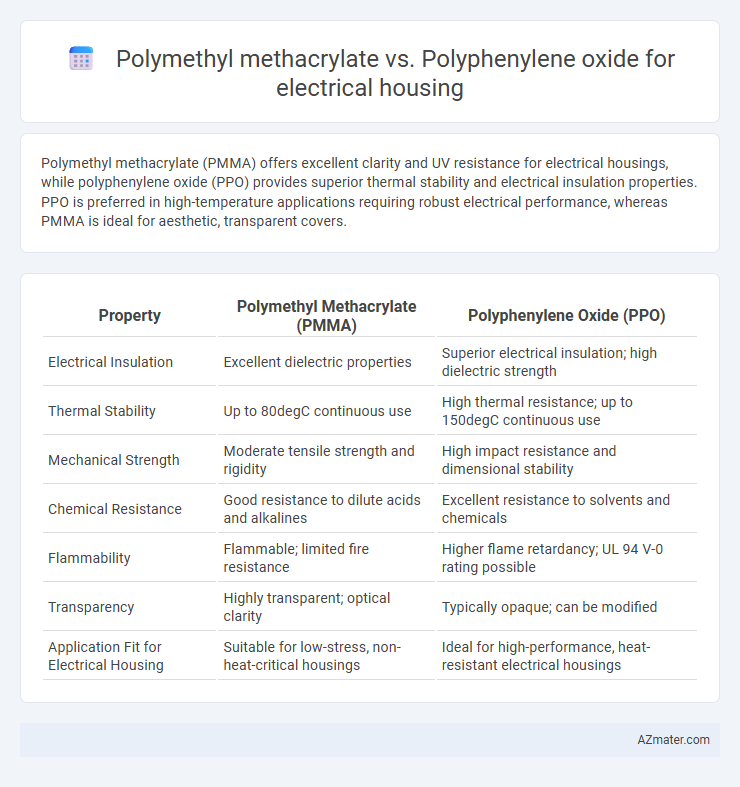
Polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA) offers excellent clarity and UV resistance for electrical housings, while polyphenylene oxide (PPO) provides superior thermal stability and electrical insulation properties. PPO is preferred in high-temperature applications requiring robust electrical performance, whereas PMMA is ideal for aesthetic, transparent covers.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Polymethyl Methacrylate (PMMA) | Polyphenylene Oxide (PPO) |
|---|---|---|
| Electrical Insulation | Excellent dielectric properties | Superior electrical insulation; high dielectric strength |
| Thermal Stability | Up to 80degC continuous use | High thermal resistance; up to 150degC continuous use |
| Mechanical Strength | Moderate tensile strength and rigidity | High impact resistance and dimensional stability |
| Chemical Resistance | Good resistance to dilute acids and alkalines | Excellent resistance to solvents and chemicals |
| Flammability | Flammable; limited fire resistance | Higher flame retardancy; UL 94 V-0 rating possible |
| Transparency | Highly transparent; optical clarity | Typically opaque; can be modified |
| Application Fit for Electrical Housing | Suitable for low-stress, non-heat-critical housings | Ideal for high-performance, heat-resistant electrical housings |
Introduction to Electrical Housing Materials
Polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA) and Polyphenylene oxide (PPO) are prominent materials used in electrical housing due to their excellent insulating properties and mechanical strength. PMMA offers superior transparency and weather resistance, making it ideal for applications where visibility of components is critical, while PPO provides exceptional thermal stability and chemical resistance, suitable for demanding electrical environments. Selection between PMMA and PPO depends on specific requirements such as impact resistance, thermal endurance, and aesthetic preferences in electrical housing design.
Overview of Polymethyl Methacrylate (PMMA)
Polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA) is a transparent thermoplastic renowned for its excellent electrical insulation properties and superior weather resistance, making it a common choice for electrical housing applications. Its high dielectric strength and low moisture absorption ensure reliable performance in electrical components, while its ease of machining and UV stability provide versatility in design and durability. Compared to polyphenylene oxide (PPO), PMMA offers greater optical clarity but generally lower impact resistance and heat deflection temperature.
