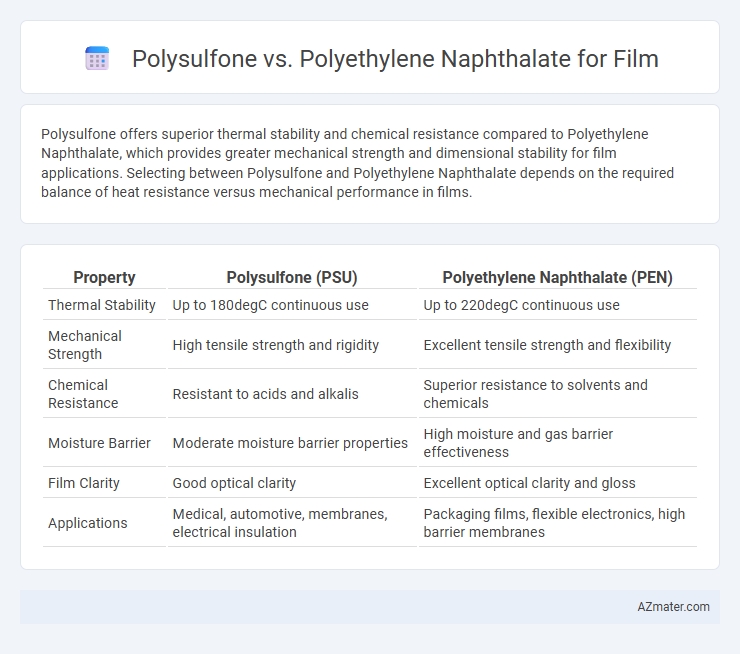
Polysulfone offers superior thermal stability and chemical resistance compared to Polyethylene Naphthalate, which provides greater mechanical strength and dimensional stability for film applications. Selecting between Polysulfone and Polyethylene Naphthalate depends on the required balance of heat resistance versus mechanical performance in films.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Polysulfone (PSU) | Polyethylene Naphthalate (PEN) |
|---|---|---|
| Thermal Stability | Up to 180degC continuous use | Up to 220degC continuous use |
| Mechanical Strength | High tensile strength and rigidity | Excellent tensile strength and flexibility |
| Chemical Resistance | Resistant to acids and alkalis | Superior resistance to solvents and chemicals |
| Moisture Barrier | Moderate moisture barrier properties | High moisture and gas barrier effectiveness |
| Film Clarity | Good optical clarity | Excellent optical clarity and gloss |
| Applications | Medical, automotive, membranes, electrical insulation | Packaging films, flexible electronics, high barrier membranes |
Introduction to Polysulfone and Polyethylene Naphthalate Films
Polysulfone films are known for their exceptional thermal stability, chemical resistance, and mechanical strength, making them ideal for demanding industrial and medical applications. Polyethylene naphthalate (PEN) films offer superior dimensional stability, excellent barrier properties against gases and moisture, and high optical clarity, commonly used in electronics and packaging. Both materials serve distinct purposes, with polysulfone excelling in durability under harsh environments and PEN providing enhanced barrier performance and clarity for precise applications.
Chemical Structure Comparison: Polysulfone vs Polyethylene Naphthalate
Polysulfone features a backbone containing aromatic rings connected by sulfone (-SO2-) groups, providing excellent thermal stability and chemical resistance. Polyethylene naphthalate (PEN) consists of repeating naphthalene units linked via ester bonds, enhancing barrier properties and mechanical strength compared to polyethylene terephthalate. The sulfone group in polysulfone imparts higher heat resistance, while PEN's fused aromatic rings contribute to improved dimensional stability and moisture resistance in film applications.
Mechanical Properties: Strength, Flexibility, and Durability
Polysulfone exhibits high tensile strength and excellent thermal stability, making it ideal for applications requiring strong, heat-resistant films. Polyethylene naphthalate offers superior flexibility and exceptional durability, with enhanced resistance to moisture and UV degradation compared to polysulfone. The mechanical properties of these polymers determine their suitability for specific film applications, with polysulfone favoring rigidity and polyethylen naphthalate balancing strength and flexibility for extended lifespan.
Thermal Resistance and Operating Temperature Range
Polysulfone films exhibit excellent thermal resistance, maintaining structural integrity up to approximately 190degC, while polyethylene naphthalate (PEN) films can withstand higher temperatures, typically up to 220degC. The operating temperature range for polysulfone is generally between -100degC and 190degC, making it suitable for applications requiring moderate heat resistance. PEN offers a broader range, from -70degC to 220degC, with superior dimensional stability and heat resistance ideal for high-performance electronics and packaging.
Optical Clarity and Light Transmission Differences
Polysulfone films exhibit excellent optical clarity with high light transmission rates typically above 85%, making them suitable for applications requiring clear, durable materials. Polyethylene naphthalate films offer superior light transmission, often exceeding 90%, and enhanced UV resistance, improving performance in optical and display applications. The significant difference lies in Polyethylene naphthalate's ability to maintain clarity under prolonged UV exposure, while polysulfone provides greater thermal stability but slightly lower optical clarity.
Chemical and Environmental Resistance
Polysulfone film exhibits excellent chemical resistance, maintaining durability against acids, bases, and oils, while offering superior thermal stability up to 150degC. Polyethylene naphthalate (PEN) film demonstrates remarkable environmental resistance, including exceptional moisture barrier properties and UV stability, surpassing traditional polyesters. Both materials excel in harsh environments, but polysulfone is preferred for chemical exposure, whereas PEN is optimal for applications demanding high environmental and UV resistance.
Processability and Manufacturing Considerations
Polysulfone offers excellent thermal stability and chemical resistance, making it suitable for high-temperature film processing with techniques like extrusion and casting, although its higher melt viscosity can demand specialized equipment. Polyethylene naphthalate (PEN) provides superior dimensional stability and barrier properties, allowing for efficient biaxial orientation in film manufacturing with faster cycle times and lower processing temperatures compared to polysulfone. Manufacturers must consider the trade-off between polysulfone's toughness and PEN's enhanced processability, especially when targeting applications requiring precise film thickness and superior optical clarity.
Typical Applications in Industry and Technology
Polysulfone films are prized for their high thermal stability, chemical resistance, and transparency, making them ideal for medical devices, membrane filtration, and electronics insulation. Polyethylene naphthalate (PEN) films excel in applications requiring excellent dimensional stability, superior barrier properties, and UV resistance, such as flexible packaging, electronic display substrates, and photovoltaic modules. The choice between polysulfone and PEN films hinges on the specific industrial needs for temperature tolerance, mechanical robustness, and environmental durability.
Cost Analysis and Material Availability
Polysulfone films generally exhibit higher material costs compared to Polyethylene Naphthalate (PEN) due to their superior thermal stability and chemical resistance, which often justifies their use in specialized applications. PEN, benefiting from larger-scale production and widespread availability, offers a more cost-effective solution for applications requiring good dimensional stability and moisture barrier properties. Material availability favors PEN, as it is produced in greater volumes globally, making it more accessible and reducing lead times relative to the more niche-market polysulfone films.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Polymer Film
Polysulfone offers superior thermal stability and chemical resistance, making it ideal for applications requiring durability under harsh conditions. Polyethylene Naphthalate (PEN) provides excellent dimensional stability and barrier properties, suitable for advanced optical and electronic films. Selecting the right polymer film depends on specific performance requirements such as temperature tolerance, mechanical strength, and environmental resistance.
Infographic: Polysulfone vs Polyethylene Naphthalate for Film
 azmater.com
azmater.com