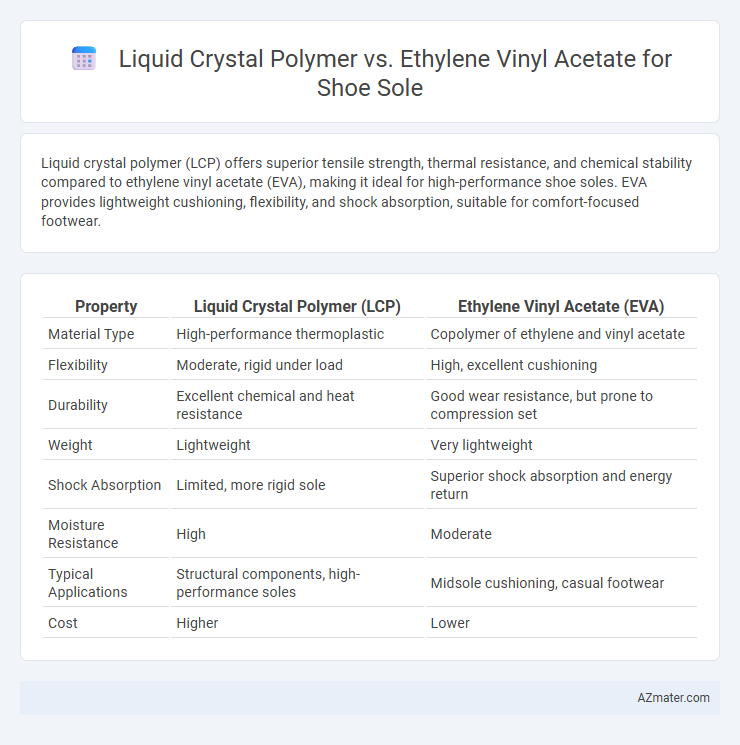
Liquid crystal polymer (LCP) offers superior tensile strength, thermal resistance, and chemical stability compared to ethylene vinyl acetate (EVA), making it ideal for high-performance shoe soles. EVA provides lightweight cushioning, flexibility, and shock absorption, suitable for comfort-focused footwear.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Liquid Crystal Polymer (LCP) | Ethylene Vinyl Acetate (EVA) |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | High-performance thermoplastic | Copolymer of ethylene and vinyl acetate |
| Flexibility | Moderate, rigid under load | High, excellent cushioning |
| Durability | Excellent chemical and heat resistance | Good wear resistance, but prone to compression set |
| Weight | Lightweight | Very lightweight |
| Shock Absorption | Limited, more rigid sole | Superior shock absorption and energy return |
| Moisture Resistance | High | Moderate |
| Typical Applications | Structural components, high-performance soles | Midsole cushioning, casual footwear |
| Cost | Higher | Lower |
Introduction to Liquid Crystal Polymer (LCP) and Ethylene Vinyl Acetate (EVA)
Liquid Crystal Polymer (LCP) is a high-performance thermoplastic known for its exceptional mechanical strength, chemical resistance, and dimensional stability, making it suitable for durable shoe sole applications requiring rigidity and wear resistance. Ethylene Vinyl Acetate (EVA) is a flexible, lightweight copolymer widely used in shoe soles for its excellent cushioning, shock absorption, and softness, providing superior comfort and impact protection. The choice between LCP and EVA depends on the balance between durability and flexibility needed in footwear design.
Material Composition and Structural Differences
Liquid crystal polymer (LCP) is a high-performance thermoplastic characterized by rigid aromatic polymer chains that align during processing, providing exceptional tensile strength and thermal stability for shoe soles. In contrast, ethylene vinyl acetate (EVA) is a copolymer composed of ethylene and vinyl acetate units, offering a flexible, lightweight, and cushioning material ideal for shock absorption. Structurally, LCP's ordered molecular arrangement results in a rigid, durable sole with high wear resistance, while EVA's amorphous, rubber-like structure delivers superior elasticity and comfort.
