Bioplastic toothbrush handles offer eco-friendly biodegradability and reduced carbon footprint compared to polyamide handles, which provide superior durability and resistance to wear. Choosing bioplastics supports sustainability initiatives, while polyamides ensure longer-lasting performance in oral care products.
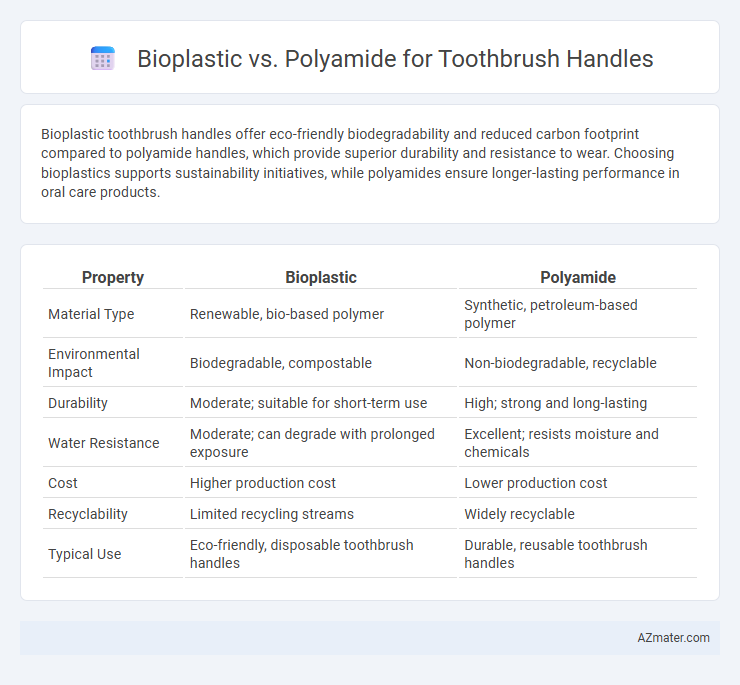
Table of Comparison
| Property | Bioplastic | Polyamide |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Renewable, bio-based polymer | Synthetic, petroleum-based polymer |
| Environmental Impact | Biodegradable, compostable | Non-biodegradable, recyclable |
| Durability | Moderate; suitable for short-term use | High; strong and long-lasting |
| Water Resistance | Moderate; can degrade with prolonged exposure | Excellent; resists moisture and chemicals |
| Cost | Higher production cost | Lower production cost |
| Recyclability | Limited recycling streams | Widely recyclable |
| Typical Use | Eco-friendly, disposable toothbrush handles | Durable, reusable toothbrush handles |
Introduction to Toothbrush Handle Materials
Toothbrush handles are commonly made from bioplastics and polyamides, each offering distinct material properties. Bioplastics provide eco-friendly benefits such as biodegradability and reduced carbon footprint, making them suitable for sustainable oral care products. Polyamide, known for its high durability, impact resistance, and water absorption stability, ensures long-lasting performance and comfort during daily brushing.
Overview of Bioplastic and Polyamide
Bioplastic, made from renewable biomass sources such as cornstarch or sugarcane, offers a sustainable alternative to traditional plastics with biodegradability and reduced carbon footprint. Polyamide, commonly known as nylon, is a durable synthetic polymer known for its high mechanical strength, chemical resistance, and long-lasting properties in toothbrush handles. Choosing between bioplastic and polyamide depends on priorities like environmental impact, durability, and production cost.
Environmental Impact: Bioplastic vs Polyamide
Bioplastic toothbrush handles offer a significantly lower carbon footprint compared to polyamide, as they are derived from renewable resources like cornstarch or sugarcane, leading to reduced greenhouse gas emissions during production. Polyamide, a petroleum-based synthetic polymer, contributes to higher environmental pollution and persists longer in landfill due to its non-biodegradable nature. Bioplastics also support compostability and improved end-of-life degradation, minimizing plastic waste accumulation in oceans and soil compared to conventional polyamide toothbrush handles.
Mechanical Strength and Durability Comparison
Bioplastic toothbrush handles typically offer moderate mechanical strength and biodegradability but may degrade faster under stress compared to polyamide, which exhibits superior tensile strength and long-term durability. Polyamide handles resist wear, impact, and moisture absorption effectively, making them ideal for sustained daily use. The enhanced mechanical properties of polyamide contribute to a longer lifespan and improved performance in challenging environments compared to many bioplastic alternatives.
Cost Analysis of Bioplastic and Polyamide Handles
Bioplastic toothbrush handles generally offer cost advantages due to lower raw material expenses and reduced environmental compliance fees compared to polyamide handles. Polyamide handles, while durable and heat-resistant, tend to incur higher production costs stemming from energy-intensive manufacturing processes and more complex recycling requirements. Evaluating total cost of ownership reveals bioplastic handles as more economically viable for mass production, whereas polyamide handles may justify their premium price through enhanced mechanical performance.
Manufacturing Process Differences
Bioplastic toothbrush handles are produced through biopolymer synthesis involving natural raw materials like cornstarch or sugarcane, utilizing extrusion and injection molding with lower energy consumption and reduced carbon footprint. Polyamide handles are manufactured by polymerizing caprolactam or other synthetic monomers in high-temperature reactors, followed by precise molding processes that yield strong, durable products but involve greater energy usage and reliance on fossil fuels. The bioplastic process emphasizes sustainability and biodegradability, whereas polyamide manufacturing prioritizes mechanical strength and longevity in toothbrush handles.
Biodegradability and End-of-Life Considerations
Bioplastic toothbrush handles offer superior biodegradability compared to polyamide, breaking down naturally in composting environments within months, reducing landfill accumulation. Polyamide handles, derived from petroleum-based polymers, resist degradation and can persist in ecosystems for decades, complicating end-of-life management. Choosing bioplastic toothbrush handles supports circular economy goals by enabling composting or industrial biowaste processing, whereas polyamide components require energy-intensive recycling or risk long-term environmental persistence.
Consumer Safety and Allergic Reactions
Bioplastic toothbrush handles are often favored for consumer safety due to their hypoallergenic properties and reduced chemical additives, minimizing the risk of allergic reactions. In contrast, polyamide handles, while durable, can sometimes cause skin irritation or allergic responses in sensitive individuals because of residual monomers or additives used during manufacturing. Choosing bioplastic enhances user safety by reducing exposure to potential allergens and harmful substances commonly associated with traditional polyamide materials.
Market Trends and Industry Adoption
The toothbrush handle market shows growing preference for bioplastic materials due to rising consumer demand for sustainable and eco-friendly products, driving significant adoption by major oral care brands. Polyamide handles maintain steady use because of their durability and cost-effectiveness, especially in mid-range toothbrush segments. Industry reports forecast a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of over 8% for bioplastic toothbrush handles through 2030, reflecting shifting market trends toward biodegradable and renewable resource-based alternatives.
Future Outlook: Innovations in Toothbrush Materials
Bioplastic toothbrush handles are evolving with advancements in biodegradable polymers and natural fiber composites, offering enhanced sustainability and reduced environmental impact. Polyamide handles continue to improve through the integration of recycled materials and increased durability, balancing performance with eco-friendly innovations. Emerging hybrid materials combining bioplastics and polyamides promise superior strength and compostability, indicating a future where toothbrush handles achieve optimal functionality and environmental responsibility.
Infographic: Bioplastic vs Polyamide for Toothbrush Handle
 azmater.com
azmater.com