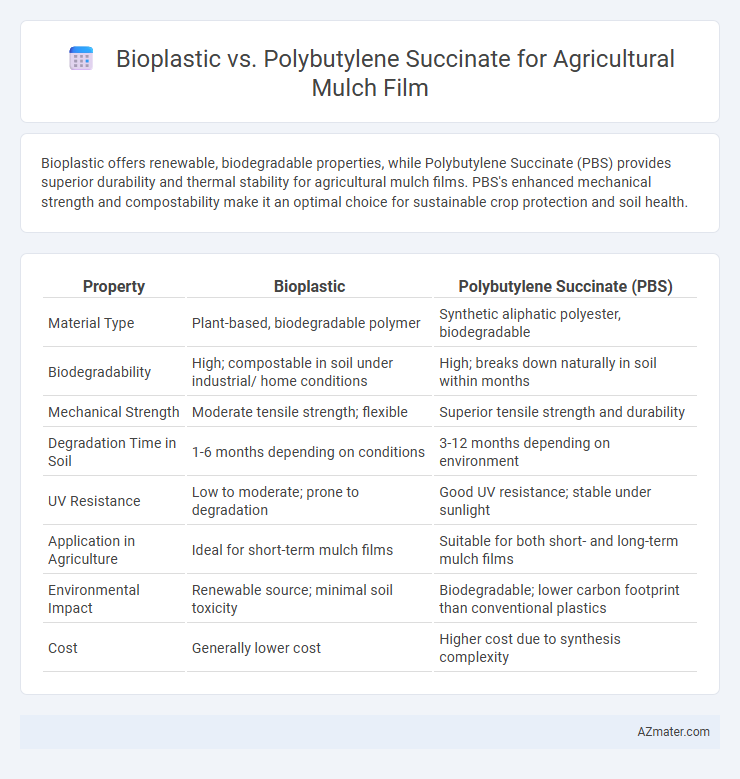
Bioplastic offers renewable, biodegradable properties, while Polybutylene Succinate (PBS) provides superior durability and thermal stability for agricultural mulch films. PBS's enhanced mechanical strength and compostability make it an optimal choice for sustainable crop protection and soil health.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Bioplastic | Polybutylene Succinate (PBS) |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Plant-based, biodegradable polymer | Synthetic aliphatic polyester, biodegradable |
| Biodegradability | High; compostable in soil under industrial/ home conditions | High; breaks down naturally in soil within months |
| Mechanical Strength | Moderate tensile strength; flexible | Superior tensile strength and durability |
| Degradation Time in Soil | 1-6 months depending on conditions | 3-12 months depending on environment |
| UV Resistance | Low to moderate; prone to degradation | Good UV resistance; stable under sunlight |
| Application in Agriculture | Ideal for short-term mulch films | Suitable for both short- and long-term mulch films |
| Environmental Impact | Renewable source; minimal soil toxicity | Biodegradable; lower carbon footprint than conventional plastics |
| Cost | Generally lower cost | Higher cost due to synthesis complexity |
Introduction to Bioplastics and Polybutylene Succinate (PBS)
Bioplastics, derived from renewable biomass sources such as corn starch and sugarcane, offer sustainable alternatives to traditional petroleum-based plastics in agricultural applications. Polybutylene succinate (PBS) is a biodegradable aliphatic polyester synthesized from succinic acid and 1,4-butanediol, notable for its excellent mechanical properties and environmental compatibility. PBS's ability to degrade under soil conditions makes it a promising material for agricultural mulch films, promoting eco-friendly crop production and reducing plastic pollution.
Importance of Sustainable Agricultural Mulch Films
Sustainable agricultural mulch films like bioplastics and polybutylene succinate (PBS) play a crucial role in reducing environmental impact by enhancing soil health and minimizing plastic waste. Bioplastic mulch films, derived from renewable resources, provide effective weed control and moisture retention while being biodegradable, reducing long-term soil contamination. Polybutylene succinate offers comparable biodegradability and mechanical strength, making it a promising alternative for eco-friendly and efficient agricultural practices.
