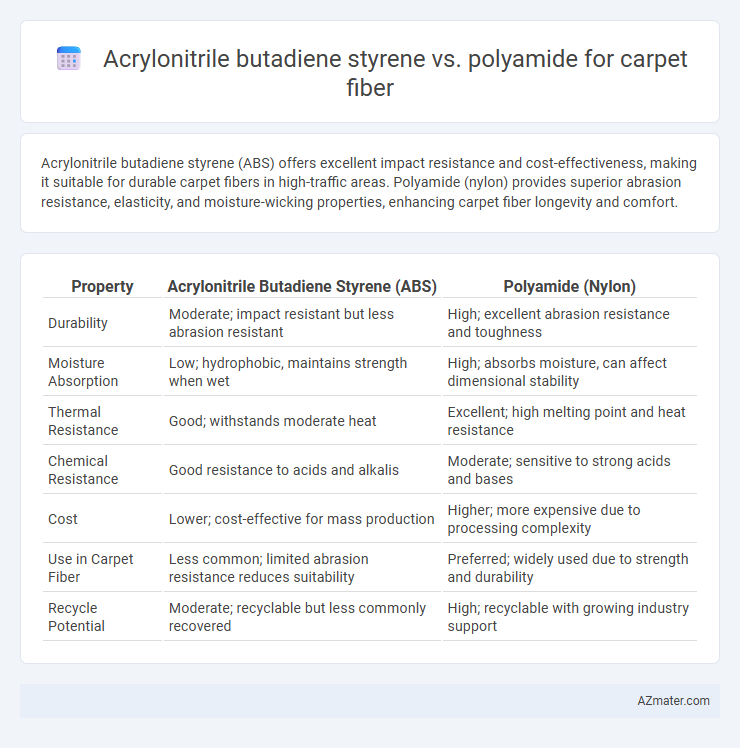
Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS) offers excellent impact resistance and cost-effectiveness, making it suitable for durable carpet fibers in high-traffic areas. Polyamide (nylon) provides superior abrasion resistance, elasticity, and moisture-wicking properties, enhancing carpet fiber longevity and comfort.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS) | Polyamide (Nylon) |
|---|---|---|
| Durability | Moderate; impact resistant but less abrasion resistant | High; excellent abrasion resistance and toughness |
| Moisture Absorption | Low; hydrophobic, maintains strength when wet | High; absorbs moisture, can affect dimensional stability |
| Thermal Resistance | Good; withstands moderate heat | Excellent; high melting point and heat resistance |
| Chemical Resistance | Good resistance to acids and alkalis | Moderate; sensitive to strong acids and bases |
| Cost | Lower; cost-effective for mass production | Higher; more expensive due to processing complexity |
| Use in Carpet Fiber | Less common; limited abrasion resistance reduces suitability | Preferred; widely used due to strength and durability |
| Recycle Potential | Moderate; recyclable but less commonly recovered | High; recyclable with growing industry support |
Introduction to Carpet Fiber Materials
Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS) is a thermoplastic known for its toughness, impact resistance, and ease of processing, making it suitable for durable carpet fibers in high-traffic areas. Polyamide, commonly referred to as nylon, offers superior elasticity, abrasion resistance, and moisture-wicking properties, which enhance carpet resilience and comfort. Both materials provide distinct advantages in carpet fiber manufacturing, with ABS favored for cost-effective rigid fibers and polyamide preferred for high-performance, long-lasting carpeting.
Overview of Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS)
Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS) is a thermoplastic polymer known for its high impact resistance, toughness, and excellent abrasion resistance, making it a durable choice for carpet fibers in high-traffic areas. Its chemical structure combines acrylonitrile, butadiene, and styrene, which provides a balanced blend of strength, flexibility, and resistance to chemical degradation. ABS fibers exhibit superior dimensional stability and resistance to moisture, enhancing their suitability for carpets exposed to varying environmental conditions compared to Polyamide alternatives.
Overview of Polyamide (Nylon)
Polyamide, commonly known as Nylon, is a highly durable synthetic fiber widely used in carpet manufacturing due to its excellent resilience, abrasion resistance, and ability to retain color vibrancy over time. Compared to Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS), Nylon offers superior elasticity and strength, making it ideal for high-traffic areas and residential or commercial settings where durability and comfort are essential. Its moisture-wicking properties and resistance to staining also contribute to its popularity as a premium carpet fiber choice.
Mechanical Strength Comparison
Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS) exhibits moderate mechanical strength with good impact resistance but lower tensile strength compared to polyamide. Polyamide fibers, commonly known as nylon, offer superior tensile strength, elasticity, and abrasion resistance, making them highly durable for carpet applications subjected to heavy foot traffic. The enhanced stiffness and toughness of polyamide contribute to longer-lasting carpets with better shape retention and resilience under mechanical stress.
Durability and Wear Resistance
Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS) and polyamide (nylon) are both used in carpet fibers, with polyamide offering superior durability and wear resistance due to its high tensile strength and excellent abrasion resistance. ABS fibers tend to be less resilient under heavy foot traffic and can degrade faster over time, making polyamide a preferred choice for high-traffic areas. Polyamide's ability to retain appearance and resist crushing enhances carpet longevity significantly compared to ABS.
Stain and Chemical Resistance
Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS) carpet fibers exhibit superior stain resistance due to their hydrophobic properties, making them less prone to absorbing liquids and chemicals. Polyamide fibers, commonly known as nylon, offer excellent chemical resistance and durability but tend to absorb oils and some solvents, which can lead to staining over time. Choosing ABS enhances resistance to common household stains and harsh cleaning agents, while polyamide requires more frequent maintenance to prevent discoloration from chemical exposure.
Comfort and Underfoot Feel
Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS) carpet fibers offer moderate comfort with a firm underfoot feel due to their rigid polymer structure, making them durable but less cushioned. Polyamide fibers, commonly known as nylon, deliver superior softness and resilience, enhancing comfort and providing a plush, springy underfoot sensation. The superior elasticity and moisture resistance of polyamide contribute to a more comfortable and durable carpet experience compared to the stiffer ABS fibers.
Cost and Availability
Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS) offers a lower cost and higher availability compared to polyamide fibers for carpet manufacturing, making it a budget-friendly option for large-scale production. Polyamide, often known as nylon, tends to be more expensive due to its superior durability and resistance to wear but is widely available from major suppliers. The choice between ABS and polyamide fibers balances cost-efficiency with performance needs, influencing carpet pricing and market accessibility.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS) carpet fibers exhibit lower biodegradability and higher reliance on fossil fuels compared to polyamide, raising concerns about long-term environmental impact and microplastic pollution. Polyamide fibers, especially when engineered with recycled content, demonstrate enhanced recyclability and reduced carbon footprint, contributing to more sustainable carpet production. Sustainable carpet choices favor polyamide due to its better lifecycle management and potential for circularity in textile manufacturing.
Best Applications for ABS vs Polyamide in Carpeting
Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS) offers excellent impact resistance and durability, making it ideal for carpets in high-traffic commercial areas where toughness and easy maintenance are essential. Polyamide (nylon) excels in elasticity, stain resistance, and color retention, making it the preferred choice for residential and hospitality carpeting that demands softness and long-lasting appearance. ABS is suited for backing or reinforcement components in carpets, while polyamide fibers are optimal for the face yarn, providing resilience and aesthetic appeal.
Infographic: Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene vs Polyamide for Carpet Fiber
 azmater.com
azmater.com