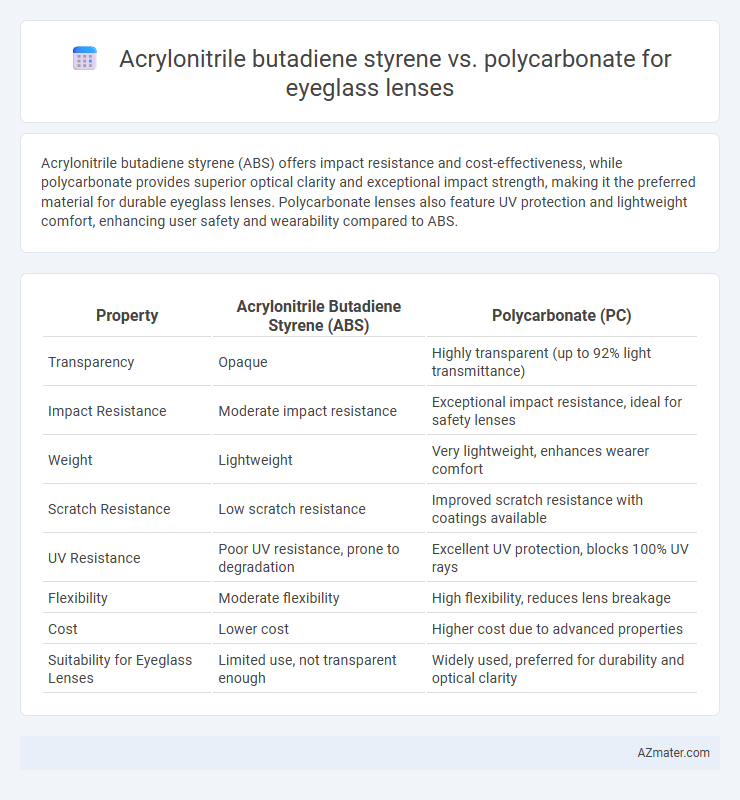
Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS) offers impact resistance and cost-effectiveness, while polycarbonate provides superior optical clarity and exceptional impact strength, making it the preferred material for durable eyeglass lenses. Polycarbonate lenses also feature UV protection and lightweight comfort, enhancing user safety and wearability compared to ABS.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS) | Polycarbonate (PC) |
|---|---|---|
| Transparency | Opaque | Highly transparent (up to 92% light transmittance) |
| Impact Resistance | Moderate impact resistance | Exceptional impact resistance, ideal for safety lenses |
| Weight | Lightweight | Very lightweight, enhances wearer comfort |
| Scratch Resistance | Low scratch resistance | Improved scratch resistance with coatings available |
| UV Resistance | Poor UV resistance, prone to degradation | Excellent UV protection, blocks 100% UV rays |
| Flexibility | Moderate flexibility | High flexibility, reduces lens breakage |
| Cost | Lower cost | Higher cost due to advanced properties |
| Suitability for Eyeglass Lenses | Limited use, not transparent enough | Widely used, preferred for durability and optical clarity |
Introduction to Eyeglass Lens Materials
Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS) and polycarbonate are common materials used in eyeglass lenses, each offering unique properties that impact comfort and durability. Polycarbonate lenses provide superior impact resistance and UV protection, making them ideal for safety glasses and sports eyewear. In contrast, ABS lenses are less expensive but generally offer lower optical clarity and impact resistance compared to polycarbonate, influencing their suitability for everyday eyeglass use.
Overview of Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS)
Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS) is a thermoplastic polymer known for its strength, impact resistance, and lightweight properties, making it suitable for various applications including eyewear frames. While ABS offers good durability and cost-effectiveness, it is less optically clear compared to Polycarbonate, which is preferred for eyeglass lenses due to superior transparency and scratch resistance. ABS is more commonly used in frame construction, providing flexibility and toughness but lacks the optical clarity required for high-quality lenses.
Key Properties of Polycarbonate
Polycarbonate lenses offer exceptional impact resistance, making them highly durable and ideal for safety or sports eyewear. Their inherent UV protection blocks 100% of harmful ultraviolet rays, preventing eye damage. Despite being lightweight, polycarbonate lenses maintain high optical clarity and scratch resistance, enhancing comfort and longevity compared to acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS) lenses.
Optical Clarity: ABS vs Polycarbonate
Polycarbonate lenses offer superior optical clarity compared to Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS), featuring higher light transmission and less distortion, making them ideal for eyeglasses requiring precise vision. ABS lenses often exhibit lower optical performance due to their intrinsic material properties that cause increased haze and reduced clarity. Polycarbonate's advanced molecular structure ensures better impact resistance while maintaining excellent transparency, positioning it as the preferred choice for high-quality eyeglass lenses.
Durability and Impact Resistance Comparison
Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS) offers moderate durability with good impact resistance, making it suitable for standard eyeglass lenses but less effective against high-impact forces. Polycarbonate lenses provide superior impact resistance, being nearly unbreakable and highly resistant to cracks and shattering, ideal for safety or sports eyewear. Durability in polycarbonate surpasses ABS due to its enhanced toughness and resistance to environmental stress, ensuring longer-lasting performance under rigorous conditions.
Weight and Comfort in Eyewear Applications
Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS) offers a lightweight structure that enhances comfort in eyewear due to its lower density compared to polycarbonate, which can result in a heavier feel on the face. Polycarbonate, although slightly heavier, provides superior impact resistance and durability, making it suitable for high-performance eyeglass lenses where protection is critical. The choice between ABS and polycarbonate for eyeglass lenses often balances weight-related comfort against the demand for toughness and optical clarity.
Scratch Resistance and Longevity
Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS) eyeglass lenses offer decent impact resistance but typically have lower scratch resistance compared to polycarbonate lenses. Polycarbonate lenses are engineered with superior hardness and often feature additional scratch-resistant coatings, enhancing their durability and lifespan significantly. For long-term use, polycarbonate lenses provide better scratch resistance and longevity, making them a preferred choice in eyewear materials.
Cost Efficiency and Availability
Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS) eyeglass lenses offer superior cost efficiency due to lower raw material and manufacturing expenses compared to polycarbonate lenses, making them a budget-friendly option for mass production. ABS lenses are widely available and easily sourced from multiple suppliers, ensuring consistent supply chains for eyewear manufacturers. Polycarbonate lenses, while more impact-resistant, tend to have higher production costs and limited availability due to specialized processing requirements.
Environmental and Safety Considerations
Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS) lenses have moderate environmental impact due to their non-biodegradable nature and the release of toxic substances during production and disposal. Polycarbonate lenses are more eco-friendly, offering high impact resistance and UV protection while being recyclable, though their manufacturing process involves hazardous chemicals like bisphenol A. Both materials require careful handling to minimize environmental harm, but polycarbonate stands out for safety performance and sustainability in eyeglass lens applications.
Best Choice: ABS or Polycarbonate for Eyeglass Lenses
Polycarbonate is the best choice for eyeglass lenses due to its superior impact resistance, lightweight nature, and excellent optical clarity compared to acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS). ABS offers good toughness and cost-effectiveness but falls short in durability and UV protection, making it less suitable for eyewear applications. Polycarbonate's high shatter resistance and scratch-resistant coatings ensure safety and long-lasting performance in eyeglass lenses.
Infographic: Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene vs Polycarbonate for Eyeglass Lens
 azmater.com
azmater.com