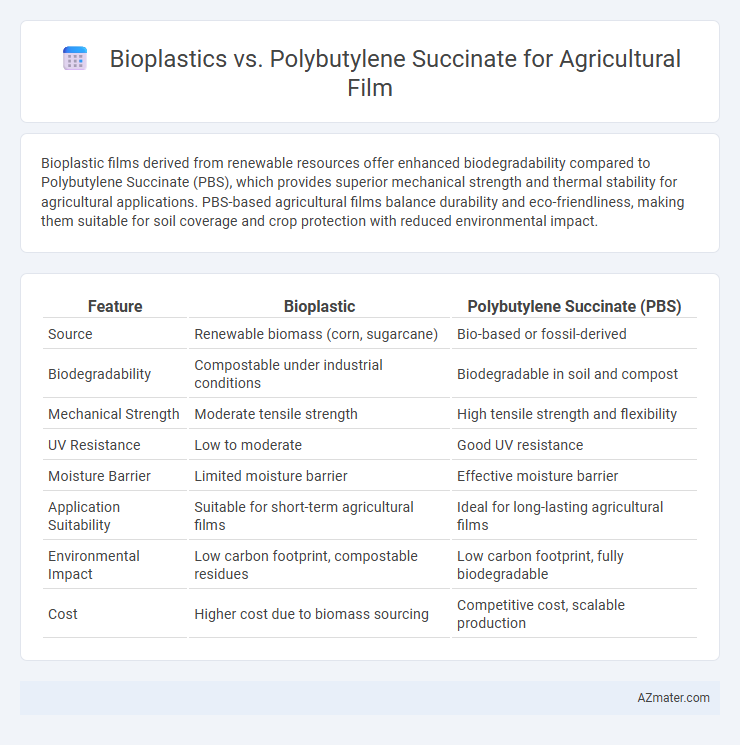
Bioplastic films derived from renewable resources offer enhanced biodegradability compared to Polybutylene Succinate (PBS), which provides superior mechanical strength and thermal stability for agricultural applications. PBS-based agricultural films balance durability and eco-friendliness, making them suitable for soil coverage and crop protection with reduced environmental impact.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Bioplastic | Polybutylene Succinate (PBS) |
|---|---|---|
| Source | Renewable biomass (corn, sugarcane) | Bio-based or fossil-derived |
| Biodegradability | Compostable under industrial conditions | Biodegradable in soil and compost |
| Mechanical Strength | Moderate tensile strength | High tensile strength and flexibility |
| UV Resistance | Low to moderate | Good UV resistance |
| Moisture Barrier | Limited moisture barrier | Effective moisture barrier |
| Application Suitability | Suitable for short-term agricultural films | Ideal for long-lasting agricultural films |
| Environmental Impact | Low carbon footprint, compostable residues | Low carbon footprint, fully biodegradable |
| Cost | Higher cost due to biomass sourcing | Competitive cost, scalable production |
Introduction to Agricultural Films
Agricultural films, primarily used for soil protection and crop enhancement, demand materials with durability, biodegradability, and environmental safety. Bioplastics, including Polybutylene succinate (PBS), offer eco-friendly alternatives to conventional polyethylene films by degrading naturally and reducing plastic pollution in farming ecosystems. PBS is particularly valued for its mechanical strength, thermal stability, and compostability, making it a competitive choice for sustainable agricultural film applications.
Overview of Bioplastics in Agriculture
Bioplastics such as Polybutylene Succinate (PBS) are increasingly used in agricultural films due to their biodegradability and reduced environmental impact compared to conventional plastics. PBS offers excellent mechanical properties, soil biodegradability, and compatibility with crop protection needs, making it a preferred choice for sustainable farming practices. The use of bioplastics in agriculture supports improved soil health and reduces plastic pollution, promoting eco-friendly crop production systems.
What is Polybutylene Succinate (PBS)?
