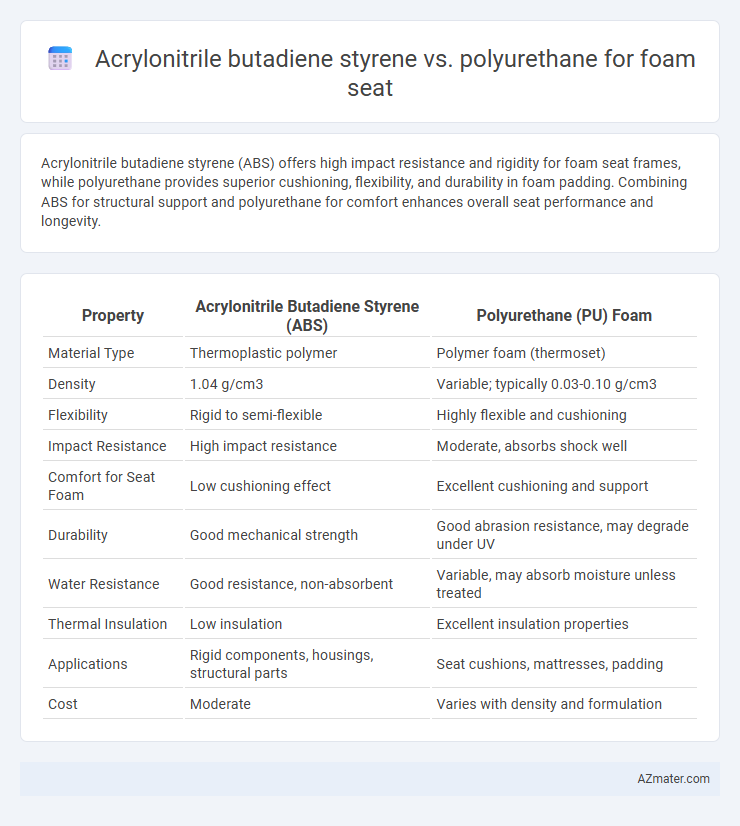
Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS) offers high impact resistance and rigidity for foam seat frames, while polyurethane provides superior cushioning, flexibility, and durability in foam padding. Combining ABS for structural support and polyurethane for comfort enhances overall seat performance and longevity.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS) | Polyurethane (PU) Foam |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Thermoplastic polymer | Polymer foam (thermoset) |
| Density | 1.04 g/cm3 | Variable; typically 0.03-0.10 g/cm3 |
| Flexibility | Rigid to semi-flexible | Highly flexible and cushioning |
| Impact Resistance | High impact resistance | Moderate, absorbs shock well |
| Comfort for Seat Foam | Low cushioning effect | Excellent cushioning and support |
| Durability | Good mechanical strength | Good abrasion resistance, may degrade under UV |
| Water Resistance | Good resistance, non-absorbent | Variable, may absorb moisture unless treated |
| Thermal Insulation | Low insulation | Excellent insulation properties |
| Applications | Rigid components, housings, structural parts | Seat cushions, mattresses, padding |
| Cost | Moderate | Varies with density and formulation |
Introduction to Foam Seat Materials
Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS) provides a rigid, impact-resistant base often used in foam seat frameworks, offering durability and structural integrity. Polyurethane foam, characterized by its versatile density and cushioning properties, enhances comfort and support in seating applications through effective energy absorption. Selecting between ABS and polyurethane materials depends on balancing rigidity with ergonomic softness for optimal foam seat performance.
Overview of Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS)
Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS) is a thermoplastic polymer characterized by its impact resistance, rigidity, and toughness, making it suitable for structural components in foam seat frames. Its chemical composition combines acrylonitrile for chemical resistance, butadiene for toughness, and styrene for rigidity, resulting in a material that balances durability and flexibility. ABS's dimensional stability and ease of molding support precision manufacturing in seat applications, contrasting with polyurethane's softer, cushioning properties.
Overview of Polyurethane (PU)
Polyurethane (PU) foam offers superior cushioning and durability compared to Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS), making it an ideal material for foam seats. Its cellular structure provides excellent resilience, comfort, and shock absorption, enhancing ergonomic support in seating applications. PU foam also boasts high resistance to wear, moisture, and chemical exposure, ensuring long-lasting performance in various environments.
Mechanical Properties: ABS vs Polyurethane
Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS) offers high impact resistance, rigidity, and good tensile strength, making it suitable for durable foam seat frames. Polyurethane foam provides excellent flexibility, superior cushioning, and resilience, which enhances comfort and shock absorption in seating applications. While ABS excels in structural support due to its stiffness and toughness, polyurethane delivers better mechanical deformation properties ideal for ergonomic foam cushioning.
Comfort and Cushioning Performance
Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS) offers a rigid and durable structure but lacks inherent cushioning properties, making it less suitable for comfort in foam seat applications. Polyurethane foam excels in comfort and cushioning performance due to its superior elasticity, density variations, and ability to absorb impact, providing enhanced ergonomic support. The material's resilience and versatility in foam density customization result in significantly better pressure distribution and prolonged comfort over extended seating periods compared to ABS-based solutions.
Durability and Lifespan Comparison
Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS) foam seats exhibit high impact resistance and moderate chemical stability, extending their durability in various environmental conditions. Polyurethane foam seats offer superior resilience and cushioning properties, with enhanced resistance to compression set and longer lifespan under continuous use. The choice between ABS and polyurethane significantly affects foam seat longevity, with polyurethane generally providing a longer service life due to better fatigue and wear resistance.
Cost Analysis: ABS vs Polyurethane
Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS) typically offers lower initial material costs compared to Polyurethane foam, making it a budget-friendly option for rigid seat components. Polyurethane foam, while more expensive upfront, provides superior cushioning and durability, which may reduce long-term replacement expenses and improve user comfort. Cost analysis must consider not only raw material prices but also manufacturing processes, lifecycle, and end-user experience to determine overall value in foam seat applications.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS) foam seats impact the environment due to their non-biodegradable nature and reliance on petroleum-based resources, resulting in higher carbon emissions during production. Polyurethane foam, while also petroleum-based, offers improved recyclability and options for bio-based polyols that reduce fossil fuel dependency and carbon footprint. Sustainable innovation in polyurethane formulations, including plant-based alternatives, enhances eco-friendliness compared to traditional ABS foam, supporting circular economy goals in seating applications.
Common Applications in Foam Seating
Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS) is commonly used in foam seating for its rigid structural support and impact resistance, often found in automotive seats and office chairs where durability is critical. Polyurethane foam excels in cushioning applications due to its superior flexibility and comfort, making it a popular choice in upholstered furniture and ergonomic seating solutions. Both materials are widely selected based on the balance between support and comfort required in various foam seating designs.
Choosing the Right Material for Your Foam Seat
Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS) offers superior rigidity and impact resistance, making it suitable for foam seat frames requiring structural support and durability. Polyurethane foam provides excellent cushioning, flexibility, and comfort, ideal for the seating surface where softness and pressure distribution are critical. Selecting the right material depends on balancing ABS's strength and Polyurethane's comfort to optimize foam seat performance and user experience.
Infographic: Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene vs Polyurethane for Foam seat
 azmater.com
azmater.com