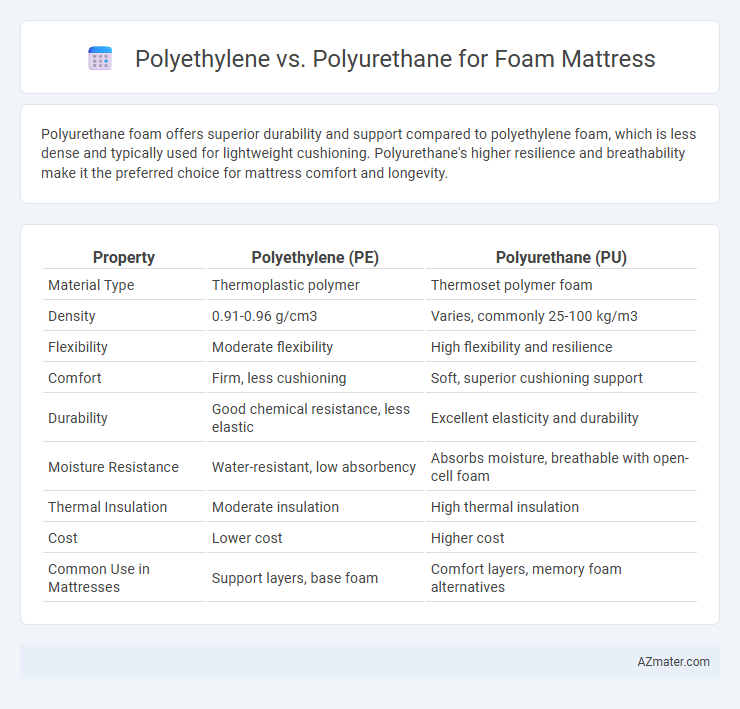
Polyurethane foam offers superior durability and support compared to polyethylene foam, which is less dense and typically used for lightweight cushioning. Polyurethane's higher resilience and breathability make it the preferred choice for mattress comfort and longevity.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Polyethylene (PE) | Polyurethane (PU) |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Thermoplastic polymer | Thermoset polymer foam |
| Density | 0.91-0.96 g/cm3 | Varies, commonly 25-100 kg/m3 |
| Flexibility | Moderate flexibility | High flexibility and resilience |
| Comfort | Firm, less cushioning | Soft, superior cushioning support |
| Durability | Good chemical resistance, less elastic | Excellent elasticity and durability |
| Moisture Resistance | Water-resistant, low absorbency | Absorbs moisture, breathable with open-cell foam |
| Thermal Insulation | Moderate insulation | High thermal insulation |
| Cost | Lower cost | Higher cost |
| Common Use in Mattresses | Support layers, base foam | Comfort layers, memory foam alternatives |
Introduction to Foam Mattress Materials
Foam mattresses primarily utilize materials like polyethylene and polyurethane, each offering distinct properties that influence comfort and durability. Polyurethane foam is popular for its softness and excellent support, commonly found in memory foam and high-resilience mattresses. Polyethylene foam, characterized by its lightweight and closed-cell structure, provides better moisture resistance and durability, making it suitable for mattresses requiring enhanced firmness and longevity.
What is Polyethylene Foam?
Polyethylene foam is a closed-cell, lightweight foam known for its high durability, excellent cushioning properties, and resistance to moisture and chemicals, making it ideal for mattress support layers. Compared to polyurethane foam, polyethylene foam offers superior water resistance and longer lifespan but typically provides a firmer feel and less conforming comfort. Its dense structure enhances impact absorption and insulation, contributing to enhanced mattress durability and comfort support.
What is Polyurethane Foam?
Polyurethane foam is a versatile material commonly used in foam mattresses due to its excellent cushioning properties and durability. It is created through the chemical reaction of polyols and diisocyanates, resulting in a lightweight, flexible, and resilient foam that provides both support and comfort. Unlike polyethylene foam, which is denser and more rigid, polyurethane foam offers superior breathability and pressure relief, making it a popular choice for bedding applications.
Key Differences Between Polyethylene and Polyurethane
Polyethylene foam is typically denser and more rigid, offering higher durability and resistance to water absorption, making it ideal for outdoor and heavy-use applications. Polyurethane foam provides superior cushioning and flexibility with excellent shock absorption, commonly used in mattress toppers and comfort layers due to its softness and breathability. Key differences include polyethylene's closed-cell structure versus polyurethane's open-cell design, influencing factors such as moisture resistance, compressive strength, and overall comfort in foam mattresses.
Comfort and Support Comparison
Polyurethane foam mattresses typically offer superior comfort and support due to their higher density and ability to contour closely to the body, reducing pressure points. Polyethylene foam, while more rigid and less expensive, provides firmer support but may lack the cushioning and responsiveness found in polyurethane. The choice between the two depends on the desired balance of softness, durability, and support for personalized sleep comfort.
Durability and Longevity
Polyurethane foam mattresses typically offer superior durability and longevity compared to polyethylene foam due to their higher resistance to compression and better ability to retain shape over time. Polyurethane foam's cellular structure provides enhanced flexibility and resilience, resulting in less sagging and extended mattress life. Polyethylene foam, while lightweight and moisture-resistant, tends to degrade faster under constant pressure, making it less suitable for long-term use in mattresses.
Safety and Health Considerations
Polyurethane foam mattresses often contain volatile organic compounds (VOCs) and flame retardants that can off-gas, potentially affecting indoor air quality and triggering allergic reactions or respiratory issues in sensitive individuals. Polyethylene foam is generally more inert, exhibiting lower emissions and reduced chemical exposure, making it a safer option for those concerned about toxicity and indoor pollutants. Both materials should be certified by health and safety standards, such as CertiPUR-US for polyurethane and GREENGUARD for polyethylene, to ensure minimized risk of harmful substances.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Polyurethane foam mattresses often contain petrochemical-based components that contribute to higher carbon emissions and are less biodegradable compared to polyethylene-based foams, which can be produced using more eco-friendly processes like bio-based polyethylene. Polyethylene foams have a lower environmental footprint due to their potential for recycling and lower toxicity during disposal. Choosing polyethylene over polyurethane can significantly reduce landfill waste and promote sustainability in mattress manufacturing.
Cost Analysis: Polyethylene vs Polyurethane Mattresses
Polyurethane foam mattresses generally offer better comfort and durability but come at a higher price point compared to polyethylene foam mattresses, which are more affordable but less resilient. Polyethylene foam is cost-effective for budget-conscious consumers due to its lower manufacturing expenses and limited lifespan. Investing in polyurethane foam mattresses tends to provide longer-term value despite the initial increased cost, reducing replacement frequency.
Which Foam is Best for Your Mattress?
Polyurethane foam offers superior durability and support for mattresses due to its higher density and resilience, making it ideal for long-term comfort and pressure relief. Polyethylene foam, while lighter and more affordable, lacks the same cushioning quality and longevity, better suited for temporary or budget-friendly mattress options. Choosing polyurethane ensures enhanced comfort, better body contouring, and greater resistance to wear, making it the preferred foam for premium mattress construction.
Infographic: Polyethylene vs Polyurethane for Foam Mattress
 azmater.com
azmater.com