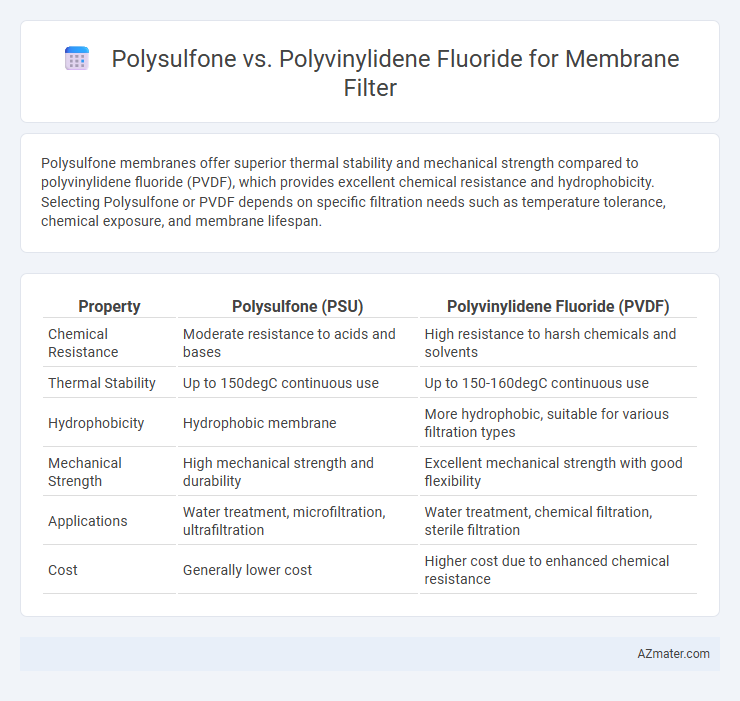
Polysulfone membranes offer superior thermal stability and mechanical strength compared to polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF), which provides excellent chemical resistance and hydrophobicity. Selecting Polysulfone or PVDF depends on specific filtration needs such as temperature tolerance, chemical exposure, and membrane lifespan.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Polysulfone (PSU) | Polyvinylidene Fluoride (PVDF) |
|---|---|---|
| Chemical Resistance | Moderate resistance to acids and bases | High resistance to harsh chemicals and solvents |
| Thermal Stability | Up to 150degC continuous use | Up to 150-160degC continuous use |
| Hydrophobicity | Hydrophobic membrane | More hydrophobic, suitable for various filtration types |
| Mechanical Strength | High mechanical strength and durability | Excellent mechanical strength with good flexibility |
| Applications | Water treatment, microfiltration, ultrafiltration | Water treatment, chemical filtration, sterile filtration |
| Cost | Generally lower cost | Higher cost due to enhanced chemical resistance |
Introduction to Membrane Filtration
Membrane filtration relies heavily on polymer materials such as Polysulfone (PSU) and Polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF) due to their distinct physicochemical properties influencing filtration efficiency and durability. Polysulfone offers excellent thermal stability, mechanical strength, and chemical resistance, making it suitable for microfiltration and ultrafiltration applications. Polyvinylidene fluoride provides superior hydrophobicity, chemical resistance, and fouling resistance, favoring its use in harsh chemical environments and ultrafiltration membranes for water and wastewater treatment.
Overview of Polysulfone (PSU) Membrane Filters
Polysulfone (PSU) membrane filters are renowned for their excellent thermal stability, chemical resistance, and mechanical strength, making them ideal for demanding filtration applications such as water treatment and biomedical processes. PSU membranes exhibit high permeability and resistance to hydrolysis, allowing effective filtration of bacteria, viruses, and particles in harsh operating conditions. Compared to polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF), PSU offers superior thermal resistance but generally lower chemical resistance to strong solvents, influencing material selection based on the filtration environment.