Bioplastic Overview: Types and Properties
Bioplastics used in agricultural mulch films primarily include polylactic acid (PLA), polyhydroxyalkanoates (PHA), and starch-based composites, each offering distinct biodegradability and mechanical properties tailored for sustainable farming. These bioplastics possess advantages such as reduced carbon footprint, enhanced soil compatibility, and controlled degradation rates compared to conventional plastics like polybutylene succinate (PBS). Their physicochemical characteristics, including tensile strength, moisture barrier, and thermal stability, are critical for optimizing mulch film performance under varying agricultural conditions.
Polybutylene Succinate (PBS): Composition and Characteristics
Polybutylene Succinate (PBS) is a biodegradable polyester synthesized from succinic acid and 1,4-butanediol, both of which can be derived from renewable resources, making it an eco-friendly alternative to conventional plastics in agricultural mulch films. PBS exhibits excellent thermal stability, high tensile strength, and good flexibility, allowing it to withstand various environmental conditions while maintaining durability and soil coverage efficiency. Its compostability and biodegradability under industrial and home composting conditions contribute to reduced plastic pollution and enhanced soil health in sustainable farming practices.
Biodegradability and Environmental Impact Comparison
Bioplastic and polybutylene succinate (PBS) both offer biodegradable solutions for agricultural mulch film, but PBS typically demonstrates faster degradation rates under composting conditions, reducing long-term soil residue. Bioplastics derived from renewable resources vary widely in composition, influencing their biodegradability and potential microplastic formation, whereas PBS provides consistent environmental benefits with lower greenhouse gas emissions during production. Evaluating lifecycle assessments reveals PBS mulch films contribute less to soil and water pollution, promoting sustainable agricultural practices with minimal ecological disruption.
Performance in Agricultural Applications
Bioplastic and polybutylene succinate (PBS) differ significantly in agricultural mulch film performance, where PBS offers superior biodegradability and mechanical strength, ensuring effective soil moisture retention and weed suppression. PBS's enhanced thermal stability allows better adaptation to varying field temperatures, promoting consistent crop growth compared to conventional bioplastics. The controlled degradation rate of PBS aligns with crop cycles, reducing residue management challenges and improving sustainability in agricultural applications.
Cost and Availability Analysis
Bioplastic mulch films typically have higher production costs and limited availability compared to polybutylene succinate (PBS), which benefits from more established manufacturing processes and economies of scale. PBS offers competitive pricing and wider market access, making it a more feasible option for large-scale agricultural applications. Cost efficiency and supply consistency position PBS as a favorable choice for farmers seeking sustainable mulch film alternatives.
Challenges in Adopting Bioplastics vs. PBS
Bioplastics used for agricultural mulch films face challenges such as higher production costs, limited mechanical strength, and variable biodegradability under field conditions compared to Polybutylene Succinate (PBS). PBS offers superior thermal stability, consistent biodegradation rates, and improved mechanical properties, making it more reliable for agricultural applications. However, limited large-scale availability and environmental concerns about feedstock sourcing remain obstacles for widespread PBS adoption.
Regulatory Standards and Certifications
Polybutylene succinate (PBS) mulch films comply with ASTM D6400 and EN 13432 standards, ensuring biodegradability and compostability that meet stringent agricultural regulations. Bioplastic mulch films often carry certifications such as OK Compost HOME and TUV AUSTRIA OK Compost INDUSTRIAL, which verify eco-friendly disposal under specific composting conditions. Regulatory standards emphasize the importance of soil biodegradation rates and non-toxicity, positioning PBS as a favorable option for sustainable agricultural practices.
Future Prospects for Mulch Film Innovation
Bioplastic and polybutylene succinate (PBS) offer promising future prospects for agricultural mulch film due to their biodegradability and reduced environmental impact compared to conventional plastics. The development of PBS-based mulch films enhances soil health by minimizing plastic residue accumulation and supports sustainable farming practices through improved compostability. Advanced research on molecular structure optimization and blending with natural polymers is expected to further increase the durability and degradation rates suitable for diverse crop cycles.
Infographic: Bioplastic vs Polybutylene Succinate for Agricultural Mulch Film
 azmater.com
azmater.com