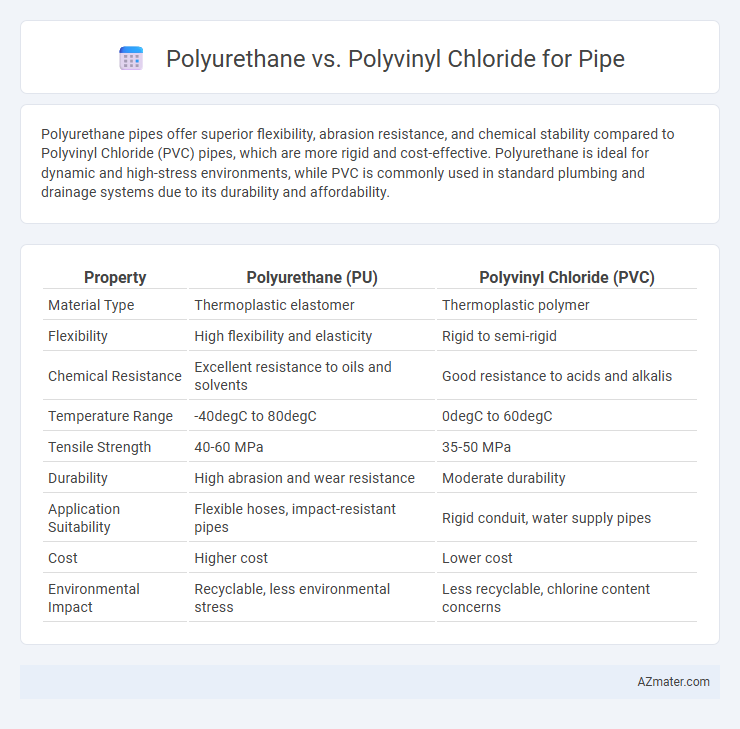
Polyurethane pipes offer superior flexibility, abrasion resistance, and chemical stability compared to Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC) pipes, which are more rigid and cost-effective. Polyurethane is ideal for dynamic and high-stress environments, while PVC is commonly used in standard plumbing and drainage systems due to its durability and affordability.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Polyurethane (PU) | Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC) |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Thermoplastic elastomer | Thermoplastic polymer |
| Flexibility | High flexibility and elasticity | Rigid to semi-rigid |
| Chemical Resistance | Excellent resistance to oils and solvents | Good resistance to acids and alkalis |
| Temperature Range | -40degC to 80degC | 0degC to 60degC |
| Tensile Strength | 40-60 MPa | 35-50 MPa |
| Durability | High abrasion and wear resistance | Moderate durability |
| Application Suitability | Flexible hoses, impact-resistant pipes | Rigid conduit, water supply pipes |
| Cost | Higher cost | Lower cost |
| Environmental Impact | Recyclable, less environmental stress | Less recyclable, chlorine content concerns |
Introduction to Polyurethane and Polyvinyl Chloride
Polyurethane is a versatile polymer known for its elasticity, durability, and resistance to abrasion, making it ideal for flexible piping applications requiring strength and longevity. Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC) is a widely used synthetic plastic polymer characterized by chemical resistance, rigid structure, and cost-effectiveness, commonly utilized in water supply and drainage pipes. Both materials offer distinct properties that influence their suitability in various piping systems, with polyurethane excelling in flexibility and impact resistance, while PVC provides rigidity and ease of installation.
Chemical Composition and Structure
Polyurethane pipes are composed of segmented polymers formed by reacting diisocyanates with polyols, resulting in flexible chains with alternating soft and hard segments that provide elasticity and resistance to abrasion. Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) pipes consist of a vinyl polymer made from repeating vinyl chloride monomers, characterized by a rigid chlorinated structure offering excellent chemical resistance and durability. The segmented urethane structure of polyurethane imparts superior impact resistance and flexibility compared to the rigid, crystalline lattice of PVC, influencing their suitability for different piping applications.
