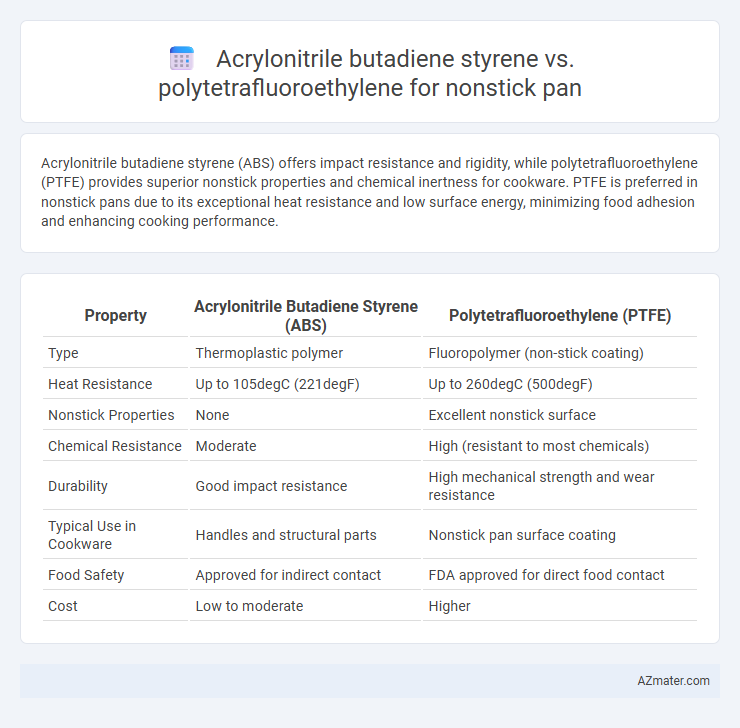
Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS) offers impact resistance and rigidity, while polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) provides superior nonstick properties and chemical inertness for cookware. PTFE is preferred in nonstick pans due to its exceptional heat resistance and low surface energy, minimizing food adhesion and enhancing cooking performance.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS) | Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) |
|---|---|---|
| Type | Thermoplastic polymer | Fluoropolymer (non-stick coating) |
| Heat Resistance | Up to 105degC (221degF) | Up to 260degC (500degF) |
| Nonstick Properties | None | Excellent nonstick surface |
| Chemical Resistance | Moderate | High (resistant to most chemicals) |
| Durability | Good impact resistance | High mechanical strength and wear resistance |
| Typical Use in Cookware | Handles and structural parts | Nonstick pan surface coating |
| Food Safety | Approved for indirect contact | FDA approved for direct food contact |
| Cost | Low to moderate | Higher |
Introduction to ABS and PTFE Nonstick Materials
Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS) offers high impact resistance, durability, and heat tolerance typically up to 80degC, making it more suitable for structural and mechanical applications than nonstick cookware. Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE), commonly known by the brand name Teflon, provides superior nonstick properties, excellent chemical resistance, and heat stability up to approximately 260degC, earning its primary use in nonstick pan coatings. The chemical inertness and low surface energy of PTFE create a frictionless surface ideal for cooking, whereas ABS lacks these attributes and is rarely used in nonstick cookware.
Chemical Composition and Structure Comparison
Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS) is a thermoplastic polymer made of acrylonitrile, butadiene, and styrene, offering toughness and impact resistance, whereas polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) is a fluoropolymer composed of carbon and fluorine atoms, known for its non-reactive, low friction surface. ABS has a complex chain structure with distinct rubbery and rigid segments, providing mechanical strength, while PTFE's linear, highly crystalline structure creates an exceptionally smooth, nonstick coating highly resistant to heat and chemical attack. The chemical makeup of PTFE ensures superior nonstick performance and durability in cooking applications compared to the more versatile but less chemically inert ABS.
Thermal Stability: ABS vs PTFE in Cookware Applications
Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) offers superior thermal stability compared to Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS) in nonstick cookware, with PTFE maintaining integrity at temperatures up to 260degC (500degF), while ABS degrades around 105degC to 125degC (221degF to 257degF). PTFE's high melting point and excellent heat resistance prevent warping and chemical leaching during high-heat cooking, ensuring safer food contact surfaces. In contrast, ABS's lower thermal threshold limits its use in cookware applications where sustained high temperatures are common, making PTFE the preferred material for durable, reliable nonstick coatings.
Nonstick Performance and Food Release
Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS) offers moderate nonstick performance but tends to degrade under high heat, affecting its food release capabilities in nonstick pans. Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE), commonly known as Teflon, provides superior nonstick properties with excellent food release, maintaining performance even at higher cooking temperatures up to 260degC (500degF). PTFE's chemical inertness and low surface energy make it the preferred choice for durable, efficient nonstick cookware compared to ABS.
Durability and Scratch Resistance
Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS) exhibits moderate durability but is prone to scratches and wear over time, making it less ideal for nonstick pans subjected to frequent utensil use. Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE), widely known as Teflon, offers superior scratch resistance and maintains its nonstick properties even after prolonged cooking, enhancing the pan's durability. PTFE's resilience against heat and abrasion makes it the preferred coating for nonstick cookware demanding long-lasting performance.
Health and Safety Considerations for Home Use
Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS) in nonstick pans poses potential health risks due to its lower heat resistance, which can lead to the release of harmful chemicals when overheated. Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE), commonly known as Teflon, offers superior heat stability and chemical inertness but may emit toxic fumes at temperatures above 260degC (500degF), posing respiratory hazards. For home use, PTFE-based pans are generally safer if used within recommended temperature limits, while ABS coatings are less common and potentially less safe under high-heat cooking conditions.
Ease of Cleaning and Maintenance
Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS) pans offer moderate ease of cleaning due to their relatively smooth surface but may require gentle scrubbing to prevent surface damage. Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) nonstick pans provide superior ease of cleaning and maintenance as their slick, nonporous surface resists food sticking, allowing for quick wipe-downs and minimal residue buildup. PTFE coatings typically demand careful use of soft utensils and avoidance of high heat to preserve the nonstick layer and extend pan lifespan.
Cost and Market Availability
Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS) offers a significantly lower cost compared to Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE), making it a more budget-friendly option for nonstick pans. PTFE, commonly known by the brand name Teflon, dominates the market due to its superior nonstick properties and heat resistance, but it comes at a premium price and is less widely available in low-cost cookware. Market availability favors PTFE-coated pans in commercial and high-end segments, while ABS-coated pans are primarily found in affordable and entry-level nonstick cookware.
Environmental Impact and Recycling
Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS) used in nonstick pans poses significant environmental challenges due to its petroleum-based origin and difficulty in biodegrading, leading to persistent plastic waste in landfills. Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE), although chemically inert and resistant to breakdown, can release toxic fumes when overheated, raising concerns about air pollution and health hazards. Both materials face recycling limitations, with ABS moderately more recyclable through mechanical processes, while PTFE's chemical stability complicates recycling efforts and often results in incineration or landfill disposal.
Final Verdict: Choosing the Right Nonstick Pan Material
Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS) offers durability and impact resistance but lacks the high-temperature tolerance and nonstick efficiency of polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE). PTFE, commonly known as Teflon, provides superior nonstick performance and heat resistance up to 260degC, making it ideal for cooking applications. For a nonstick pan, PTFE's proven nonstick properties and thermal stability make it the optimal choice over ABS for reliable, easy-to-clean cookware.
Infographic: Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene vs Polytetrafluoroethylene for Nonstick Pan
 azmater.com
azmater.com