Bioplastic disposable cutlery is derived from renewable plant-based materials, offering enhanced biodegradability and reduced environmental impact compared to polystyrene, which is petroleum-based and contributes to long-lasting plastic pollution. Choosing bioplastic reduces landfill waste and supports sustainable practices in single-use utensil production.
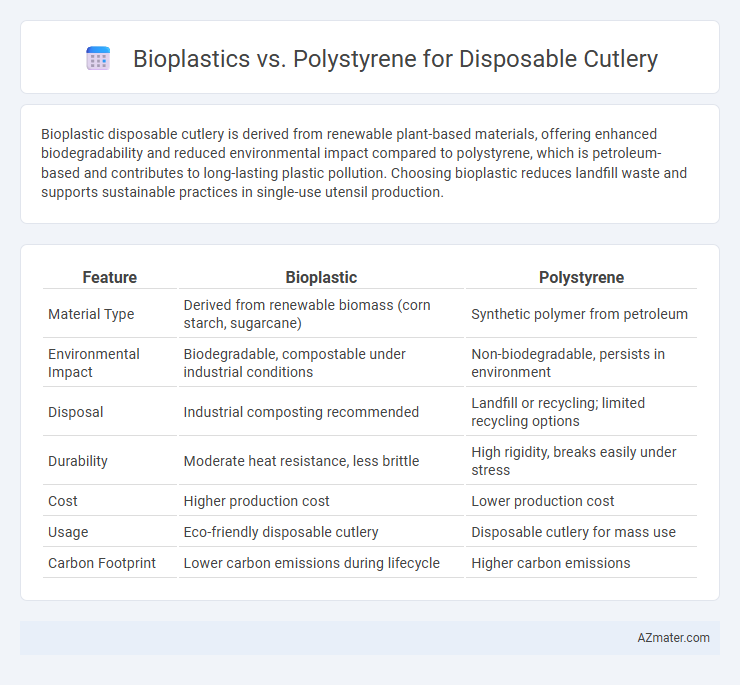
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Bioplastic | Polystyrene |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Derived from renewable biomass (corn starch, sugarcane) | Synthetic polymer from petroleum |
| Environmental Impact | Biodegradable, compostable under industrial conditions | Non-biodegradable, persists in environment |
| Disposal | Industrial composting recommended | Landfill or recycling; limited recycling options |
| Durability | Moderate heat resistance, less brittle | High rigidity, breaks easily under stress |
| Cost | Higher production cost | Lower production cost |
| Usage | Eco-friendly disposable cutlery | Disposable cutlery for mass use |
| Carbon Footprint | Lower carbon emissions during lifecycle | Higher carbon emissions |
Introduction to Bioplastic and Polystyrene Cutlery
Bioplastic disposable cutlery is made from renewable plant-based materials like cornstarch or sugarcane, offering a biodegradable and compostable alternative to traditional plastic. Polystyrene cutlery, derived from petroleum, is rigid, lightweight, and inexpensive but poses significant environmental challenges due to its non-biodegradable nature and contribution to plastic pollution. The growing demand for sustainable alternatives has propelled bioplastic cutlery as an eco-friendly solution in the disposable utensil market.
Material Composition and Origins
Bioplastic disposable cutlery is primarily derived from renewable biomass sources such as corn starch, sugarcane, or cellulose, making it biodegradable and compostable under industrial conditions. Polystyrene cutlery, on the other hand, is synthesized from petroleum-based styrene monomers through polymerization, resulting in a non-biodegradable plastic with significant environmental persistence. The contrasting origins highlight bioplastics' potential for reduced carbon footprint and waste, whereas polystyrene's petrochemical base contributes to resource depletion and landfill accumulation.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Bioplastic cutlery, derived from renewable resources like cornstarch and sugarcane, offers a significantly lower carbon footprint and biodegrades more rapidly compared to polystyrene, which is petroleum-based and non-biodegradable. Polystyrene contributes to long-term environmental pollution, accumulating in landfills and oceans, whereas bioplastics decompose under industrial composting conditions, reducing landfill volume and microplastic contamination. Sustainable disposable cutlery solutions increasingly favor bioplastics due to their alignment with circular economy principles and reduced ecological impact.
