Polyethylene terephthalate (PET) offers superior clarity and gas barrier properties, making it ideal for microwaveable food trays requiring fresh food preservation. Polypropylene (PP) provides higher heat resistance and durability, ensuring safe microwave use and structural integrity during reheating.
Table of Comparison
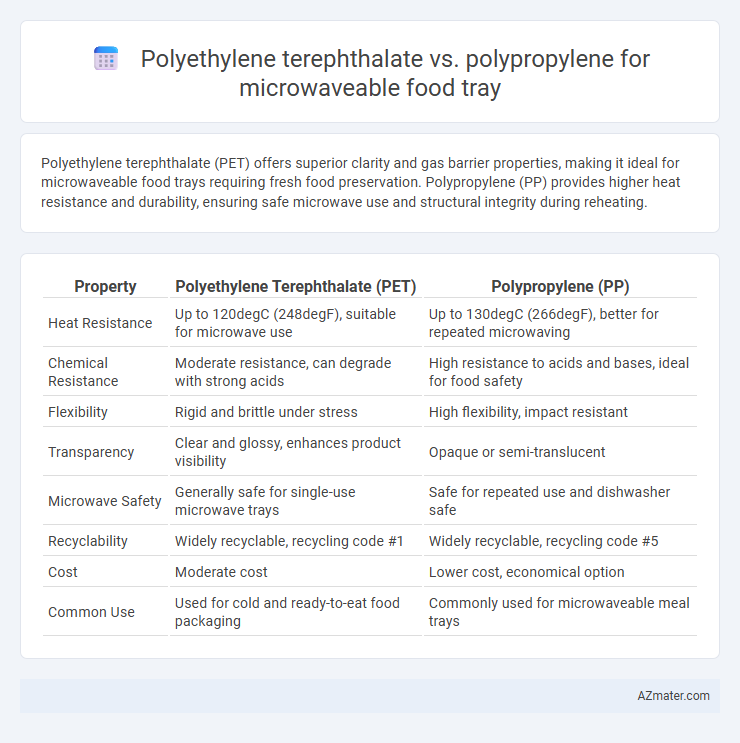
| Property | Polyethylene Terephthalate (PET) | Polypropylene (PP) |
|---|---|---|
| Heat Resistance | Up to 120degC (248degF), suitable for microwave use | Up to 130degC (266degF), better for repeated microwaving |
| Chemical Resistance | Moderate resistance, can degrade with strong acids | High resistance to acids and bases, ideal for food safety |
| Flexibility | Rigid and brittle under stress | High flexibility, impact resistant |
| Transparency | Clear and glossy, enhances product visibility | Opaque or semi-translucent |
| Microwave Safety | Generally safe for single-use microwave trays | Safe for repeated use and dishwasher safe |
| Recyclability | Widely recyclable, recycling code #1 | Widely recyclable, recycling code #5 |
| Cost | Moderate cost | Lower cost, economical option |
| Common Use | Used for cold and ready-to-eat food packaging | Commonly used for microwaveable meal trays |
Introduction to Microwaveable Food Tray Materials
Polyethylene terephthalate (PET) and polypropylene (PP) are commonly used materials for microwaveable food trays due to their distinct thermal and chemical properties. PET offers excellent clarity and strong barrier resistance against moisture and gases, making it suitable for packaging fresh foods. Polypropylene stands out for its high heat tolerance and microwave safety, providing durability and resistance to warping during reheating processes.
Overview of Polyethylene Terephthalate (PET)
Polyethylene terephthalate (PET) is a widely used thermoplastic polymer renowned for its excellent strength, clarity, and barrier properties, making it a preferred choice for microwaveable food trays. PET's high melting point, typically around 250degC, allows it to withstand typical microwave temperatures without deforming or releasing harmful substances. Its superior gas and moisture barrier qualities ensure food freshness and prevent contamination, positioning PET as a reliable and safe material for microwave-safe food packaging.
Overview of Polypropylene (PP)
Polypropylene (PP) is a thermoplastic polymer widely used for microwaveable food trays due to its excellent heat resistance, chemical stability, and lightweight nature. Its high melting point, typically around 160-170degC, makes it suitable for repeated microwave heating without deformation or leaching of harmful substances. Compared to polyethylene terephthalate (PET), PP offers superior flexibility and durability under thermal stress, enhancing safety and performance in microwave applications.
Heat Resistance: PET vs Polypropylene
Polypropylene demonstrates superior heat resistance compared to polyethylene terephthalate, sustaining temperatures up to 170degC, making it more suitable for microwaveable food trays. Polyethylene terephthalate typically withstands heat only up to around 120degC, which limits its use in high-temperature microwave applications. This thermal property difference directly impacts the safety, durability, and performance of food trays in microwave environments.
Safety Considerations for Microwave Use
Polyethylene terephthalate (PET) exhibits limited heat resistance and may release harmful chemicals when exposed to high microwave temperatures, making it less suitable for microwaveable food trays. Polypropylene (PP) offers superior thermal stability and is generally recognized as microwave-safe due to its higher melting point and lower risk of chemical leaching. Safety considerations emphasize choosing PP trays for microwave use to minimize potential toxic exposure and ensure the integrity of the food container under repeated heating cycles.
Barrier Properties and Food Preservation
Polyethylene terephthalate (PET) offers superior barrier properties against oxygen and moisture compared to polypropylene (PP), making PET more effective in preserving food freshness in microwaveable trays. PET's high oxygen barrier reduces oxidation, extending shelf life, while PP allows more gas permeability, which may lead to faster food spoilage. Both materials are microwave-safe, but PET's enhanced barrier performance better maintains food quality during storage and reheating.
Environmental Impact and Recyclability
Polyethylene terephthalate (PET) offers higher recyclability due to widespread infrastructure and yields less environmental pollution compared to polypropylene (PP), which is less commonly recycled and may persist longer in landfills. PET's production involves more energy consumption but supports circular recycling processes, reducing overall environmental impact when properly managed. PP's lower density contributes to reduced transportation emissions, yet limited recycling options worsen its ecological footprint in microwaveable food tray applications.
Cost Efficiency and Manufacturing
Polypropylene (PP) typically offers greater cost efficiency for microwaveable food trays due to its lower raw material price and easier processing compared to polyethylene terephthalate (PET). Manufacturing with PP allows for faster cycle times and better mold release, reducing production costs and increasing throughput. PET trays provide superior clarity and rigidity but often require higher energy input and more complex processing, making PP the preferred choice for cost-conscious manufacturers.
Consumer Preferences and Industry Trends
Polyethylene terephthalate (PET) and polypropylene (PP) serve distinct roles in microwaveable food trays, with consumer preferences increasingly favoring PP due to its superior heat resistance and microwave safety. Industry trends highlight a shift towards PP because of its recyclability and compliance with food safety regulations, meeting growing environmental concerns. Market analysis indicates that PET trays, while popular for their clarity and rigidity, are less favored for microwaving because they can deform under high temperatures, influencing manufacturers to prioritize PP in product development.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Material for Microwaveable Food Trays
Polyethylene terephthalate (PET) offers excellent clarity and strong barrier properties, making it suitable for premium microwaveable food trays that require visibility and freshness retention. Polypropylene (PP) demonstrates superior heat resistance, chemical stability, and microwave safety, making it ideal for containers that undergo repeated heating cycles. Selecting the right material depends on balancing factors such as thermal performance, cost-effectiveness, and consumer safety, with polypropylene generally preferred for durable, microwave-safe trays.
Infographic: Polyethylene terephthalate vs Polypropylene for Microwaveable Food Tray
 azmater.com
azmater.com