Overview of Polyphenylene Oxide (PPO)
Polyphenylene oxide (PPO) is a high-performance thermoplastic known for its excellent electrical insulation properties, dimensional stability, and resistance to heat and chemicals, making it ideal for electrical housing applications. Compared to polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA), PPO offers superior mechanical strength and thermal resistance, which ensures durability and safety in demanding electrical environments. Its low moisture absorption and inherent flame retardancy further enhance its suitability for protecting sensitive electrical components.
Electrical Insulation Properties: PMMA vs PPO
Polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA) exhibits excellent electrical insulation properties with a high dielectric strength typically around 15-20 kV/mm, making it suitable for electrical housing applications requiring reliable insulation. Polyphenylene oxide (PPO) offers superior electrical insulation performance with a dielectric constant of approximately 3.2 and low dielectric loss, maintaining stability under high-temperature conditions up to 180degC. PPO's enhanced thermal resistance combined with its consistent dielectric properties makes it preferable for demanding electrical housings compared to PMMA.
Mechanical Strength and Durability Comparison
Polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA) offers excellent mechanical strength with high rigidity and impact resistance suitable for electrical housing, while polyphenylene oxide (PPO) provides superior thermal stability and dimensional stability under prolonged heat exposure. PMMA typically exhibits higher tensile strength but lower heat distortion temperature compared to PPO, which enhances durability in demanding electrical environments. PPO's balanced mechanical properties and resistance to chemical degradation make it more reliable for long-term usage in electrical housings subject to thermal and mechanical stress.
Thermal Stability and Heat Resistance
Polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA) offers moderate thermal stability with a glass transition temperature around 105degC, making it suitable for applications with limited heat exposure. Polyphenylene oxide (PPO) exhibits superior thermal stability and heat resistance, with a continuous use temperature up to 180-200degC and excellent dimensional stability under thermal stress. For electrical housing requiring high heat resistance and long-term thermal performance, PPO is the preferred material due to its enhanced ability to maintain mechanical integrity at elevated temperatures.
Chemical and Environmental Resistance
Polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA) offers excellent chemical resistance against dilute acids and alkalis but has limited resistance to organic solvents, impacting its suitability for harsh chemical environments in electrical housing. Polyphenylene oxide (PPO) exhibits superior chemical resistance, maintaining stability against a broad spectrum of solvents, oils, and fuels, making it ideal for demanding electrical enclosures. Both materials provide good environmental resistance; however, PPO's higher thermal stability and inherent flame retardancy enhance its performance in fluctuating and challenging environmental conditions.
Ease of Fabrication and Processing
Polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA) offers superior ease of fabrication and processing for electrical housing due to its excellent clarity, good dimensional stability, and compatibility with various molding techniques like injection molding and extrusion. Polyphenylene oxide (PPO) provides robust thermal resistance and mechanical strength but requires higher processing temperatures and more precise control during molding, potentially increasing manufacturing complexity. The choice between PMMA and PPO depends on prioritizing ease of fabrication versus thermal and mechanical performance requirements in electrical housing applications.
Cost Efficiency and Availability
Polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA) offers excellent transparency and moderate cost, making it a cost-efficient choice for electrical housing where budget constraints exist. Polyphenylene oxide (PPO) provides superior thermal stability and electrical insulation but comes at a higher price and limited availability compared to PMMA. For large-scale production requiring balance between performance and cost, PMMA often proves more accessible and economical, while PPO is preferred for demanding environments despite its premium cost.
Application Suitability: PMMA vs PPO in Electrical Housing
Polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA) offers excellent optical clarity and UV resistance, making it suitable for electrical housings requiring visibility of internal components or light transmission. Polyphenylene oxide (PPO) demonstrates superior thermal stability, dimensional accuracy, and electrical insulation properties, ideal for high-temperature electrical housings with strict mechanical and dielectric demands. For applications prioritizing thermal resistance and electrical insulation, PPO outperforms PMMA, while PMMA is preferred in designs where transparency and aesthetic appearance are critical.
Infographic: Polymethyl methacrylate vs Polyphenylene oxide for Electrical housing
 azmater.com
azmater.com