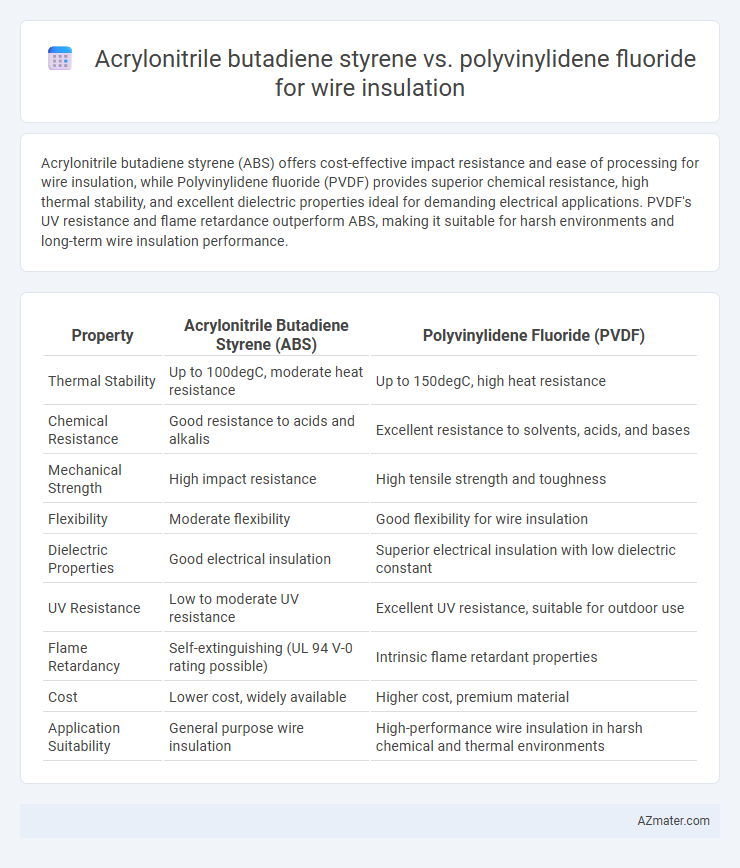
Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS) offers cost-effective impact resistance and ease of processing for wire insulation, while Polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF) provides superior chemical resistance, high thermal stability, and excellent dielectric properties ideal for demanding electrical applications. PVDF's UV resistance and flame retardance outperform ABS, making it suitable for harsh environments and long-term wire insulation performance.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS) | Polyvinylidene Fluoride (PVDF) |
|---|---|---|
| Thermal Stability | Up to 100degC, moderate heat resistance | Up to 150degC, high heat resistance |
| Chemical Resistance | Good resistance to acids and alkalis | Excellent resistance to solvents, acids, and bases |
| Mechanical Strength | High impact resistance | High tensile strength and toughness |
| Flexibility | Moderate flexibility | Good flexibility for wire insulation |
| Dielectric Properties | Good electrical insulation | Superior electrical insulation with low dielectric constant |
| UV Resistance | Low to moderate UV resistance | Excellent UV resistance, suitable for outdoor use |
| Flame Retardancy | Self-extinguishing (UL 94 V-0 rating possible) | Intrinsic flame retardant properties |
| Cost | Lower cost, widely available | Higher cost, premium material |
| Application Suitability | General purpose wire insulation | High-performance wire insulation in harsh chemical and thermal environments |
Introduction to Wire Insulation Materials
Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS) and Polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF) are widely used wire insulation materials with distinct properties impacting their suitability. ABS offers excellent mechanical strength and good electrical insulation, making it cost-effective for general wiring applications. PVDF provides superior chemical resistance, high thermal stability, and exceptional dielectric properties, preferred for harsh environments and high-performance electrical insulation.
What is Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS)?
Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS) is a thermoplastic polymer known for its high impact resistance, toughness, and good insulating properties, making it a common choice for wire insulation applications. ABS offers excellent chemical resistance and dimensional stability, which helps protect wires in various industrial environments. Compared to Polyvinylidene Fluoride (PVDF), ABS is generally more cost-effective but may have lower temperature resistance and UV stability.
