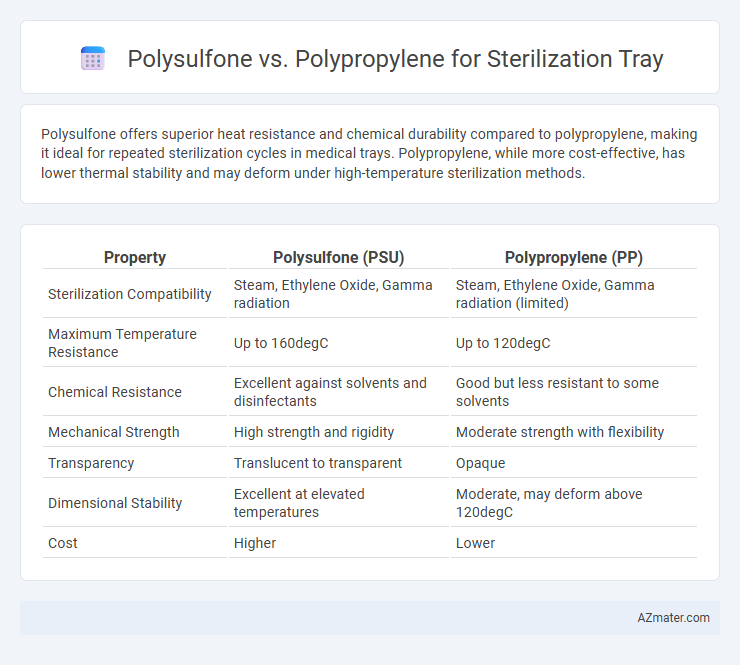
Polysulfone offers superior heat resistance and chemical durability compared to polypropylene, making it ideal for repeated sterilization cycles in medical trays. Polypropylene, while more cost-effective, has lower thermal stability and may deform under high-temperature sterilization methods.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Polysulfone (PSU) | Polypropylene (PP) |
|---|---|---|
| Sterilization Compatibility | Steam, Ethylene Oxide, Gamma radiation | Steam, Ethylene Oxide, Gamma radiation (limited) |
| Maximum Temperature Resistance | Up to 160degC | Up to 120degC |
| Chemical Resistance | Excellent against solvents and disinfectants | Good but less resistant to some solvents |
| Mechanical Strength | High strength and rigidity | Moderate strength with flexibility |
| Transparency | Translucent to transparent | Opaque |
| Dimensional Stability | Excellent at elevated temperatures | Moderate, may deform above 120degC |
| Cost | Higher | Lower |
Introduction to Sterilization Trays
Sterilization trays are essential in healthcare for organizing and safely transporting surgical instruments during sterilization processes. Polysulfone and polypropylene are common materials used, with polysulfone offering superior heat resistance and durability for repeated steam sterilization cycles. Polypropylene provides cost-effective, lightweight options but may have limitations in high-temperature sterilization environments.
Overview of Polysulfone Material
Polysulfone is a high-performance thermoplastic known for its excellent thermal stability, chemical resistance, and mechanical strength, making it ideal for sterilization trays used in medical environments. Its ability to withstand repeated steam sterilization cycles without degrading ensures durability and safety for sterilized instruments. Compared to polypropylene, polysulfone offers superior heat resistance and structural integrity, supporting strict sterilization protocols.
Overview of Polypropylene Material
Polypropylene is a thermoplastic polymer widely used in sterilization trays due to its excellent chemical resistance and high impact strength, allowing for repeated sterilization without degradation. Its low density makes it lightweight yet durable, while its resistance to steam and chemical disinfectants ensures compatibility with common sterilization processes such as autoclaving. Polypropylene's cost-effectiveness and ease of fabrication make it a preferred material compared to polysulfone in applications requiring frequent exposure to heat and moisture.
Key Properties Relevant to Sterilization
Polysulfone offers superior high-temperature resistance up to 180degC and excellent chemical resistance, making it ideal for repeated steam sterilization cycles in autoclaves. Polypropylene, while cost-effective and lightweight, has a lower melting point around 160degC and can degrade with frequent exposure to high heat and aggressive sterilants. Key properties favoring polysulfone include dimensional stability, impact resistance, and resistance to hydrolysis, ensuring durability and safety during rigorous sterilization processes.
Heat Resistance Comparison
Polysulfone exhibits superior heat resistance compared to polypropylene, maintaining structural integrity at temperatures up to 150degC, while polypropylene typically withstands heat only up to 100degC. This makes polysulfone ideal for sterilization trays requiring repeated exposure to high-temperature steam or autoclave cycles. The enhanced thermal stability of polysulfone prevents deformation and ensures long-term durability in demanding sterilization environments.
Chemical Resistance and Compatibility
Polysulfone exhibits superior chemical resistance to sterilization agents such as autoclave steam, ethylene oxide, and hydrogen peroxide, maintaining structural integrity and clarity after repeated cycles. Polypropylene, while cost-effective and resistant to many chemicals, may degrade or warp under prolonged exposure to aggressive sterilizing chemicals and high-temperature steam. Compatibility-wise, polysulfone's higher heat deflection temperature and chemical stability make it more suitable for sterilization trays requiring frequent exposure to harsh sterilants.
Durability and Longevity
Polysulfone offers superior durability and high-temperature resistance, making it ideal for repeated sterilization cycles without losing structural integrity, unlike polypropylene which may warp or degrade under heat. The inherent toughness of polysulfone ensures extended longevity and reliability in demanding medical environments, whereas polypropylene is more susceptible to chemical and thermal stress over time. Choosing polysulfone for sterilization trays enhances product lifespan and maintains performance under rigorous sterilization protocols.
Cost Efficiency Analysis
Polysulfone offers superior heat resistance and chemical durability for sterilization trays but comes at a higher material and processing cost compared to polypropylene. Polypropylene provides cost efficiency through lower raw material prices, ease of molding, and reduced production times, making it suitable for high-volume, budget-conscious manufacturing. Evaluating the total cost of ownership, including lifecycle, reusability, and sterilization method compatibility, is critical for selecting the optimal tray material in healthcare settings.
Application Suitability: Hospital and Laboratory Use
Polysulfone offers superior heat resistance and chemical stability, making it highly suitable for sterilization trays in hospital and laboratory settings where repeated autoclaving is required. Polypropylene provides cost-effective, lightweight trays with moderate chemical resistance, ideal for single-use or low-temperature sterilization applications. The choice depends on the sterilization method and frequency, with polysulfone preferred for high-temperature steam sterilization and polypropylene favored for ethylene oxide or gamma radiation sterilization.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Material
Polysulfone offers superior heat resistance and chemical durability, making it ideal for sterilization trays exposed to repeated autoclaving cycles. Polypropylene provides cost-effectiveness and adequate performance for less demanding sterilization processes but may degrade faster under high-temperature sterilization. Selecting the right material depends on balancing sterilization method requirements, budget constraints, and long-term tray performance.
Infographic: Polysulfone vs Polypropylene for Sterilization Tray
 azmater.com
azmater.com