Recycled plastic for plastic furniture offers significant environmental benefits by reducing landfill waste and lowering carbon emissions compared to virgin plastic. Despite slight variations in durability, recycled plastic maintains comparable strength and longevity, making it a sustainable alternative for high-quality furniture production.
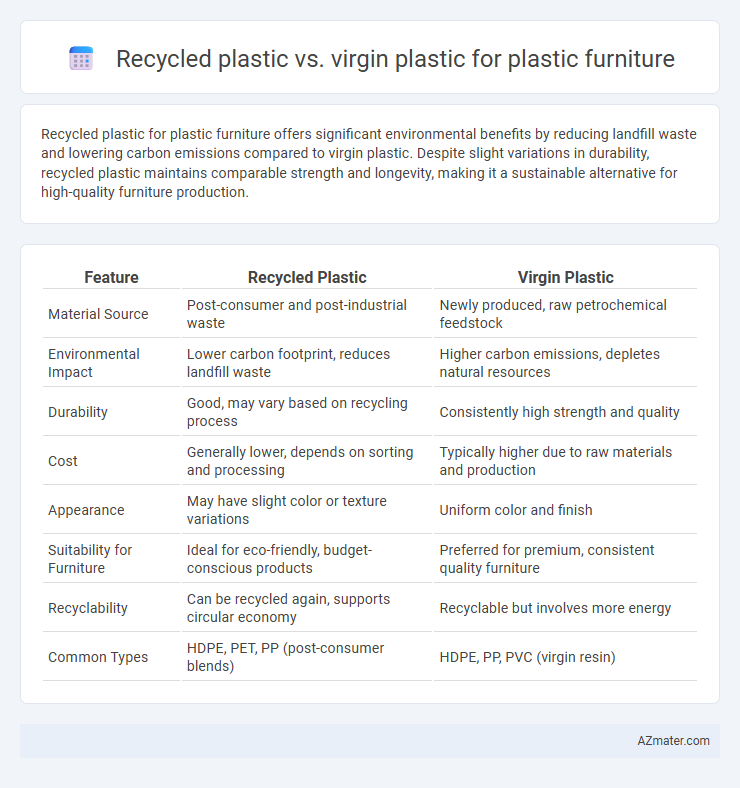
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Recycled Plastic | Virgin Plastic |
|---|---|---|
| Material Source | Post-consumer and post-industrial waste | Newly produced, raw petrochemical feedstock |
| Environmental Impact | Lower carbon footprint, reduces landfill waste | Higher carbon emissions, depletes natural resources |
| Durability | Good, may vary based on recycling process | Consistently high strength and quality |
| Cost | Generally lower, depends on sorting and processing | Typically higher due to raw materials and production |
| Appearance | May have slight color or texture variations | Uniform color and finish |
| Suitability for Furniture | Ideal for eco-friendly, budget-conscious products | Preferred for premium, consistent quality furniture |
| Recyclability | Can be recycled again, supports circular economy | Recyclable but involves more energy |
| Common Types | HDPE, PET, PP (post-consumer blends) | HDPE, PP, PVC (virgin resin) |
Introduction: Recycled vs Virgin Plastic in Furniture
Recycled plastic in furniture manufacturing reduces environmental impact by minimizing raw material extraction and energy consumption compared to virgin plastic. Virgin plastic offers consistent quality and durability, making it a preferred choice for high-strength furniture applications. The decision between recycled and virgin plastic depends on balancing sustainability goals with performance requirements in plastic furniture production.
Material Composition and Source
Recycled plastic furniture is primarily made from post-consumer or post-industrial plastic waste, including polyethylene terephthalate (PET) and high-density polyethylene (HDPE), reducing environmental impact by repurposing used materials. Virgin plastic furniture uses newly synthesized polymers derived from petroleum-based raw materials, offering consistent quality and strength due to controlled production processes. The choice between recycled and virgin plastic hinges on material composition purity and source sustainability, with recycled plastic promoting circular economy principles and virgin plastic ensuring uniformity and durability.