What is Polyvinylidene Fluoride (PVDF)?
Polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF) is a high-performance thermoplastic fluoropolymer known for its excellent chemical resistance, high dielectric strength, and thermal stability, making it ideal for wire insulation in harsh environments. Unlike acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS), PVDF offers superior UV resistance, low friction, and strong mechanical properties, ensuring longevity and reliability in demanding electrical applications. PVDF's unique properties enable it to maintain insulation integrity under extreme temperatures and exposure to corrosive substances, outperforming ABS in specialized wire insulation tasks.
Mechanical Properties Comparison: ABS vs PVDF
Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS) offers moderate mechanical strength and impact resistance, making it suitable for cost-effective wire insulation with good toughness and rigidity. Polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF) provides superior mechanical properties, including higher tensile strength, exceptional chemical resistance, and excellent flexibility, enhancing durability in demanding environments. PVDF's enhanced mechanical performance outperforms ABS in applications requiring long-term reliability and resistance to abrasion, chemicals, and extreme temperatures.
Thermal Resistance: ABS vs PVDF in Wire Insulation
Polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF) offers superior thermal resistance compared to Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS) in wire insulation applications, with PVDF maintaining stability up to approximately 150-170degC, whereas ABS typically withstands temperatures only up to around 90-100degC. PVDF's high melting point and low thermal degradation rate make it ideal for environments requiring sustained thermal endurance. In contrast, ABS is more prone to deformation and thermal breakdown at elevated temperatures, limiting its use in high-heat wire insulation scenarios.
Chemical Resistance and Durability
Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS) offers good chemical resistance against acids and alkalis but is less effective against strong solvents and UV exposure, limiting its durability in harsh environments. Polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF) exhibits superior chemical resistance to a broad range of solvents, acids, and bases, ensuring enhanced durability and long-term performance for wire insulation in aggressive chemical settings. PVDF's excellent thermal stability and resistance to environmental degradation make it a preferred choice over ABS for demanding industrial wire insulation applications.
Electrical Performance and Safety Factors
Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS) offers moderate electrical insulation properties with a dielectric strength typically around 16-20 kV/mm, making it suitable for general wire insulation where impact resistance and cost-effectiveness are priorities. Polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF) exhibits superior electrical performance with a dielectric constant of approximately 8.4 and a dielectric strength of up to 40 kV/mm, providing enhanced insulation and stability in high-voltage applications. In terms of safety, PVDF's excellent chemical resistance, UV stability, and flame retardancy reduce risks of insulation degradation and fire hazards, while ABS may require additional treatments to meet stringent safety standards in harsh environments.
Cost and Availability for Electrical Applications
Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS) offers a cost-effective and widely available solution for wire insulation, making it suitable for numerous electrical applications where budget constraints are critical. Polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF), although more expensive, provides superior chemical resistance, thermal stability, and flame retardancy, but its limited availability can increase lead times for specialized projects. Choosing between ABS and PVDF hinges on balancing the required electrical insulation performance with cost efficiency and supplier accessibility.
Sustainability and Environmental Impact
Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS) offers lower energy consumption during production but poses recycling challenges due to its mixed polymer composition, contributing to long-term environmental concerns in wire insulation applications. Polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF) provides superior chemical resistance and durability, leading to extended product life cycles that reduce waste generation, yet its fluorinated structure raises concerns about persistence and potential bioaccumulation in ecosystems. Selecting PVDF enhances sustainability through longevity, whereas ABS requires improved recycling infrastructures to mitigate ecological impact in electrical wire insulation.
Choosing the Right Material: ABS or PVDF for Wire Insulation
Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS) offers excellent impact resistance and cost-effectiveness, making it suitable for wire insulation in applications requiring moderate chemical resistance and durability. Polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF) excels in thermal stability, chemical resistance, and electrical insulation properties, ideal for harsh environments and high-performance electrical wiring. Selecting between ABS and PVDF depends on specific requirements such as temperature range, exposure to chemicals, and mechanical stress tolerance for optimal wire insulation performance.
Infographic: Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene vs Polyvinylidene fluoride for Wire insulation
 azmater.com
azmater.com