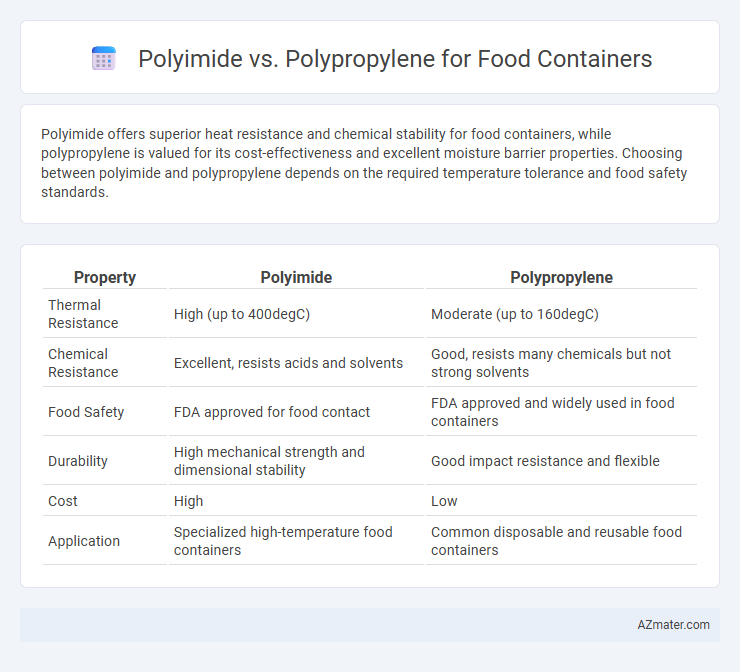
Polyimide offers superior heat resistance and chemical stability for food containers, while polypropylene is valued for its cost-effectiveness and excellent moisture barrier properties. Choosing between polyimide and polypropylene depends on the required temperature tolerance and food safety standards.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Polyimide | Polypropylene |
|---|---|---|
| Thermal Resistance | High (up to 400degC) | Moderate (up to 160degC) |
| Chemical Resistance | Excellent, resists acids and solvents | Good, resists many chemicals but not strong solvents |
| Food Safety | FDA approved for food contact | FDA approved and widely used in food containers |
| Durability | High mechanical strength and dimensional stability | Good impact resistance and flexible |
| Cost | High | Low |
| Application | Specialized high-temperature food containers | Common disposable and reusable food containers |
Introduction to Food Container Materials
Polyimide and polypropylene are widely used materials in food containers, each offering distinct advantages based on their chemical and thermal properties. Polypropylene is favored for its excellent moisture resistance, lightweight nature, and ability to withstand temperatures up to 100degC, making it suitable for microwave use and general food storage. Polyimide, known for its superior thermal stability up to 400degC and exceptional chemical resistance, is ideal for high-temperature applications and environments requiring durability against harsh conditions.
Overview of Polyimide
Polyimide is a high-performance polymer known for its exceptional thermal stability, chemical resistance, and mechanical strength, making it suitable for advanced food container applications. Its ability to withstand temperatures up to 400degC without degradation ensures safe use in extreme cooking or sterilization processes. Unlike polypropylene, polyimide offers superior durability and resistance to harsh chemicals, although it is generally more expensive and less flexible.
Overview of Polypropylene
Polypropylene is a thermoplastic polymer widely used for food containers due to its excellent chemical resistance, low moisture absorption, and high melting point around 160degC, making it safe for microwave and dishwasher usage. Its lightweight nature and cost-effectiveness contribute to its popularity in disposable and reusable food packaging, ensuring durability and food safety compliance. Polypropylene's non-toxic characteristics and ability to form tight seals protect food from contamination and extend shelf life.
Thermal Resistance Comparison
Polyimide exhibits superior thermal resistance withstanding continuous temperatures up to 400degC, making it ideal for high-heat food container applications. Polypropylene resists heat effectively but only up to approximately 100-120degC before deforming or melting, limiting its use in high-temperature environments. This significant difference highlights polyimide's advantage in durability and safety for hot food storage and reheating.
Chemical Resistance and Food Safety
Polyimide exhibits exceptional chemical resistance to solvents, acids, and alkalis, making it highly suitable for food containers exposed to harsh cleaning agents or aggressive ingredients. Polypropylene offers good chemical resistance against fats, oils, and mild acids, ensuring safe contact with a wide range of common food products. Both materials are FDA-approved for food contact, but polyimide's superior thermal and chemical stability provides enhanced food safety in demanding environments.
Durability and Lifespan
Polyimide offers exceptional durability and a longer lifespan for food containers due to its high thermal stability and chemical resistance, maintaining integrity under extreme temperatures and frequent use. Polypropylene, while cost-effective and resistant to many acids and bases, tends to degrade faster with repeated microwave heating or dishwasher cycles, limiting its longevity. For applications requiring robust, long-term performance, polyimide containers outperform polypropylene by providing superior resistance to wear, heat, and chemical exposure.
Environmental Impact and Recyclability
Polypropylene (PP) offers superior environmental benefits for food containers due to its high recyclability and lower carbon footprint compared to polyimide, which is less commonly recycled and has more complex chemical stability. Polypropylene's widespread acceptance in recycling programs reduces landfill waste and enables material reuse, promoting a circular economy. In contrast, polyimide's durability and heat resistance come with challenges in recycling processes, leading to higher environmental impact over the container's lifecycle.
Cost Efficiency and Availability
Polypropylene is highly favored for food containers due to its low cost and widespread availability, making it a cost-efficient choice for mass production. Polyimide, although offering superior thermal stability and chemical resistance, tends to be significantly more expensive and less readily available in large quantities. For applications prioritizing budget and ease of sourcing, polypropylene is the optimal material.
Applications in Food Storage and Packaging
Polyimide exhibits exceptional thermal stability and chemical resistance, making it ideal for high-temperature food storage, such as microwaveable containers or oven-safe trays. Polypropylene is widely used for food packaging due to its low cost, excellent moisture barrier properties, and good impact resistance, suitable for disposable containers and refrigerated storage. Both materials ensure food safety compliance, but polyimide is preferred for specialty applications requiring durability under extreme conditions, while polypropylene dominates everyday food packaging.
Conclusion: Choosing Between Polyimide and Polypropylene
Polypropylene is widely favored for food containers due to its excellent chemical resistance, affordability, and microwave-safe properties, making it ideal for everyday use. Polyimide offers superior thermal stability and mechanical strength but is less common in food packaging due to higher costs and manufacturing complexity. Selecting between the two depends on specific needs: polypropylene suits mass-market food storage, while polyimide is better for specialized applications requiring extreme heat resistance.
Infographic: Polyimide vs Polypropylene for Food container
 azmater.com
azmater.com