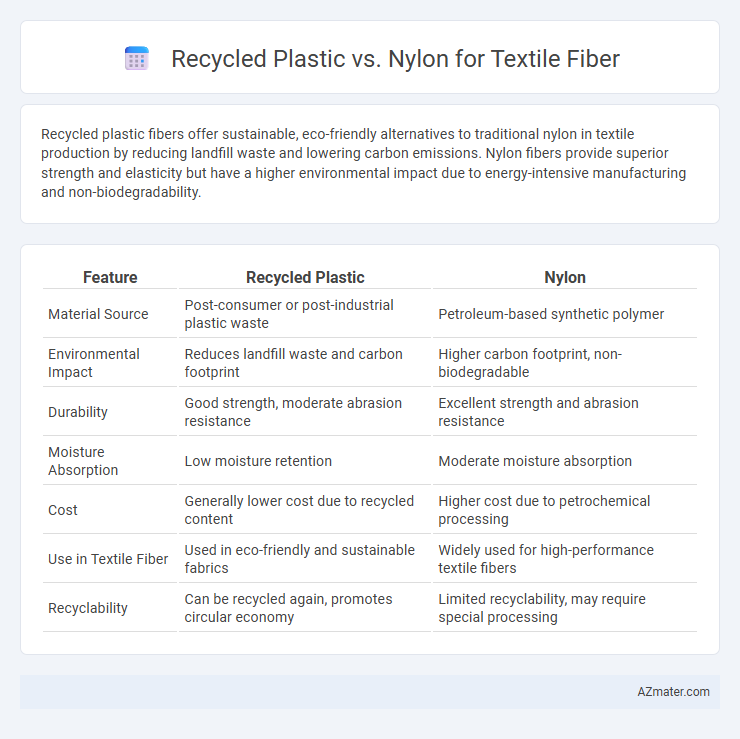
Recycled plastic fibers offer sustainable, eco-friendly alternatives to traditional nylon in textile production by reducing landfill waste and lowering carbon emissions. Nylon fibers provide superior strength and elasticity but have a higher environmental impact due to energy-intensive manufacturing and non-biodegradability.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Recycled Plastic | Nylon |
|---|---|---|
| Material Source | Post-consumer or post-industrial plastic waste | Petroleum-based synthetic polymer |
| Environmental Impact | Reduces landfill waste and carbon footprint | Higher carbon footprint, non-biodegradable |
| Durability | Good strength, moderate abrasion resistance | Excellent strength and abrasion resistance |
| Moisture Absorption | Low moisture retention | Moderate moisture absorption |
| Cost | Generally lower cost due to recycled content | Higher cost due to petrochemical processing |
| Use in Textile Fiber | Used in eco-friendly and sustainable fabrics | Widely used for high-performance textile fibers |
| Recyclability | Can be recycled again, promotes circular economy | Limited recyclability, may require special processing |
Overview of Recycled Plastic and Nylon in Textile Fibers
Recycled plastic fibers, primarily derived from PET bottles, offer sustainability through reduced waste and lower carbon footprint compared to virgin materials. Nylon fibers, known for their exceptional strength, elasticity, and durability, are widely used in high-performance textiles but typically require more energy-intensive processes and non-renewable resources. Advances in recycling technologies have enhanced the quality of recycled plastic fibers, making them competitive alternatives to traditional nylon in applications like activewear and upholstery.
Environmental Impact Comparison
Recycled plastic fibers significantly reduce environmental impact by diverting plastic waste from landfills and oceans, lowering carbon emissions by up to 60% compared to virgin nylon production. Nylon manufacturing consumes large amounts of energy and releases nitrous oxide, a potent greenhouse gas, whereas recycled plastic fibers utilize existing materials, minimizing resource extraction. The use of recycled plastic fibers promotes circular economy practices, reducing dependency on fossil fuels and decreasing water usage compared to conventional nylon fibers.
