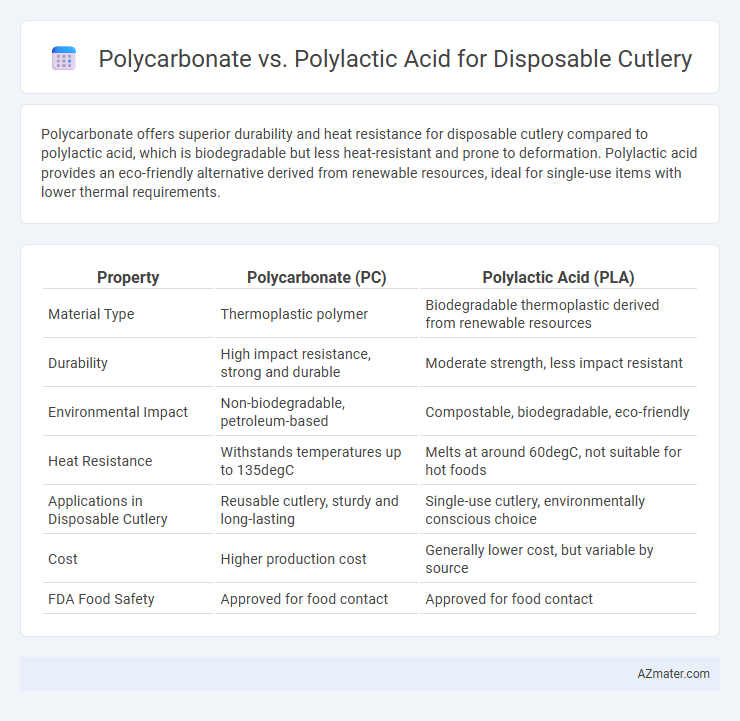
Polycarbonate offers superior durability and heat resistance for disposable cutlery compared to polylactic acid, which is biodegradable but less heat-resistant and prone to deformation. Polylactic acid provides an eco-friendly alternative derived from renewable resources, ideal for single-use items with lower thermal requirements.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Polycarbonate (PC) | Polylactic Acid (PLA) |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Thermoplastic polymer | Biodegradable thermoplastic derived from renewable resources |
| Durability | High impact resistance, strong and durable | Moderate strength, less impact resistant |
| Environmental Impact | Non-biodegradable, petroleum-based | Compostable, biodegradable, eco-friendly |
| Heat Resistance | Withstands temperatures up to 135degC | Melts at around 60degC, not suitable for hot foods |
| Applications in Disposable Cutlery | Reusable cutlery, sturdy and long-lasting | Single-use cutlery, environmentally conscious choice |
| Cost | Higher production cost | Generally lower cost, but variable by source |
| FDA Food Safety | Approved for food contact | Approved for food contact |
Introduction to Disposable Cutlery Materials
Disposable cutlery commonly utilizes materials like polycarbonate (PC) and polylactic acid (PLA), each offering distinct properties suited for single-use applications. Polycarbonate is a durable, heat-resistant plastic derived from petroleum, known for its clarity and strength, making it ideal for heavy-duty disposable utensils. In contrast, PLA is a biodegradable thermoplastic derived from renewable resources like corn starch, favored for its eco-friendly profile despite lower heat resistance and strength compared to polycarbonate.
Overview of Polycarbonate (PC)
Polycarbonate (PC) is a durable, transparent thermoplastic extensively used in disposable cutlery due to its high impact resistance and heat tolerance, making it ideal for repeated use and hot food applications. Its chemical stability resists degradation from acids and oils, ensuring safety and longevity in food service environments. The material's ability to be easily molded and sterilized enhances its practicality for disposable cutlery manufacturing compared to more environmentally focused alternatives like polylactic acid (PLA).
