Polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA) offers superior clarity and UV resistance compared to polyethylene, making it ideal for high-visibility packaging applications. Polyethylene excels in flexibility, moisture barrier properties, and cost-effectiveness, preferred for food packaging and lightweight protective wraps.
Table of Comparison
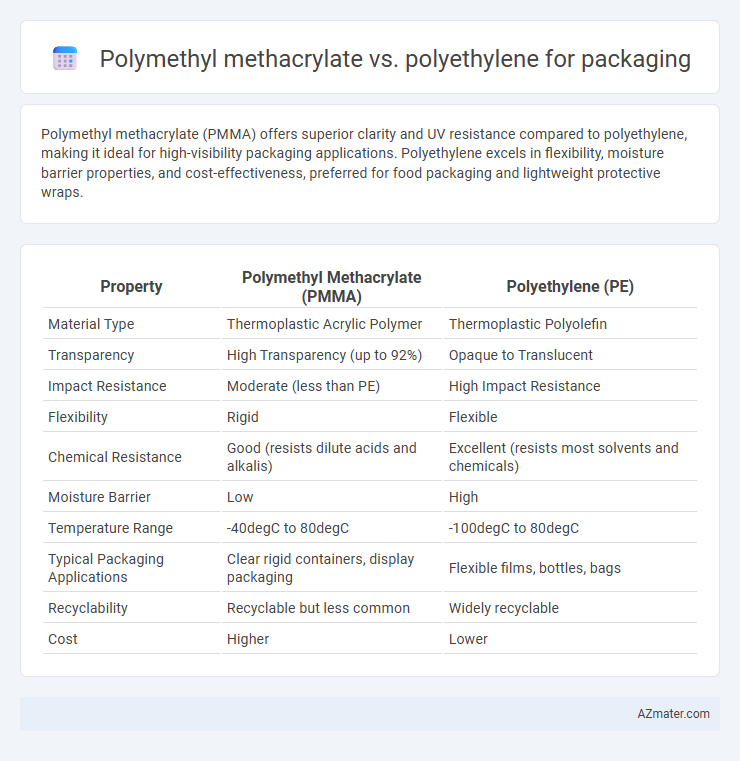
| Property | Polymethyl Methacrylate (PMMA) | Polyethylene (PE) |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Thermoplastic Acrylic Polymer | Thermoplastic Polyolefin |
| Transparency | High Transparency (up to 92%) | Opaque to Translucent |
| Impact Resistance | Moderate (less than PE) | High Impact Resistance |
| Flexibility | Rigid | Flexible |
| Chemical Resistance | Good (resists dilute acids and alkalis) | Excellent (resists most solvents and chemicals) |
| Moisture Barrier | Low | High |
| Temperature Range | -40degC to 80degC | -100degC to 80degC |
| Typical Packaging Applications | Clear rigid containers, display packaging | Flexible films, bottles, bags |
| Recyclability | Recyclable but less common | Widely recyclable |
| Cost | Higher | Lower |
Introduction to Polymethyl Methacrylate and Polyethylene
Polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA) is a transparent thermoplastic often used as a lightweight, shatter-resistant alternative to glass, prized in packaging for its high clarity and UV resistance. Polyethylene (PE), the most widely produced plastic globally, is valued in packaging for its excellent chemical resistance, flexibility, and moisture barrier properties. Both materials serve distinct packaging needs, with PMMA favored for rigid, clear applications and PE dominating in flexible, durable packaging solutions.
Chemical Composition and Structure
Polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA) is a transparent thermoplastic composed of methyl methacrylate monomers with a linear polymer chain, characterized by strong glass-like clarity and rigidity. Polyethylene (PE) consists of repeating ethylene units forming a flexible, semi-crystalline polymer with variations like HDPE and LDPE influencing density and mechanical properties. The distinct chemical compositions result in PMMA's superior optical properties and rigidity, whereas PE offers better flexibility and chemical resistance for diverse packaging applications.