Mechanical Strength and Durability
Polyurethane pipes exhibit superior mechanical strength with high tensile and impact resistance, making them ideal for applications requiring flexibility and toughness. Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC) pipes offer good rigidity and chemical resistance but are more prone to brittleness and cracking under heavy mechanical stress or extreme temperatures. The durability of polyurethane under dynamic loads and wear conditions surpasses PVC, which tends to degrade faster in harsh environments.
Flexibility and Elasticity Comparison
Polyurethane pipes exhibit superior flexibility and elasticity compared to polyvinyl chloride (PVC) pipes, making them ideal for applications requiring frequent bending and resistance to deformation. Polyurethane's elastic modulus ranges between 10-50 MPa, enabling it to return to its original shape after significant stretching, whereas PVC's modulus is higher, around 2,400 MPa, indicating rigidity and lower elastic recovery. This enhanced flexibility and elasticity translate to better performance in dynamic environments, such as pneumatic systems or flexible conduit installations.
Corrosion and Chemical Resistance
Polyurethane pipes exhibit superior chemical resistance compared to polyvinyl chloride (PVC) pipes, making them highly effective in environments with aggressive chemicals and solvents. PVC pipes are prone to corrosion when exposed to strong acids or alkaline substances, while polyurethane maintains structural integrity and resists degradation under similar conditions. The enhanced corrosion resistance of polyurethane extends the lifespan of piping systems in industrial applications where harsh chemical exposure is common.
Temperature and UV Stability
Polyurethane pipes exhibit superior flexibility and maintain structural integrity at temperatures ranging from -40degC to 80degC, outperforming polyvinyl chloride (PVC) which typically tolerates temperatures between 0degC and 60degC. UV stability is a critical factor, where polyurethane demonstrates enhanced resistance to UV degradation due to its chemical composition, whereas PVC pipes may become brittle and discolored over prolonged UV exposure without additives. Selecting polyurethane ensures longer service life and durability in outdoor and extreme temperature applications compared to standard PVC piping.
Cost and Economic Considerations
Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC) pipes generally offer a lower initial cost compared to Polyurethane (PU) pipes, making PVC a more economical choice for large-scale infrastructure projects. However, Polyurethane pipes provide superior durability and resistance to abrasion, chemicals, and impact, leading to lower maintenance and replacement expenses over time. Evaluating lifecycle costs reveals that while PVC is cost-effective upfront, Polyurethane's longer service life can result in better long-term economic value for demanding applications.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Polyurethane pipes offer superior environmental benefits due to their high durability and resistance to corrosion, reducing the need for frequent replacements and minimizing waste. Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) production involves chlorine, posing potential risks of toxic byproducts and challenges in recycling, which can contribute to environmental pollution. Polyurethane's recyclability and lower carbon footprint make it a more sustainable choice for pipe applications in eco-conscious projects.
Common Applications in Piping Systems
Polyurethane pipes excel in applications requiring high flexibility, abrasion resistance, and durability, commonly used in hydraulic systems, pneumatic lines, and industrial fluid transfer. Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC) pipes are widely employed in residential plumbing, irrigation, and sewage systems due to their corrosion resistance, affordability, and ease of installation. Both materials are integral to piping systems but are chosen based on specific performance needs such as chemical exposure, pressure ratings, and environmental conditions.
Choosing the Right Material: Key Takeaways
Polyurethane offers superior flexibility, abrasion resistance, and chemical stability, making it ideal for dynamic or harsh environments in piping systems. Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC) provides excellent cost-efficiency, corrosion resistance, and ease of installation, suitable for standard water and irrigation applications. Selecting between polyurethane and PVC depends on specific requirements such as mechanical stress tolerance, environmental exposure, and budget constraints to ensure optimal pipe performance and longevity.
Infographic: Polyurethane vs Polyvinyl Chloride for Pipe
 azmater.com
azmater.com