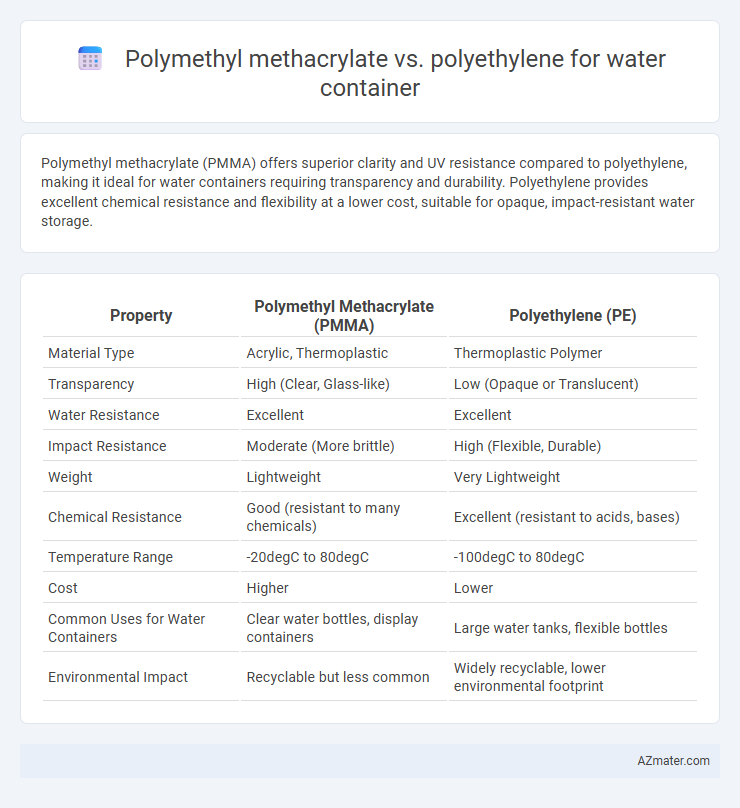
Polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA) offers superior clarity and UV resistance compared to polyethylene, making it ideal for water containers requiring transparency and durability. Polyethylene provides excellent chemical resistance and flexibility at a lower cost, suitable for opaque, impact-resistant water storage.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Polymethyl Methacrylate (PMMA) | Polyethylene (PE) |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Acrylic, Thermoplastic | Thermoplastic Polymer |
| Transparency | High (Clear, Glass-like) | Low (Opaque or Translucent) |
| Water Resistance | Excellent | Excellent |
| Impact Resistance | Moderate (More brittle) | High (Flexible, Durable) |
| Weight | Lightweight | Very Lightweight |
| Chemical Resistance | Good (resistant to many chemicals) | Excellent (resistant to acids, bases) |
| Temperature Range | -20degC to 80degC | -100degC to 80degC |
| Cost | Higher | Lower |
| Common Uses for Water Containers | Clear water bottles, display containers | Large water tanks, flexible bottles |
| Environmental Impact | Recyclable but less common | Widely recyclable, lower environmental footprint |
Introduction to Water Container Materials
Polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA) and polyethylene (PE) are common materials used for manufacturing water containers, each offering distinct properties suited for specific applications. PMMA, known for its excellent clarity, UV resistance, and rigidity, provides a visually appealing and durable option ideal for transparent or display water containers. Polyethylene, particularly high-density polyethylene (HDPE), is favored for its high chemical resistance, impact toughness, and cost-effectiveness, making it suitable for everyday water storage and transport solutions.
Overview of Polymethyl Methacrylate (PMMA)
Polymethyl Methacrylate (PMMA) is a transparent thermoplastic often used as a lightweight, shatter-resistant alternative to glass in water containers. Its high clarity, UV resistance, and excellent weatherability make it suitable for durable and visually appealing water storage solutions. PMMA also offers good chemical resistance, but it is less flexible than polyethylene, impacting durability under impact stress.
Overview of Polyethylene (PE)
Polyethylene (PE) is a widely used thermoplastic polymer known for its high chemical resistance, durability, and low moisture absorption, making it ideal for water containers. Its excellent impact strength and lightweight properties enable efficient transportation and handling compared to polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA). PE's ability to withstand a broad temperature range and its recyclability further enhance its suitability for safe and sustainable water storage.
Mechanical Strength Comparison
Polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA) exhibits higher tensile strength and rigidity compared to polyethylene, making it more resistant to deformation under mechanical stress in water container applications. Polyethylene offers superior impact resistance and flexibility, allowing it to absorb shocks without cracking, which is beneficial in dynamic environments. The choice between PMMA and polyethylene hinges on balancing the need for mechanical strength with durability under impact and environmental stress.
Chemical Resistance and Durability
Polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA) offers excellent chemical resistance against a wide range of substances, including acids and alkalis, making it suitable for water containers exposed to various chemicals. Polyethylene (PE), especially high-density polyethylene (HDPE), also provides strong chemical resistance and superior impact durability, ensuring longevity under physical stress and environmental exposure. PMMA exhibits greater hardness and clarity, while PE stands out with better flexibility and resistance to cracking, influencing the choice based on specific durability requirements.
Transparency and Aesthetic Properties
Polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA) offers superior transparency with a light transmittance of up to 92%, making it ideal for water containers requiring clear visibility and aesthetic appeal. Polyethylene (PE), while durable and chemical-resistant, displays a more opaque and less visually attractive surface, limiting its use in applications where clarity is crucial. The glass-like clarity of PMMA enhances aesthetic properties and enables elegant, visually pleasing water container designs, setting it apart from the more utilitarian appearance of polyethylene.
Safety and Food-Grade Compliance
Polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA) offers excellent clarity and is FDA-approved for food contact, ensuring high safety and food-grade compliance in water containers. Polyethylene, especially high-density polyethylene (HDPE), is widely recognized for its chemical resistance and is also FDA-compliant, making it a common choice for safe, food-grade water storage. Both materials are non-toxic and BPA-free, but polyethylene typically provides superior impact resistance and greater versatility in food-grade applications.
Cost and Manufacturing Considerations
Polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA) offers higher clarity and aesthetic appeal but comes with increased material and processing costs compared to polyethylene, which is more affordable and widely used for water containers due to its lower density and ease of manufacturing. Polyethylene's thermoplastic properties allow for efficient large-scale production via blow molding, significantly reducing manufacturing time and costs. The choice between PMMA and polyethylene hinges on budget constraints and application requirements, with polyethylene favored for cost-effective, durable containers and PMMA selected when optical clarity and rigidity are critical.
Environmental Impact and Recyclability
Polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA) exhibits lower recyclability compared to polyethylene (PE) due to its complex chemical structure and limited recycling facilities, resulting in increased environmental impact through prolonged degradation periods. Polyethylene, especially high-density polyethylene (HDPE), is widely recycled and has a well-established recycling infrastructure, reducing landfill waste and its carbon footprint. The environmental impact of PMMA is further intensified by its energy-intensive production process, whereas polyethylene benefits from lower energy requirements and higher circular economy compatibility.
Conclusion: Best Material for Water Containers
Polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA) offers superior clarity, UV resistance, and chemical stability, making it ideal for water containers requiring transparency and aesthetic appeal. Polyethylene (PE), especially high-density polyethylene (HDPE), provides excellent impact resistance, low cost, and superior chemical inertness, which makes it the preferred choice for durable, food-safe water storage. For the best overall performance in water containers, HDPE is generally favored due to its balance of strength, safety, and affordability.
Infographic: Polymethyl methacrylate vs Polyethylene for Water Container
 azmater.com
azmater.com