Environmental Impact Comparison
Recycled plastic furniture significantly reduces environmental impact by lowering carbon emissions by up to 60% compared to virgin plastic production, which relies heavily on fossil fuel extraction and processing. The use of recycled materials minimizes landfill waste and conserves natural resources, contributing to a circular economy in the plastics industry. Virgin plastic furniture production involves higher energy consumption and generates greater pollution, making recycled plastic a more sustainable choice for eco-friendly furniture manufacturing.
Durability and Strength Differences
Recycled plastic for plastic furniture often exhibits slightly reduced durability and strength compared to virgin plastic due to the presence of contaminants and polymer degradation during the recycling process. Virgin plastic furniture typically offers superior impact resistance, tensile strength, and consistent structural integrity, making it more suitable for load-bearing applications. However, advances in recycling technologies have increasingly minimized these performance gaps, enhancing the feasibility of recycled plastic in durable outdoor and commercial furniture products.
Aesthetic and Design Flexibility
Recycled plastic offers a unique range of color variations and textures due to the blend of different plastic sources, which can add character but might limit uniformity in aesthetic appeal compared to virgin plastic. Virgin plastic provides superior design flexibility with consistent color, smooth finishes, and precise molding, enabling intricate shapes and high-quality surface details critical for premium plastic furniture. Designers targeting innovative forms and vibrant, flawless finishes often prefer virgin plastic to achieve exact aesthetic standards and visual consistency.
Cost Analysis: Recycled vs Virgin Plastic
Recycled plastic furniture often costs 20-30% less than virgin plastic due to reduced raw material expenses and lower energy consumption during production. Virgin plastic, derived from petrochemicals, involves higher extraction and processing costs, which are reflected in the final product price. Long-term savings with recycled plastic also come from increasing demand and advances in recycling technology, making it a more cost-effective choice for sustainable furniture manufacturing.
Maintenance and Longevity Prospects
Recycled plastic furniture offers high resistance to moisture, insects, and fading, requiring minimal maintenance compared to virgin plastic. Virgin plastic typically provides greater structural strength and durability, ensuring longer longevity under heavy use and harsh environmental conditions. Choosing recycled plastic contributes to sustainability without significantly compromising maintenance ease or lifespan.
Health and Safety Considerations
Recycled plastic furniture often contains additives or contaminants from previous uses that can emit volatile organic compounds (VOCs), posing potential health risks compared to virgin plastic, which typically meets stricter safety standards. Virgin plastic is manufactured under controlled conditions, reducing the presence of harmful chemicals and ensuring greater material consistency and durability, crucial for safe indoor use. Evaluating certifications such as GREENGUARD or FDA approvals helps ensure that both recycled and virgin plastic furniture comply with health and safety regulations.
Market Trends and Consumer Preferences
Recycled plastic furniture is gaining traction in the market due to increasing environmental awareness and demand for sustainable products, driving manufacturers to adopt recycled materials over virgin plastics. Consumer preferences are shifting towards eco-friendly options, with many prioritizing durability, cost-effectiveness, and recyclability, which enhances the appeal of recycled plastic furniture. Market trends indicate a steady growth in the recycled plastic segment, supported by advancements in recycling technologies and regulatory incentives promoting circular economy practices in the plastic furniture industry.
Future Outlook for Sustainable Plastic Furniture
Recycled plastic offers a promising future for sustainable plastic furniture by significantly reducing environmental impact and conserving natural resources compared to virgin plastic, which relies on new petrochemical production. Innovations in recycling technologies and material blends are enhancing the durability and aesthetic appeal of recycled plastic furniture, driving increased adoption in eco-conscious markets. As regulatory pressures and consumer preferences shift towards sustainability, the growth of recycled plastic furniture is expected to outpace virgin plastic alternatives, promoting a circular economy in the furniture industry.
Infographic: Recycled plastic vs Virgin plastic for Plastic furniture
 azmater.com
azmater.com