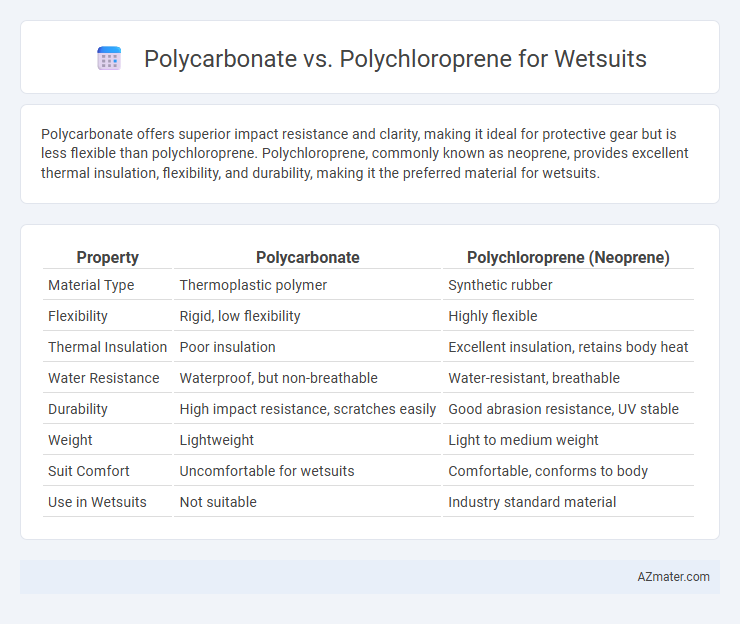
Polycarbonate offers superior impact resistance and clarity, making it ideal for protective gear but is less flexible than polychloroprene. Polychloroprene, commonly known as neoprene, provides excellent thermal insulation, flexibility, and durability, making it the preferred material for wetsuits.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Polycarbonate | Polychloroprene (Neoprene) |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Thermoplastic polymer | Synthetic rubber |
| Flexibility | Rigid, low flexibility | Highly flexible |
| Thermal Insulation | Poor insulation | Excellent insulation, retains body heat |
| Water Resistance | Waterproof, but non-breathable | Water-resistant, breathable |
| Durability | High impact resistance, scratches easily | Good abrasion resistance, UV stable |
| Weight | Lightweight | Light to medium weight |
| Suit Comfort | Uncomfortable for wetsuits | Comfortable, conforms to body |
| Use in Wetsuits | Not suitable | Industry standard material |
Introduction to Wetsuit Materials
Wetsuit materials like polycarbonate and polychloroprene significantly impact performance and durability. Polycarbonate offers exceptional rigidity and impact resistance, often used in protective wetsuit components. Polychloroprene, commonly known as neoprene, provides superior flexibility, insulation, and comfort essential for thermal protection in water sports.
Overview of Polycarbonate
Polycarbonate is a highly durable, impact-resistant thermoplastic known for its clarity and toughness, making it ideal in manufacturing protective gear and eyewear. Its excellent insulation properties and resistance to temperature variations contribute to enhanced thermal protection in wetsuits. Compared to polychloroprene, polycarbonate offers superior structural integrity but lacks the flexible, insulating qualities that make polychloroprene the standard neoprene choice for wetsuit materials.
Overview of Polychloroprene (Neoprene)
Polychloroprene, commonly known as neoprene, is a synthetic rubber widely used in wetsuits due to its excellent insulation properties and flexibility in cold water environments. Its closed-cell structure traps gas bubbles, providing effective thermal insulation and buoyancy, making it superior for maintaining body heat during prolonged water exposure. Neoprene also offers high abrasion resistance and durability, ensuring wetsuits withstand harsh marine conditions and repeated use.
Thermal Insulation Properties
Polycarbonate and polychloroprene differ significantly in thermal insulation properties for wetsuits. Polychloroprene, commonly known as neoprene, offers superior thermal insulation due to its closed-cell foam structure that traps heat effectively. Polycarbonate lacks this foam structure, making it less efficient at retaining body heat in cold water conditions.
Flexibility and Comfort Comparison
Polycarbonate wetsuit materials offer moderate flexibility but tend to be stiffer than polychloroprene, impacting overall comfort during extended use. Polychloroprene, commonly known as neoprene, provides superior elasticity and conforms better to body movements, enhancing flexibility and ensuring a snug, comfortable fit. The enhanced stretchability of polychloroprene makes it the preferred choice for wetsuits requiring dynamic performance and prolonged wear comfort.
Durability and Lifespan
Polycarbonate materials offer superior durability for wetsuits due to their high impact resistance and excellent abrasion properties, making them ideal for prolonged use in harsh aquatic environments. Polychloroprene, while flexible and resistant to temperature changes, generally has a shorter lifespan because it is more susceptible to UV degradation and wear over time. Choosing polycarbonate-based wetsuits extends longevity, especially for frequent divers requiring reliable performance and minimal material fatigue.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Polycarbonate and polychloroprene differ significantly in environmental impact and sustainability within wetsuit manufacturing. Polycarbonate is a recyclable thermoplastic derived from fossil fuels, but its production involves high carbon emissions and energy consumption. Polychloroprene, commonly known as neoprene, is a synthetic rubber with a challenging environmental footprint due to chlorine content and non-biodegradability, though recent innovations aim to develop limestone-based or plant-based alternatives to reduce ecological damage.
Cost Effectiveness
Polycarbonate wetsuits generally have a higher upfront cost due to durability and impact resistance, but they offer long-term savings by reducing the need for frequent replacements. Polychloroprene wetsuits, commonly known as neoprene, are more affordable initially and provide excellent flexibility and insulation, making them cost-effective for casual divers and surfers. Evaluating total cost of ownership, polycarbonate suits excel in longevity, while polychloroprene suits offer budget-friendly performance for everyday water activities.
Typical Applications in Wetsuit Manufacturing
Polycarbonate is commonly used in wetsuit manufacturing for protective elements such as face shields and goggles due to its high impact resistance and clarity, enhancing durability and visibility in water sports. Polychloroprene, also known as neoprene, serves as the primary material for wetsuit construction, providing excellent thermal insulation, flexibility, and water resistance essential for maintaining body heat in cold water environments. While polycarbonate contributes to accessory components, polychloroprene remains the core fabric choice in wetsuit production because of its superior elasticity and durability in aquatic conditions.
Choosing the Right Material for Your Needs
Selecting the right wetsuit material depends on your activity and environmental conditions; polycarbonate offers exceptional durability and impact resistance for rugged use, while polychloroprene (neoprene) provides superior flexibility and thermal insulation ideal for extended cold-water exposure. Polycarbonate's hard, lightweight nature suits protective outer layers or reinforcements, whereas polychloroprene's closed-cell foam structure traps heat efficiently, enhancing warmth and comfort. Prioritize polychloroprene for warmth and flexibility in cold waters, and consider polycarbonate for abrasion resistance and structural support in challenging physical activities.
Infographic: Polycarbonate vs Polychloroprene for Wetsuit
 azmater.com
azmater.com