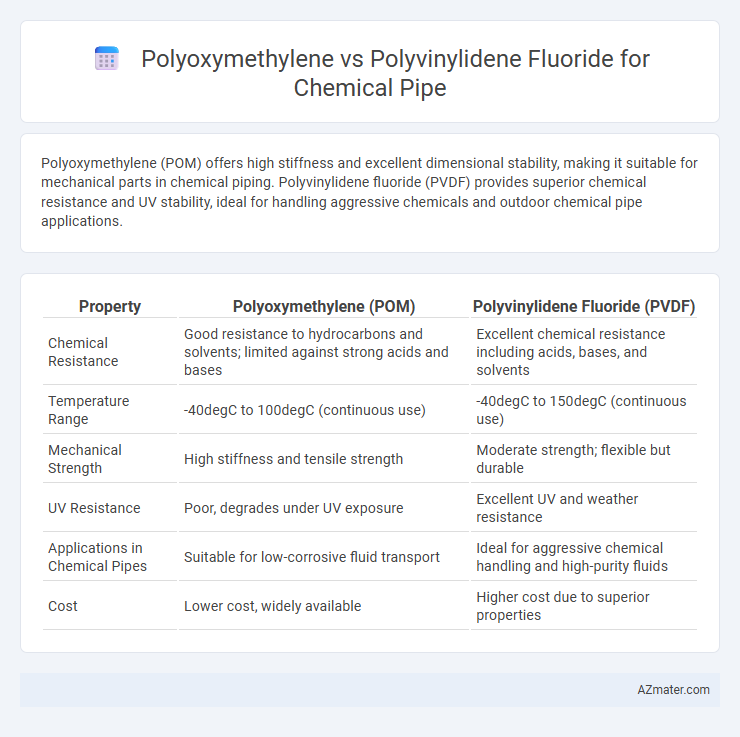
Polyoxymethylene (POM) offers high stiffness and excellent dimensional stability, making it suitable for mechanical parts in chemical piping. Polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF) provides superior chemical resistance and UV stability, ideal for handling aggressive chemicals and outdoor chemical pipe applications.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Polyoxymethylene (POM) | Polyvinylidene Fluoride (PVDF) |
|---|---|---|
| Chemical Resistance | Good resistance to hydrocarbons and solvents; limited against strong acids and bases | Excellent chemical resistance including acids, bases, and solvents |
| Temperature Range | -40degC to 100degC (continuous use) | -40degC to 150degC (continuous use) |
| Mechanical Strength | High stiffness and tensile strength | Moderate strength; flexible but durable |
| UV Resistance | Poor, degrades under UV exposure | Excellent UV and weather resistance |
| Applications in Chemical Pipes | Suitable for low-corrosive fluid transport | Ideal for aggressive chemical handling and high-purity fluids |
| Cost | Lower cost, widely available | Higher cost due to superior properties |
Introduction to Chemical Piping Materials
Polyoxymethylene (POM) and Polyvinylidene Fluoride (PVDF) are widely used materials in chemical piping systems due to their excellent chemical resistance and mechanical properties. PVDF offers superior resistance to a broad range of aggressive chemicals, including strong acids and bases, making it ideal for highly corrosive environments, while POM exhibits high stiffness and low friction but lower chemical resistance compared to PVDF. Selection between POM and PVDF depends on specific chemical exposure, temperature requirements, and mechanical stress in piping applications within chemical processing industries.
Overview of Polyoxymethylene (POM) in Chemical Piping
Polyoxymethylene (POM), known for its high mechanical strength and excellent dimensional stability, serves as a reliable material in chemical piping applications where rigidity and wear resistance are crucial. Its low moisture absorption and chemical resistance to hydrocarbons, solvents, and alkalis make POM suitable for transporting a variety of chemicals, although it is less resistant to strong acids compared to Polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF). POM's ability to maintain structural integrity under mechanical stress and moderate chemical exposure positions it as an efficient and cost-effective choice for specific chemical piping systems.