Production Processes: Recycled Plastic vs Nylon
Recycled plastic textile fibers are produced by collecting, cleaning, and melting post-consumer PET plastics, which are then extruded into yarns, significantly reducing environmental waste and energy consumption compared to virgin materials. Nylon fibers undergo a chemical synthesis process involving the polymerization of caprolactam or adipic acid and hexamethylenediamine, requiring higher energy input and releasing greenhouse gases like nitrous oxide. The production of recycled plastic fibers offers a more sustainable and energy-efficient alternative to traditional nylon manufacturing, supporting circular economy principles in the textile industry.
Durability and Longevity of Fibers
Recycled plastic fibers, such as those made from PET bottles, demonstrate high durability with strong resistance to wear, moisture, and UV exposure, contributing to their extended lifespan in textile applications. Nylon fibers are renowned for exceptional strength, elasticity, and abrasion resistance, resulting in superior longevity even under frequent mechanical stress. While recycled plastic fibers provide sustainable durability, nylon often outperforms in longevity due to its engineered resilience and ability to maintain structural integrity over prolonged use.
Cost Efficiency in Manufacturing
Recycled plastic fibers generally offer greater cost efficiency in textile manufacturing due to lower raw material costs and reduced energy consumption during production compared to nylon fibers. Nylon, derived from petrochemicals, involves higher energy inputs and more complex chemical processing, which drives up manufacturing expenses. Choosing recycled plastic fibers can significantly lower production costs while supporting sustainable manufacturing practices.
Performance and Functional Properties
Recycled plastic fibers exhibit high durability and resistance to moisture, making them ideal for sustainable textile applications with enhanced environmental benefits. Nylon fibers outperform recycled plastics in tensile strength, elasticity, and abrasion resistance, providing superior stretch and longevity for high-performance garments. Both materials offer unique functional properties; recycled plastic fibers excel in UV resistance and moisture-wicking, while nylon delivers excellent dye affinity and quick-drying capabilities.
Applications in Fashion and Industrial Textiles
Recycled plastic fibers exhibit strong potential in fashion for sustainability-focused apparel, offering durability and moisture resistance comparable to nylon while reducing environmental impact through waste plastic reuse. Nylon remains favored in industrial textiles due to its superior tensile strength, abrasion resistance, and elasticity, making it ideal for applications such as safety gear, conveyor belts, and automotive components. The choice between recycled plastic and nylon fibers depends on balancing eco-consciousness with performance requirements specific to fashion or industrial end-uses.
Challenges and Limitations of Each Material
Recycled plastic fibers face challenges such as inconsistent quality, limited mechanical strength, and potential contamination from mixed waste streams, which can affect durability and color retention in textiles. Nylon, although prized for its strength and elasticity, presents limitations including higher production costs, environmental concerns due to petroleum-based origins, and difficulty in biodegradation. Both materials encounter processing complexities, where recycled plastic may require extensive cleaning and melting refinement, while nylon can be sensitive to high temperatures and UV exposure, impacting fabric longevity.
Consumer Perception and Market Trends
Recycled plastic fibers are increasingly favored by environmentally conscious consumers seeking sustainable alternatives to traditional nylon, which is associated with higher environmental impact due to petroleum-based production. Market trends show a growing demand for recycled plastic textiles driven by eco-friendly branding and regulatory pressure on reducing plastic waste. Despite nylon's superior durability and performance characteristics, consumer preference is shifting towards recycled fibers for their lower carbon footprint and contribution to circular economy initiatives.
Future Prospects and Sustainable Innovations
Recycled plastic fibers are gaining traction due to their reduced environmental footprint and potential to lower carbon emissions compared to traditional nylon, which relies heavily on fossil fuels. Innovations in biodegradable and bio-based nylons are emerging to address sustainability concerns, offering enhanced durability and recyclability. Future prospects emphasize hybrid fibers combining recycled plastics and advanced nylon variants, aiming to maximize eco-efficiency and support circular textile economies.
Infographic: Recycled plastic vs Nylon for Textile fiber
 azmater.com
azmater.com