Mechanical Properties Comparison
Polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA) offers higher tensile strength and superior rigidity compared to polyethylene (PE), making it ideal for packaging requiring durability and resistance to deformation. PE exhibits excellent impact resistance and flexibility, which enhances shock absorption but results in lower stiffness than PMMA. The choice between PMMA and PE depends on packaging needs, balancing PMMA's stronger mechanical robustness against PE's flexibility and toughness.
Transparency and Optical Characteristics
Polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA) offers superior optical clarity with light transmittance up to 92%, making it highly transparent compared to polyethylene (PE), which typically exhibits lower clarity due to its semi-crystalline structure. PMMA maintains excellent resistance to UV degradation and maintains optical clarity over time, whereas PE can yellow and lose transparency under prolonged UV exposure. The inherent rigidity and glass-like transparency of PMMA make it ideal for high-end packaging applications requiring clear visibility, while polyethylene's flexibility and cost-effectiveness suit less visually demanding packaging needs.
Barrier Properties and Permeability
Polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA) exhibits superior oxygen barrier properties compared to polyethylene (PE), making it ideal for packaging sensitive products requiring extended shelf life. PE shows higher permeability to moisture and gases, which limits its use where airtightness is crucial but offers flexibility and cost-effectiveness for less demanding applications. The choice between PMMA and PE depends largely on the desired balance between barrier performance and mechanical flexibility in packaging design.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA) and polyethylene (PE) differ significantly in environmental impact and sustainability, with polyethylene offering higher recyclability rates and lower energy consumption during production. PMMA, while providing superior clarity and durability for packaging, poses challenges in recycling due to its chemical structure and lower biodegradability. Polyethylene's widespread adoption in sustainable packaging initiatives is driven by advancements in bio-based and recycled material formulations that reduce carbon footprint and landfill accumulation.
Cost Efficiency and Availability
Polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA) generally incurs higher costs than polyethylene (PE) due to its superior clarity and rigidity, making it less cost-efficient for large-scale packaging applications. Polyethylene's widespread availability and low production cost contribute to its dominant use in packaging, especially for flexible and high-volume products. While PMMA offers enhanced aesthetic appeal and strength, polyethylene remains the preferred material where cost efficiency and supply consistency are critical.
Application Suitability in Packaging
Polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA) excels in packaging applications requiring high optical clarity and UV resistance, making it ideal for display windows, food containers, and cosmetic packaging where visibility and aesthetics are critical. Polyethylene (PE), particularly low-density (LDPE) and high-density (HDPE) variants, offers superior chemical resistance, flexibility, and moisture barrier properties, making it suitable for flexible packaging, bottles, and industrial containers. The choice between PMMA and PE depends on the packaging's functional demands, with PMMA favored for rigidity and transparency, while PE is preferred for durability and moisture protection.
Recycling and End-of-Life Options
Polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA) offers superior clarity and UV resistance but faces recycling challenges due to limited industrial recycling facilities and higher processing costs. Polyethylene (PE), widely used in packaging, benefits from established recycling streams and multiple end-of-life options such as mechanical recycling, chemical recycling, and energy recovery. The choice between PMMA and PE in packaging significantly impacts sustainability, with PE currently providing more practical and scalable recycling solutions.
Future Trends in Packaging Materials
Polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA) offers superior clarity and weather resistance, making it ideal for premium packaging applications, while polyethylene (PE) provides cost-effective flexibility and excellent moisture barrier properties favored in mass market packaging. Emerging trends emphasize bio-based and recyclable variants of both PMMA and PE to meet increasing sustainability demands and regulatory pressures. Innovations in nanocomposite enhancements and functional coatings are driving improved strength, biodegradability, and active packaging capabilities in future packaging materials.
Infographic: Polymethyl methacrylate vs Polyethylene for Packaging
 azmater.com
azmater.com