Biodegradability and Decomposition Rates
Bioplastic disposable cutlery offers superior biodegradability compared to traditional polystyrene, breaking down within 3 to 6 months under industrial composting conditions, whereas polystyrene can persist in the environment for hundreds of years. The decomposition rates of bioplastics are significantly faster due to their organic composition, which microbes can efficiently metabolize, resulting in reduced environmental impact and lower landfill accumulation. Polystyrene not only degrades slowly but also releases toxic chemicals during breakdown, making bioplastic a more sustainable choice for single-use utensils.
Manufacturing Process and Energy Consumption
Bioplastic disposable cutlery is commonly produced via extrusion and injection molding using renewable raw materials such as cornstarch or sugarcane, resulting in lower greenhouse gas emissions during manufacturing compared to petroleum-based polystyrene. Polystyrene cutlery manufacturing relies on polymerization of styrene monomers, followed by injection molding, which typically demands higher energy input due to the fossil fuel-derived feedstocks and heat-intensive processing stages. Energy consumption for bioplastic cutlery production can be 30-50% less than polystyrene counterparts, contributing to a reduced carbon footprint in disposable utensil manufacturing.
Cost Comparison: Bioplastic vs Polystyrene
Bioplastic disposable cutlery typically incurs higher production costs due to raw material expenses and specialized manufacturing processes, resulting in retail prices approximately 20-30% above polystyrene alternatives. Polystyrene cutlery benefits from low-cost petroleum-based raw materials and established mass production techniques, making it the most cost-effective option for large-scale disposable cutlery. The price gap narrows as bioplastic technologies advance and economies of scale improve, but current market data consistently shows polystyrene's dominance in cost efficiency.
Performance and Functionality in Use
Bioplastic disposable cutlery offers comparable strength and heat resistance to polystyrene, making it suitable for both hot and cold foods without warping or melting. Polystyrene excels in rigidity and cost-effectiveness but may become brittle at low temperatures and deform under heat exposure. Bioplastics provide enhanced biodegradability and reduced environmental impact while maintaining functional integrity during typical use scenarios.
Regulatory Compliance and Safety
Bioplastic disposable cutlery often complies with stringent food safety regulations such as FDA and EFSA standards, ensuring non-toxicity and biodegradability, which aligns with eco-friendly policies. Polystyrene cutlery faces increased regulatory scrutiny due to its potential leaching of harmful chemicals like styrene, leading to restrictions in several regions worldwide. Manufacturers must navigate evolving compliance frameworks prioritizing human health and environmental impact when choosing between bioplastic and polystyrene materials.
Consumer Perception and Market Trends
Consumer perception increasingly favors bioplastic disposable cutlery due to its eco-friendly image and biodegradability compared to conventional polystyrene, which is often criticized for environmental pollution and non-recyclability. Market trends reveal a rising demand for sustainable alternatives, driving growth in bioplastic production and innovation despite higher costs and limited durability. Polystyrene remains dominant in low-cost, high-volume segments, but regulatory pressures and shifting consumer preferences are accelerating the shift toward bioplastics in foodservice and retail industries.
Future Prospects in Disposable Cutlery Materials
Bioplastic offers promising future prospects in disposable cutlery due to its renewable raw materials and enhanced biodegradability, aligning with increasing environmental regulations and consumer demand for sustainable products. Polystyrene, although cost-effective and lightweight, faces regulatory restrictions and environmental concerns related to its persistence and non-biodegradable nature. Innovations in bioplastic composites and improved production scalability indicate a significant market shift favoring bioplastics over polystyrene for eco-friendly disposable cutlery solutions.
Infographic: Bioplastic vs Polystyrene for Disposable cutlery
 azmater.com
azmater.com