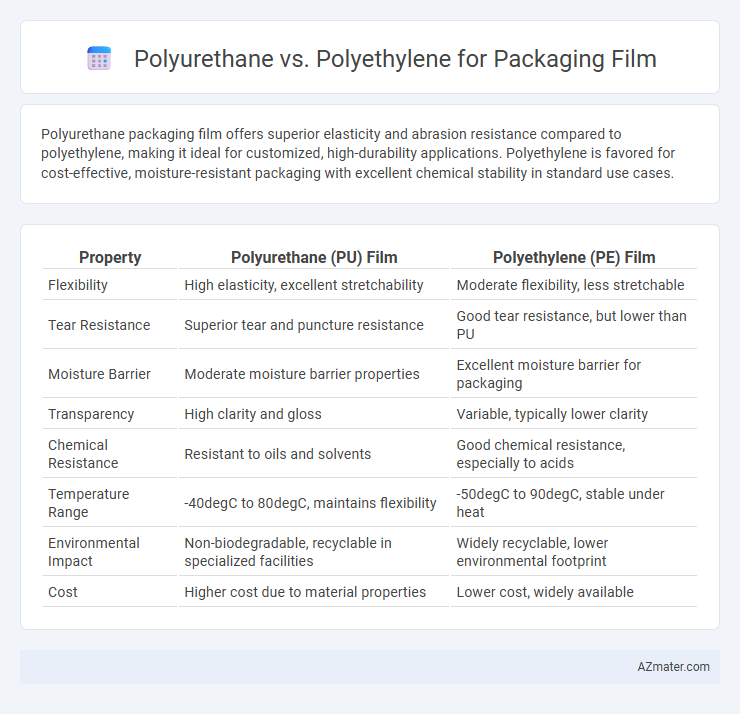
Polyurethane packaging film offers superior elasticity and abrasion resistance compared to polyethylene, making it ideal for customized, high-durability applications. Polyethylene is favored for cost-effective, moisture-resistant packaging with excellent chemical stability in standard use cases.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Polyurethane (PU) Film | Polyethylene (PE) Film |
|---|---|---|
| Flexibility | High elasticity, excellent stretchability | Moderate flexibility, less stretchable |
| Tear Resistance | Superior tear and puncture resistance | Good tear resistance, but lower than PU |
| Moisture Barrier | Moderate moisture barrier properties | Excellent moisture barrier for packaging |
| Transparency | High clarity and gloss | Variable, typically lower clarity |
| Chemical Resistance | Resistant to oils and solvents | Good chemical resistance, especially to acids |
| Temperature Range | -40degC to 80degC, maintains flexibility | -50degC to 90degC, stable under heat |
| Environmental Impact | Non-biodegradable, recyclable in specialized facilities | Widely recyclable, lower environmental footprint |
| Cost | Higher cost due to material properties | Lower cost, widely available |
Introduction to Polyurethane and Polyethylene
Polyurethane packaging film offers excellent elasticity and abrasion resistance, making it ideal for protective applications requiring flexibility and durability. Polyethylene, a widely used thermoplastic, provides cost-effective moisture barrier properties and chemical resistance, commonly utilized in food and industrial packaging. Comparing their molecular structures reveals polyurethane's segmented polymer chains contribute to superior mechanical performance, whereas polyethylene's simpler hydrocarbon chains offer ease of processing and recyclability.
Chemical Structure and Properties
Polyurethane packaging films possess a segmented polymer structure with hard urethane linkages and flexible soft segments, offering excellent abrasion resistance, elasticity, and chemical resistance. Polyethylene films consist of long chains of ethylene monomers forming a semi-crystalline structure, providing high moisture barrier, tensile strength, and chemical inertness. The unique urethane groups in polyurethane enable superior durability and flexibility compared to polyethylene's simpler hydrocarbon backbone, making each suitable for specific packaging applications based on mechanical and barrier property requirements.
Manufacturing Processes
Polyurethane (PU) packaging film is produced through a chemical reaction involving polyols and isocyanates, allowing for precise control over film thickness and elasticity, which enhances durability and flexibility in applications. Polyethylene (PE) packaging film is primarily manufactured using polymerization of ethylene monomers via techniques such as blown film extrusion and cast film extrusion, resulting in a lightweight, cost-effective material with excellent moisture barrier properties. The manufacturing process of PU films is generally more complex and costly but offers superior mechanical performance compared to the simpler, high-speed production methods of PE films.
Mechanical Strength and Durability
Polyurethane packaging films exhibit superior mechanical strength with high tensile and tear resistance, making them ideal for applications requiring durability under stress. Polyethylene films offer good flexibility and impact resistance but generally have lower tensile strength compared to polyurethane. The enhanced abrasion resistance and elasticity of polyurethane result in longer-lasting packaging solutions, especially in demanding environments.
Flexibility and Elasticity
Polyurethane films exhibit superior flexibility and elasticity compared to polyethylene, allowing them to stretch and recover without permanent deformation, which is essential for protecting irregularly shaped products. Polyethylene films, while providing good tensile strength, tend to be less elastic and more prone to tearing under repetitive stress. The high elongation at break and excellent shape recovery of polyurethane make it ideal for flexible packaging applications requiring durability and repeated handling.
Moisture and Chemical Resistance
Polyurethane packaging films offer superior moisture resistance due to their dense molecular structure, effectively preventing water vapor transmission compared to polyethylene films. Polyethylene excels in chemical resistance, particularly against acids and alkalis, making it ideal for packaging reactive substances. Selecting between polyurethane and polyethylene depends on specific packaging requirements, balancing moisture barrier properties with chemical exposure tolerance.
Environmental Impact and Recyclability
Polyurethane packaging films offer enhanced durability and flexibility but pose challenges in recyclability due to complex chemical structures that hinder standard recycling processes. Polyethylene films are widely preferred for packaging because of their higher recyclability rates and lower environmental footprint during production, contributing to reduced landfill waste. Advancements in biodegradable polyethylene variants and integration into circular recycling systems further promote sustainable packaging solutions compared to polyurethane alternatives.
Cost Comparison
Polyethylene packaging film generally offers a lower cost option compared to polyurethane due to its widespread production and simpler manufacturing process, resulting in more affordable raw material prices. Polyurethane films, while providing superior flexibility and abrasion resistance, tend to have higher production costs that elevate their market price. Cost efficiency in packaging applications often favors polyethylene where budget constraints are critical, whereas polyurethane is selected for premium or specialized uses despite the increased expense.
Typical Applications in Packaging
Polyurethane packaging films are widely used for flexible packaging applications requiring high abrasion resistance and elasticity, such as food wraps and medical packaging. Polyethylene films dominate in general packaging due to their excellent moisture barrier properties and cost-effectiveness, commonly applied in grocery bags, shrink wraps, and stretch films. The choice between polyurethane and polyethylene depends on the performance requirements, with polyurethane preferred for protective cushioning and polyethylene for bulk packaging and moisture-sensitive products.
Choosing the Right Material for Your Packaging Needs
Polyurethane offers superior elasticity and abrasion resistance, making it ideal for packaging applications requiring flexibility and durability. Polyethylene provides excellent moisture barrier properties and cost-effectiveness, preferred for lightweight and economical packaging solutions. Selecting the right material depends on balancing factors like mechanical strength, environmental resistance, and budget constraints to meet specific packaging needs.
Infographic: Polyurethane vs Polyethylene for Packaging Film
 azmater.com
azmater.com