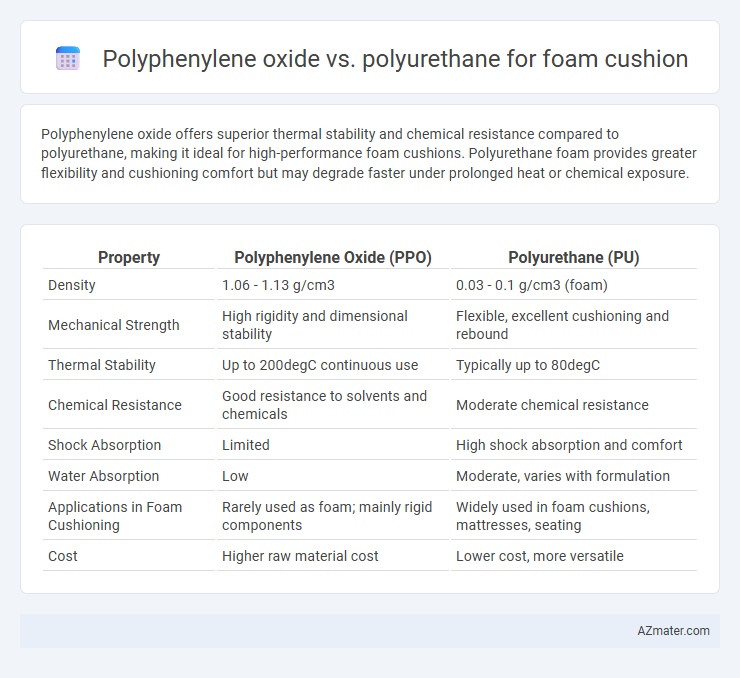
Polyphenylene oxide offers superior thermal stability and chemical resistance compared to polyurethane, making it ideal for high-performance foam cushions. Polyurethane foam provides greater flexibility and cushioning comfort but may degrade faster under prolonged heat or chemical exposure.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Polyphenylene Oxide (PPO) | Polyurethane (PU) |
|---|---|---|
| Density | 1.06 - 1.13 g/cm3 | 0.03 - 0.1 g/cm3 (foam) |
| Mechanical Strength | High rigidity and dimensional stability | Flexible, excellent cushioning and rebound |
| Thermal Stability | Up to 200degC continuous use | Typically up to 80degC |
| Chemical Resistance | Good resistance to solvents and chemicals | Moderate chemical resistance |
| Shock Absorption | Limited | High shock absorption and comfort |
| Water Absorption | Low | Moderate, varies with formulation |
| Applications in Foam Cushioning | Rarely used as foam; mainly rigid components | Widely used in foam cushions, mattresses, seating |
| Cost | Higher raw material cost | Lower cost, more versatile |
Introduction to Foam Cushion Materials
Polyphenylene oxide (PPO) offers high thermal stability, excellent mechanical strength, and resistance to moisture, making it suitable for durable foam cushions in automotive and furniture applications. Polyurethane (PU) foam is widely used for its superior comfort, flexibility, and shock absorption, providing versatile cushioning with customizable density and firmness. Comparing PPO and PU foams highlights PPO's robustness and chemical resistance against PU's elasticity and comfort properties, key considerations for selecting foam cushion materials.
Overview of Polyphenylene Oxide (PPO)
Polyphenylene oxide (PPO) is a high-performance thermoplastic known for its excellent mechanical strength, thermal stability, and chemical resistance, making it suitable for foam cushion applications requiring durability and structural integrity. Its inherent dimensional stability and resistance to moisture absorption enhance the longevity and comfort of foam cushions compared to polyurethane counterparts. PPO foam cushions offer superior resistance to compression set and thermal degradation, providing consistent cushioning performance in demanding environments.
Overview of Polyurethane (PU)
Polyurethane (PU) is a versatile polymer widely used in foam cushions due to its excellent flexibility, durability, and cushioning properties. It offers a high resilience and energy absorption capacity, making it ideal for seating applications and mattresses where long-term comfort and support are critical. Compared to polyphenylene oxide, PU foam provides superior elasticity and shock absorption, enhancing its performance in various foam cushion products.
Mechanical Properties Comparison
Polyphenylene oxide (PPO) foam cushions demonstrate superior mechanical properties such as higher tensile strength and better thermal stability compared to polyurethane (PU) foams, making them ideal for high-performance applications. PPO exhibits excellent dimensional stability and resistance to compression set, ensuring prolonged durability and shape retention under cyclic loads. Polyurethane foams offer greater flexibility and impact absorption but tend to degrade faster under mechanical stress and elevated temperatures compared to PPO.
Comfort and Cushioning Performance
Polyphenylene oxide (PPO) foam cushions provide superior breathability and durability, resulting in consistent support and enhanced comfort over prolonged use. Polyurethane foam offers excellent initial softness and cushioning performance, adapting well to body contours for pressure relief, but may degrade faster under heavy use. For long-term comfort and resilience, PPO foam is often preferred in high-performance cushioning applications due to its stable structure and moisture resistance.
Durability and Longevity
Polyphenylene oxide (PPO) exhibits superior chemical stability and resistance to heat, making it highly durable for foam cushion applications exposed to fluctuating temperatures and potential oxidation. Polyurethane foam offers excellent flexibility and cushioning but tends to degrade faster under prolonged stress, UV exposure, and moisture, leading to reduced longevity compared to PPO-based materials. The inherent structural integrity of PPO ensures longer-lasting foam cushions with minimal compression set over time, enhancing durability in high-use environments.
Resistance to Heat and Chemicals
Polyphenylene oxide (PPO) foam cushions exhibit superior resistance to heat, maintaining structural integrity at temperatures up to 150degC, whereas polyurethane (PU) foams typically degrade above 80degC. PPO demonstrates excellent chemical resistance, effectively withstanding exposure to oils, acids, and solvents without significant breakdown or loss of mechanical properties. In contrast, polyurethane foams are more susceptible to chemical attack, particularly from hydrocarbons and oxidizing agents, which can cause swelling, softening, or degradation over time.
Environmental Impact and Recyclability
Polyphenylene oxide (PPO) foam cushions offer higher environmental sustainability due to their thermal stability and chemical resistance, which contribute to longer product life and reduced waste. Polyurethane (PU) foams, while versatile and commonly used, pose challenges in recyclability because of their cross-linked polymer structure, often leading to landfill disposal and higher environmental impact. Recent advances in chemical recycling and biodegradable PU formulations are improving eco-friendliness, but PPO remains preferable for sustainable foam cushioning applications due to better recyclability and lower ecological footprint.
Cost-Effectiveness Analysis
Polyphenylene oxide foam offers superior thermal stability and water resistance, making it a durable choice with moderate material costs. Polyurethane foam generally provides greater cushioning comfort at a lower initial price but may incur higher long-term expenses due to faster degradation. Evaluating cost-effectiveness requires balancing material longevity and performance against upfront investment and maintenance requirements.
Choosing the Right Material for Foam Cushions
Polyphenylene oxide (PPO) foam offers excellent thermal stability, chemical resistance, and dimensional stability, making it ideal for high-performance foam cushions requiring durability and long-term shape retention. Polyurethane (PU) foam provides superior flexibility, breathability, and cushioning comfort, commonly used in furniture and automotive applications where softness and resilience are priorities. Selecting between PPO and PU foam depends on the specific requirements for durability, comfort, and environmental exposure in the intended cushion application.
Infographic: Polyphenylene oxide vs Polyurethane for Foam Cushion
 azmater.com
azmater.com