutylene terephthalate (PBT) foam cushions exhibit superior chemical resistance and dimensional stability, contributing to enhanced durability in high-stress applications compared to polyurethane (PU) foam. Polyurethane foam offers excellent initial cushioning and flexibility but tends to degrade faster due to hydrolysis and oxidation, resulting in a shorter lifespan under prolonged exposure to moisture and UV light. Selecting PBT foam ensures longer-term performance and reduced material fatigue in environments requiring consistent mechanical resilience.
Safety and Environmental Impact
Polybutylene terephthalate (PBT) foam cushions offer superior chemical resistance, low smoke toxicity, and better thermal stability, making them safer for indoor air quality compared to polyurethane (PU) foams, which often release volatile organic compounds (VOCs) and isocyanates during manufacturing and use. PBT foams demonstrate higher recyclability and lower environmental impact due to their recyclable polyester backbone, whereas PU foams largely rely on petrochemical-based polyols and isocyanates resulting in greater carbon emissions and landfill persistence. Choosing PBT foam cushions contributes to reduced toxic exposure and improved sustainability, critical factors in eco-conscious consumer and industrial applications.
Cost-effectiveness and Availability
Polybutylene terephthalate (PBT) foam cushions offer higher cost-effectiveness due to lower material costs and greater manufacturing efficiency compared to polyurethane (PU) foams. PBT foam availability is more limited and specialized, typically used in niche applications, whereas polyurethane foam is widely available worldwide with a mature supply chain. The selection between PBT and PU foams depends significantly on budget constraints, production volume, and specific performance requirements.
Applications in Foam Cushioning
Polybutylene terephthalate (PBT) is commonly used in foam cushioning for applications requiring high dimensional stability, chemical resistance, and durability, such as automotive interiors and electronic device padding. Polyurethane foam excels in comfort and flexibility, making it ideal for furniture cushions, mattresses, and packaging materials due to its superior elasticity and shock absorption capabilities. The choice between PBT and polyurethane depends on the specific cushioning application, balancing factors like mechanical strength, flexibility, and resistance to environmental stressors.
Choosing the Best Material for Foam Cushions
Polybutylene terephthalate (PBT) offers excellent dimensional stability, chemical resistance, and durability, making it suitable for foam cushions exposed to repetitive stress and harsh environments. Polyurethane (PU) foam excels in comfort due to its superior elasticity, cushioning effect, and wide range of hardness options, ideal for ergonomic applications. Selecting the best material depends on balancing mechanical strength and comfort, where PBT suits structural support and PU foam prioritizes softness and flexibility in cushion design.
Infographic: Polybutylene terephthalate vs Polyurethane for Foam cushion
 azmater.com
azmater.com