Overview of Polyvinylidene Fluoride (PVDF) Membrane Filters
Polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF) membrane filters are renowned for their exceptional chemical resistance and high mechanical strength, making them ideal for aggressive solvent filtration and sterilization processes. PVDF membranes offer superior thermal stability up to 150degC and exhibit low protein binding, enhancing sample recovery in biotechnological and pharmaceutical applications. Compared to polysulfone membranes, PVDF provides increased hydrophobicity, which contributes to better filtration efficiency in aqueous and organic solvent environments.
Chemical and Thermal Stability Comparison
Polysulfone membranes exhibit excellent chemical resistance to acidic and alkaline solutions, maintaining stability in pH ranges from 2 to 11, while polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF) membranes offer superior chemical resistance across a broader pH spectrum from 1 to 14, including strong oxidizing agents. Thermal stability of polysulfone membranes typically withstands continuous service temperatures up to 150degC, whereas PVDF membranes can endure higher temperatures up to 170degC, making PVDF more suitable for high-temperature applications. The enhanced chemical and thermal durability of PVDF membranes positions them as a preferred choice for aggressive filtration environments compared to polysulfone membranes.
Mechanical Strength and Durability
Polysulfone membranes exhibit superior mechanical strength with high tensile resistance and excellent hydrolytic stability, making them ideal for applications requiring robust structural integrity under harsh conditions. Polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF) membranes offer outstanding chemical resistance and thermal stability but generally have lower mechanical strength compared to polysulfone, which can affect durability under high-stress filtration environments. Polysulfone's enhanced mechanical properties result in longer service life and greater resistance to physical deformation, whereas PVDF's durability is optimized for chemical-heavy applications where flexibility is less critical.
Filtration Performance and Efficiency
Polysulfone membranes exhibit high thermal stability and mechanical strength, making them ideal for filtration processes requiring durability and resistance to harsh chemicals. Polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF) membranes provide superior chemical resistance and hydrophobicity, which enhances filtration efficiency for oil-water separation and microfiltration applications. PVDF membranes typically offer higher flux rates and better fouling resistance compared to polysulfone, improving overall filtration performance in demanding environments.
Fouling Resistance and Cleanability
Polysulfone membranes exhibit moderate fouling resistance due to their hydrophobic nature, which can lead to higher organic fouling but they maintain good mechanical strength and thermal stability for effective cleaning protocols. Polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF) membranes offer superior fouling resistance thanks to their inherent hydrophobicity combined with high chemical resistance, making them easier to clean with aggressive solvents and oxidative agents. PVDF filters are generally preferred in applications requiring rigorous cleanability and durability against a wide range of fouling substances, while polysulfone remains relevant for processes where mechanical robustness is critical.
Applications in Water Treatment and Biotechnology
Polysulfone membranes exhibit high thermal and chemical resistance, making them ideal for microfiltration and ultrafiltration in water treatment waste management and bioprocessing. Polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF) membranes offer superior hydrophobicity and mechanical strength, favoring their use in membrane bioreactors (MBRs) and protein filtration in biotechnology applications. Both materials provide durability, but PVDF's resistance to fouling and broad chemical compatibility make it more suitable for aggressive industrial water treatment environments.
Cost and Scalability Considerations
Polysulfone membranes typically offer a lower production cost compared to polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF), making them more economical for large-scale applications. PVDF membranes provide superior chemical resistance and durability, but their higher material and processing costs can limit scalability in cost-sensitive projects. The choice between polysulfone and PVDF largely depends on balancing initial investment against long-term performance requirements and volume production needs.
Conclusion: Choosing Between Polysulfone and PVDF
Polysulfone membranes offer excellent chemical resistance and thermal stability, making them suitable for harsh filtration environments, while PVDF membranes provide superior hydrophobicity and mechanical strength, ideal for applications requiring high durability and fouling resistance. The choice between polysulfone and polyvinylidene fluoride depends on specific filtration needs, such as chemical compatibility, temperature tolerance, and fouling tendencies. Evaluating operating conditions and target contaminants ensures optimal membrane performance and longevity.
Infographic: Polysulfone vs Polyvinylidene fluoride for Membrane filter
 azmater.com
azmater.com