Polybutylene Succinate (PBS) is a biodegradable polyester synthesized from renewable resources such as succinic acid and 1,4-butanediol, making it an eco-friendly alternative to traditional plastics in agricultural films. It exhibits excellent mechanical properties, thermal stability, and UV resistance, which are critical for durable and effective crop protection and soil coverage. PBS's biodegradability and compostability support sustainable farming by reducing plastic residue in soil and minimizing environmental impact compared to conventional bioplastics.
Bioplastic Types Used in Agricultural Films
Bioplastics used in agricultural films primarily include polylactic acid (PLA), polyhydroxyalkanoates (PHA), and starch blends, offering biodegradability and reduced environmental impact compared to conventional plastics. Polybutylene succinate (PBS), a type of bioplastic, provides excellent mechanical properties and biodegradability suitable for mulching films, enhancing soil health by breaking down after use. The choice between general bioplastics and PBS depends on factors like tensile strength, degradation rate, and cost-effectiveness for specific agricultural applications.
Performance Comparison: Bioplastic vs PBS
Bioplastic films derived from materials like starch or PLA generally offer lower mechanical strength and heat resistance compared to Polybutylene Succinate (PBS), which exhibits superior tensile strength, elongation, and thermal stability, making it more suitable for demanding agricultural applications. PBS provides enhanced biodegradability in varied soil conditions, maintaining film integrity during crop growth while ensuring effective degradation post-harvest to minimize environmental impact. The oxygen and moisture barrier properties of PBS also outperform many bioplastics, supporting optimal crop protection and soil microclimate regulation in agricultural film uses.
Environmental Impact and Biodegradability
Bioplastic films, often derived from renewable resources like starch or cellulose, offer reduced carbon footprints and enhanced compatibility with soil ecosystems compared to traditional plastics. Polybutylene succinate (PBS), a biodegradable aliphatic polyester synthesized from renewable monomers, demonstrates rapid degradation under composting conditions, minimizing long-term environmental persistence. The environmental impact of PBS is generally lower due to its high biodegradability and lower greenhouse gas emissions during production, making it a preferable choice for sustainable agricultural films.
Cost Analysis: Bioplastic vs PBS Films
Bioplastic films generally present higher production costs due to raw material expenses and complex manufacturing processes compared to Polybutylene Succinate (PBS) films, which benefit from lower-priced feedstocks and established synthesis methods. PBS films offer competitive cost advantages in large-scale agricultural applications, as they combine biodegradability with cost-effectiveness, making them a preferred choice for budget-sensitive farming operations. Cost analysis further reveals that while bioplastics may entail premium pricing, PBS's market availability and performance balance provide an economically viable option for sustainable agricultural film.
Crop Yield and Soil Health Impacts
Bioplastic films, particularly those made from natural polymers, offer improved biodegradability that enhances soil health by reducing microplastic accumulation compared to conventional polyethylene films. Polybutylene succinate (PBS) agricultural films demonstrate excellent mechanical properties and controlled degradation rates, promoting better soil structure and moisture retention, which can positively influence crop yield. Studies indicate PBS films can maintain or increase crop yields by improving root aeration and nutrient availability while minimizing harmful residue build-up in the soil.
Regulatory and Certification Standards
Bioplastic agricultural films must comply with global regulatory frameworks such as EN 17033 for biodegradable mulch films and ASTM D6400 for compostability to ensure environmental safety and performance. Polybutylene succinate (PBS) is frequently certified under standards like ISO 17556 for aerobic biodegradability in soil, highlighting its suitability for sustainable agriculture. Compliance with these certifications supports market acceptance by demonstrating non-toxicity, biodegradability in soil, and reduced ecological impact compared to conventional polyethylene films.
Future Prospects in Agricultural Film Materials
Polybutylene succinate (PBS) offers superior biodegradability and mechanical strength compared to traditional bioplastics, making it highly suitable for sustainable agricultural film applications. Advances in enzymatic degradation and compostability of PBS are expected to accelerate its adoption, promoting eco-friendly crop protection and soil health. Ongoing research focuses on enhancing PBS's thermal stability and UV resistance to expand its usability across diverse climatic conditions in modern agriculture.
Infographic: Bioplastic vs Polybutylene succinate for Agricultural film
 azmater.com
azmater.com