Overview of Polyvinylidene Fluoride (PVDF) in Chemical Piping
Polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF) offers exceptional chemical resistance, high purity, and mechanical strength, making it ideal for chemical piping systems handling aggressive solvents, acids, and bases. Its superior thermal stability up to 150degC and resistance to UV radiation ensure long-term durability in harsh industrial environments. Compared to polyoxymethylene (POM), PVDF provides enhanced corrosion resistance and better performance in high-temperature and high-pressure applications within chemical processing industries.
Chemical Resistance: POM vs PVDF
Polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF) exhibits superior chemical resistance compared to Polyoxymethylene (POM), making it ideal for pipes exposed to highly corrosive chemicals and aggressive solvents. PVDF withstands strong acids, alkalis, and organic solvents without degradation, whereas POM is more susceptible to chemical attack, particularly by strong acids and oxidizing agents. This enhanced chemical resistance of PVDF ensures longer service life and reliability in demanding chemical piping applications.
Mechanical Strength and Durability Comparison
Polyoxymethylene (POM) offers high mechanical strength and excellent rigidity, making it suitable for chemical pipe applications requiring dimensional stability under stress. Polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF) demonstrates superior chemical resistance and durability, especially in harsh corrosive environments, with notable resistance to UV radiation and temperature fluctuations. While POM excels in load-bearing capacity, PVDF provides enhanced long-term durability and resistance to chemical degradation, crucial for extended service life in aggressive chemical transport.
Temperature and Thermal Stability Analysis
Polyoxymethylene (POM) offers excellent mechanical strength but has a lower thermal stability, with a maximum continuous use temperature around 80degC, limiting its application in high-temperature chemical piping. Polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF) exhibits superior thermal resistance, maintaining integrity and chemical resistance at temperatures up to 150degC, making it ideal for aggressive chemical transport under elevated temperatures. The higher melting point and thermal stability of PVDF enable longer service life and improved safety in industrial piping systems exposed to fluctuating or high thermal conditions.
Installation and Maintenance Considerations
Polyoxymethylene (POM) pipes offer excellent dimensional stability and ease of machining, leading to straightforward installation with commonly available tools, while requiring routine maintenance to monitor for potential stress cracking in aggressive chemical environments. Polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF) pipes provide superior chemical resistance and UV stability, demanding specialized welding techniques for secure joints and minimal maintenance due to their high resistance to corrosion and biofouling. Choosing between POM and PVDF pipes depends on balancing ease of installation against long-term maintenance demands specific to the chemical process conditions.
Cost Effectiveness and Lifecycle Analysis
Polyoxymethylene (POM) offers superior cost effectiveness for chemical pipe applications due to its lower raw material and processing costs compared to Polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF), making it ideal for budget-sensitive projects. However, PVDF excels in lifecycle performance with exceptional chemical resistance, UV stability, and thermal durability, leading to reduced maintenance and replacement frequency in highly corrosive environments. Evaluating total cost of ownership reveals that while POM has initial savings, PVDF's longer service life and reliability often justify its higher upfront investment in aggressive chemical piping systems.
Safety and Environmental Impact
Polyoxymethylene (POM) demonstrates superior mechanical strength and chemical resistance, making it suitable for chemical pipe applications where durability and safety are critical to prevent leaks and contamination. Polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF) excels in chemical inertness and UV resistance, ensuring long-term environmental safety by minimizing degradation and chemical leaching in harsh environments. PVDF's low toxicity and recyclability contribute to a reduced environmental footprint compared to POM, which can release formaldehyde under certain conditions, posing potential health risks.
Choosing the Right Material: POM or PVDF?
Polyoxymethylene (POM) offers excellent mechanical strength and dimensional stability, making it ideal for chemical pipes requiring rigidity and precision. Polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF) provides superior chemical resistance and is highly effective against a wide range of aggressive solvents and acids, ensuring long-term durability in corrosive environments. Selecting POM or PVDF depends on application-specific factors such as chemical exposure, temperature range, and mechanical stress, where PVDF excels in harsh chemical conditions while POM is better suited for structurally demanding uses.
Infographic: Polyoxymethylene vs Polyvinylidene fluoride for Chemical pipe
 azmater.com
azmater.com