Overview of Polylactic Acid (PLA)
Polylactic Acid (PLA) is a biodegradable thermoplastic derived from renewable resources such as corn starch or sugarcane, making it an eco-friendly alternative for disposable cutlery. PLA offers good clarity and rigidity but has lower heat resistance compared to polycarbonate, which limits its use in high-temperature applications. Widely used in sustainable food service products, PLA provides compostability under industrial conditions, aligning with increasing environmental regulations and consumer demand for green materials.
Mechanical Strength and Durability Comparison
Polycarbonate disposable cutlery exhibits superior mechanical strength with high impact resistance and flexibility, making it less prone to cracking or breaking during use compared to polylactic acid (PLA). PLA, derived from renewable resources, offers adequate rigidity but tends to be more brittle and prone to deformation under stress or heat, limiting its durability. The enhanced durability of polycarbonate ensures longer usability and better performance in demanding food-service applications where strength and resilience are critical.
Heat Resistance and Performance Analysis
Polycarbonate exhibits superior heat resistance, withstanding temperatures up to 135degC, making it ideal for hot food applications in disposable cutlery. Polylactic Acid (PLA), derived from renewable resources, has a lower melting point around 60degC, which limits its use with hot foods but offers compostability and biodegradability. Performance analysis reveals polycarbonate cutlery's durability and resistance to deformation under heat, whereas PLA cutlery provides an eco-friendly alternative with sufficient strength for cold or room-temperature use.
Environmental Impact: Polycarbonate vs Polylactic Acid
Polylactic acid (PLA) cutlery offers a significant environmental advantage over polycarbonate (PC) due to its biodegradability and compostability derived from renewable resources like corn starch or sugarcane. Polycarbonate, being petroleum-based, contributes to higher carbon emissions and persists in landfills for centuries, posing long-term pollution challenges. Life cycle assessments show PLA cutlery reduces greenhouse gas emissions and energy consumption by up to 50% compared to polycarbonate counterparts.
Safety and Food Contact Regulations
Polycarbonate (PC) and Polylactic Acid (PLA) are widely used materials for disposable cutlery, each governed by strict food contact safety regulations. Polycarbonate is generally approved for food contact by agencies such as the FDA and EFSA but raises concerns due to potential BPA migration, prompting shifts towards BPA-free formulations. Polylactic Acid, derived from renewable resources, complies with FDA food contact substance regulations and is biodegradable, offering a safer, eco-friendly alternative with lower migration risks and enhanced consumer safety.
Cost and Manufacturing Considerations
Polycarbonate disposable cutlery typically incurs higher manufacturing costs due to its petroleum-based origin and complex molding processes, while polylactic acid (PLA) is derived from renewable resources like corn starch, offering a cost-effective and eco-friendly production alternative. PLA production benefits from lower energy consumption and biodegradability, but it may require specialized equipment to maintain optimal processing conditions during extrusion and injection molding. Cost differences also reflect durability--polycarbonate cutlery delivers superior heat resistance and longevity, justifying higher prices in commercial food service, whereas PLA suits short-term use with competitive pricing aligned to sustainability trends.
Consumer Preferences and Market Trends
Polycarbonate disposable cutlery offers superior durability and heat resistance, making it preferred by consumers seeking reusable options in food service. Polylactic acid (PLA), derived from renewable resources, appeals to eco-conscious buyers due to its biodegradability and compostability, aligning with increasing demand for sustainable products. Market trends indicate a growing shift towards PLA cutlery in fast food and catering sectors, driven by regulatory pressures and heightened environmental awareness.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Material for Disposable Cutlery
Polycarbonate offers exceptional durability and heat resistance, making it suitable for reusable or heavy-use disposable cutlery, while polylactic acid (PLA) provides biodegradability and compostability ideal for environmentally conscious single-use options. The choice depends on balancing performance needs with sustainability goals, as PLA's plant-based origin reduces plastic waste but has lower heat tolerance compared to polycarbonate. Selecting the right material involves considering the specific application, environmental impact, and user requirements to optimize both functionality and ecological responsibility.
Infographic: Polycarbonate vs Polylactic Acid for Disposable Cutlery
 azmater.com
azmater.com