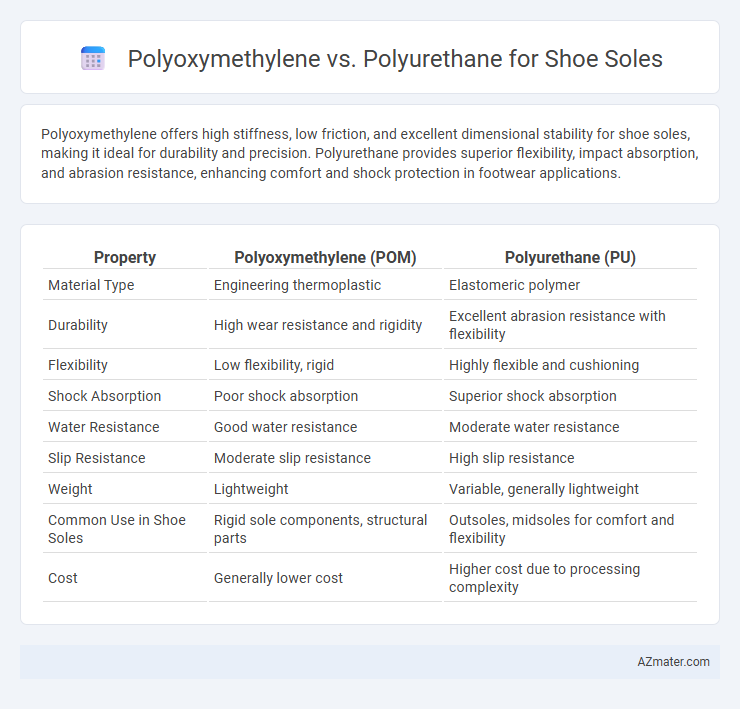
Polyoxymethylene offers high stiffness, low friction, and excellent dimensional stability for shoe soles, making it ideal for durability and precision. Polyurethane provides superior flexibility, impact absorption, and abrasion resistance, enhancing comfort and shock protection in footwear applications.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Polyoxymethylene (POM) | Polyurethane (PU) |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Engineering thermoplastic | Elastomeric polymer |
| Durability | High wear resistance and rigidity | Excellent abrasion resistance with flexibility |
| Flexibility | Low flexibility, rigid | Highly flexible and cushioning |
| Shock Absorption | Poor shock absorption | Superior shock absorption |
| Water Resistance | Good water resistance | Moderate water resistance |
| Slip Resistance | Moderate slip resistance | High slip resistance |
| Weight | Lightweight | Variable, generally lightweight |
| Common Use in Shoe Soles | Rigid sole components, structural parts | Outsoles, midsoles for comfort and flexibility |
| Cost | Generally lower cost | Higher cost due to processing complexity |
Introduction to Polyoxymethylene and Polyurethane
Polyoxymethylene (POM) is a high-performance engineering thermoplastic known for its excellent rigidity, low friction, and superior wear resistance, making it suitable for durable and precise shoe sole applications. Polyurethane (PU) is a versatile polymer offering exceptional elasticity, abrasion resistance, and cushioning properties, widely used in shoe soles for comfort and impact absorption. Comparing POM and PU highlights POM's strength and dimensional stability against PU's flexibility and shock absorption in footwear design.
Chemical Structure and Composition
Polyoxymethylene (POM) features a linear, semi-crystalline structure composed of repeating -CH2-O- units, offering high stiffness and low friction ideal for durable shoe soles. Polyurethane (PU) consists of segmented polymers with alternating soft ether or ester segments and hard urethane linkages (-NH-CO-O-), providing superior flexibility and impact resistance for comfortable footwear. The chemical composition of POM ensures rigidity and wear resistance, while PU's diverse molecular architecture enables customizable elasticity and cushioning in shoe sole applications.
Common Uses in Footwear Industry
Polyoxymethylene (POM) is widely used in shoe soles for its high stiffness, low friction, and excellent wear resistance, making it ideal for durable and supportive footwear like sports shoes and work boots. Polyurethane (PU) provides superior flexibility, cushioning, and shock absorption, making it a popular choice for running shoes, casual sneakers, and comfort-focused footwear. Both materials are essential in the footwear industry, with POM favored for structural components and PU preferred for midsoles and outsoles requiring enhanced comfort and resilience.
Mechanical Properties Comparison
Polyoxymethylene (POM) offers high stiffness, excellent dimensional stability, and superior wear resistance, making it ideal for rigid shoe soles requiring durability and shape retention. Polyurethane (PU) provides greater flexibility, impact absorption, and tear resistance, enhancing comfort and shock damping in footwear applications. The choice between POM and PU soles depends on balancing mechanical properties like hardness, elasticity, and abrasion resistance to meet specific performance and durability needs.
Durability and Wear Resistance
Polyoxymethylene (POM) offers exceptional durability and wear resistance for shoe soles due to its high tensile strength and low friction properties, making it ideal for long-lasting footwear in demanding environments. Polyurethane (PU), known for its flexibility and shock absorption, provides superior abrasion resistance and cushioning, which enhances comfort while maintaining resilience under repetitive stress. Choosing between POM and PU for shoe soles depends on the balance required between rigidity and flexibility to optimize performance and lifespan.
Comfort and Flexibility Factors
Polyurethane offers superior comfort and flexibility for shoe soles due to its elastic nature and cushioning properties that adapt well to foot movements. Polyoxymethylene, known for its rigidity and high durability, provides less flexibility, making it less ideal for cushioning needs in footwear. The choice heavily favors polyurethane when prioritizing shock absorption and prolonged comfort in daily wear shoes.
Cost Analysis: Polyoxymethylene vs Polyurethane
Polyoxymethylene (POM) generally incurs higher initial material costs compared to polyurethane (PU), influencing overall production expenses for shoe soles. Polyurethane offers cost-effective manufacturing due to its lower raw material price and versatility in processing methods, leading to reduced labor and energy costs. Long-term cost benefits of POM depend on its superior wear resistance and durability, potentially lowering replacement frequency despite higher upfront investment.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Polyoxymethylene (POM) offers durability and resistance but is derived from non-renewable petroleum sources, contributing to environmental concerns due to its non-biodegradability and challenges in recyclability. Polyurethane (PU) soles provide flexibility and cushioning, with some formulations incorporating bio-based polyols to improve sustainability, though traditional PU still poses issues related to energy-intensive production and limited end-of-life recyclability. Emerging innovations in bio-based and recyclable polyurethane materials enhance sustainability prospects, making PU increasingly favorable over POM in eco-conscious shoe sole manufacturing.
Performance in Different Shoe Types
Polyoxymethylene (POM) offers high stiffness, excellent wear resistance, and low friction, making it ideal for rigid and supportive shoe soles such as in hiking boots and work shoes. Polyurethane (PU) excels in flexibility, cushioning, and impact absorption, which enhances comfort and shock resistance in running, casual, and athletic footwear. Performance differences are pronounced with POM delivering durability under heavy stress, while PU provides superior energy return and adaptive cushioning for dynamic movements.
Choosing the Right Material for Shoe Soles
Polyoxymethylene (POM) offers high stiffness, low friction, and excellent wear resistance, making it ideal for durable shoe sole components in high-performance applications. Polyurethane (PU) provides superior cushioning, flexibility, and shock absorption, enhancing comfort and impact resistance for everyday footwear. Selecting between POM and PU depends on the shoe's intended use, balancing durability and rigidity against comfort and flexibility requirements.
Infographic: Polyoxymethylene vs Polyurethane for Shoe Sole
 azmater.com
azmater.com