Mechanical Properties and Durability Comparison
Liquid crystal polymer (LCP) exhibits significantly higher tensile strength and stiffness compared to ethylene vinyl acetate (EVA), making it ideal for high-performance shoe soles requiring rigidity and impact resistance. EVA offers superior flexibility and cushioning but has lower abrasion resistance and compressive durability than LCP, which retains mechanical integrity under repetitive stress and elevated temperatures. The durability profile of LCP translates into longer-lasting soles with minimal deformation, whereas EVA soles may show faster wear and permanent compression over time.
Cushioning and Comfort Evaluation
Liquid crystal polymer (LCP) offers superior rigidity and high tensile strength, which contributes to durable yet firm shoe soles, while ethylene vinyl acetate (EVA) is renowned for its excellent cushioning properties due to its flexibility and shock absorption capabilities. EVA soles provide enhanced comfort through lightweight, soft materials that reduce impact forces on the foot, making them highly suitable for athletic and casual footwear. In contrast, LCP's stiffness may limit cushioning but improves structural support, favoring applications where durability and stability are prioritized over plush comfort.
Weight and Flexibility in Shoe Sole Applications
Liquid crystal polymer (LCP) offers significantly lower density compared to ethylene vinyl acetate (EVA), resulting in lighter shoe soles that enhance wearability and reduce fatigue. LCP exhibits superior rigidity and dimensional stability while maintaining moderate flexibility, ideal for performance footwear requiring structural support. EVA provides greater elasticity and cushioning but at the cost of increased weight and less durability under repetitive stress conditions.
Resistance to Environmental Factors (Heat, Moisture, Chemicals)
Liquid crystal polymers (LCP) exhibit superior resistance to heat, maintaining structural integrity at temperatures up to 300degC, outperforming ethylene vinyl acetate (EVA), which softens above 80degC. LCPs also demonstrate excellent moisture resistance, showing minimal water absorption compared to EVA's higher hygroscopicity that can compromise shoe sole durability in wet conditions. Chemical resistance in LCPs is robust against oils, solvents, and acids, whereas EVA may degrade or swell when exposed to aggressive chemicals, making LCP a more durable choice for harsh environmental applications in footwear.
Manufacturing Process and Cost Considerations
Liquid crystal polymer (LCP) manufacturing for shoe soles involves precise injection molding with high temperature resistance, enabling intricate designs and superior mechanical properties but demands specialized equipment and longer cycle times, increasing production costs. Ethylene vinyl acetate (EVA) is processed through simpler methods like compression molding or injection molding at lower temperatures, resulting in faster production cycles and reduced equipment expenses, making it a cost-effective choice for large-scale manufacturing. Cost considerations favor EVA due to its lower raw material price and energy-efficient processing, while LCP offers enhanced durability and performance at a premium expense.
Sustainability and Eco-Friendliness Assessment
Liquid crystal polymer (LCP) offers superior durability and recyclability compared to ethylene vinyl acetate (EVA), contributing to longer-lasting shoe soles with less frequent replacements. EVA, while lightweight and flexible, is derived from petrochemicals and has limited biodegradability, presenting challenges for eco-friendly disposal. Sustainability assessments favor LCP for its potential in reducing environmental footprint through enhanced material efficiency and recyclability in shoe sole manufacturing.
Market Adoption and Real-World Performance
Liquid crystal polymer (LCP) offers superior tensile strength and chemical resistance, driving its adoption in high-performance athletic shoe soles where durability and lightweight properties are critical. Ethylene vinyl acetate (EVA) dominates the mass market due to its excellent cushioning, flexibility, and cost-effectiveness, making it the preferred choice for casual and running shoes. Real-world performance tests highlight LCP's enhanced abrasion resistance and dimensional stability, whereas EVA provides superior shock absorption and comfort.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Material for Shoe Soles
Liquid crystal polymer (LCP) offers superior mechanical strength, high heat resistance, and excellent dimensional stability, making it ideal for high-performance shoe soles requiring durability and precision. Ethylene vinyl acetate (EVA) provides lightweight cushioning, flexibility, and shock absorption, enhancing comfort for everyday footwear applications. Selecting the right material depends on the intended use: LCP suits technical, high-wear environments, while EVA excels in casual, comfort-focused designs.
Infographic: Liquid crystal polymer vs Ethylene vinyl acetate for Shoe Sole
 azmater.com
azmater.com