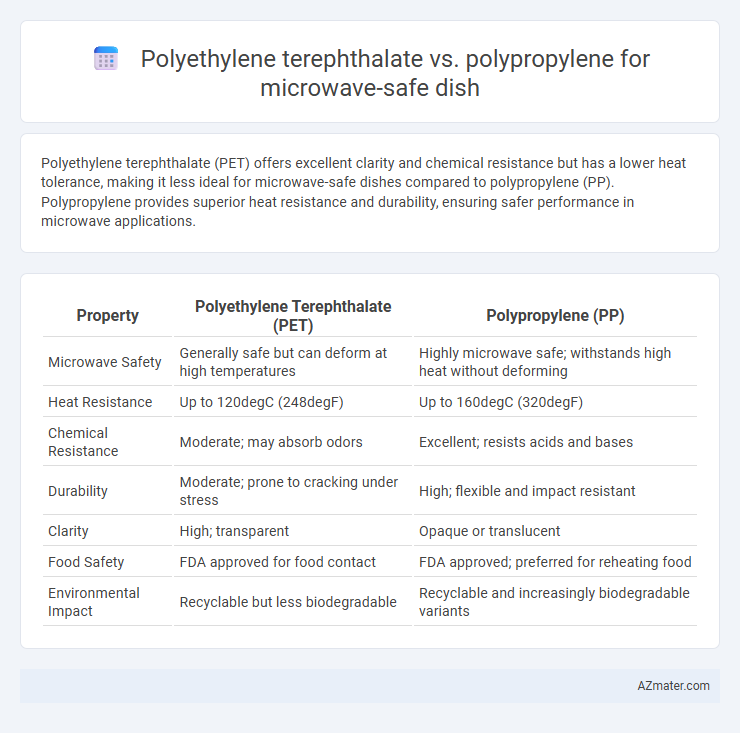
Polyethylene terephthalate (PET) offers excellent clarity and chemical resistance but has a lower heat tolerance, making it less ideal for microwave-safe dishes compared to polypropylene (PP). Polypropylene provides superior heat resistance and durability, ensuring safer performance in microwave applications.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Polyethylene Terephthalate (PET) | Polypropylene (PP) |
|---|---|---|
| Microwave Safety | Generally safe but can deform at high temperatures | Highly microwave safe; withstands high heat without deforming |
| Heat Resistance | Up to 120degC (248degF) | Up to 160degC (320degF) |
| Chemical Resistance | Moderate; may absorb odors | Excellent; resists acids and bases |
| Durability | Moderate; prone to cracking under stress | High; flexible and impact resistant |
| Clarity | High; transparent | Opaque or translucent |
| Food Safety | FDA approved for food contact | FDA approved; preferred for reheating food |
| Environmental Impact | Recyclable but less biodegradable | Recyclable and increasingly biodegradable variants |
Introduction to Microwave Safe Plastics
Microwave safe plastics must withstand high temperatures without melting, warping, or releasing harmful chemicals. Polyethylene terephthalate (PET) offers durability and clarity but has limited heat resistance, making it less ideal for repeated microwave use. Polypropylene (PP) exhibits superior heat resistance and chemical stability, making it a preferred choice for microwave safe dishes due to its ability to maintain integrity under microwave heating.
Overview of Polyethylene Terephthalate (PET)
Polyethylene terephthalate (PET) is a common thermoplastic polymer widely used in food packaging due to its clarity, strength, and chemical resistance. PET offers excellent microwave-safe properties as it can withstand moderate heat without melting or releasing harmful chemicals. Its low permeability to gases and moisture maintains food freshness, making it a preferred material for microwave-safe dishes compared to polypropylene.
Overview of Polypropylene (PP)
Polypropylene (PP) is a thermoplastic polymer widely recognized for its excellent microwave safety due to its high melting point around 160degC (320degF) and resistance to heat deformation, making it ideal for microwave-safe dishes. Compared to polyethylene terephthalate (PET), which has a lower melting point and can release harmful substances under high heat, PP offers superior durability, chemical resistance, and food safety compliance, especially in reheating applications. Its lightweight nature and ability to withstand repeated microwave cycles without leaching chemicals solidify polypropylene as a preferred choice for microwave-safe containers.
Chemical Structure Differences: PET vs PP
Polyethylene terephthalate (PET) features a rigid aromatic polymer backbone with ester functional groups, contributing to its strength and clarity but making it less heat resistant compared to polyethylene polypropylene (PP), which has a semi-crystalline, saturated hydrocarbon structure consisting of repeating propylene units with methyl side groups. The ester linkages in PET make it more susceptible to hydrolysis and thermal degradation under microwave conditions, whereas PP's hydrocarbon chains provide superior thermal stability and lower water absorption, enhancing its microwave safety. These chemical differences influence their microwave compatibility, with PP generally preferred for microwave-safe dishes due to its higher heat resistance and chemical inertness.
Heat Resistance and Microwave Safety
Polyethylene terephthalate (PET) exhibits moderate heat resistance with a maximum service temperature around 70-80degC, making it less suitable for microwave use due to potential warping or melting. Polypropylene (PP) withstands higher temperatures up to approximately 120-130degC, offering superior heat resistance and better microwave safety without releasing harmful chemicals. Microwave-safe dishes often prefer polypropylene for its durability, chemical stability, and resistance to heat-induced deformation during heating cycles.
Leaching Potential and Food Safety Concerns
Polyethylene terephthalate (PET) generally exhibits low leaching potential when used for microwave-safe dishes, maintaining food safety by resisting chemical migration under typical heating conditions. In contrast, polypropylene (PP) also demonstrates strong microwave stability, with minimal risk of releasing harmful substances, making it a preferred choice for microwaveable containers due to its heat resistance and inertness. Both polymers comply with FDA regulations for food contact materials, but polypropylene's higher melting point and better chemical resistance provide an added safety margin during repeated microwave exposure.
Durability and Reusability in Microwave Use
Polyethylene terephthalate (PET) offers moderate durability for microwave-safe dishes but tends to degrade faster with repeated microwave exposure due to its lower heat resistance compared to polypropylene (PP). Polypropylene is highly durable and maintains structural integrity through numerous microwave cycles, making it a preferred choice for reusable microwave-safe containers. The superior heat tolerance of polypropylene ensures longer-lasting usability without warping or releasing harmful substances during microwave use.
Environmental Impact: PET vs PP
Polyethylene terephthalate (PET) and polypropylene (PP) differ significantly in environmental impact when used for microwave-safe dishes. PET is highly recyclable and often made from recycled materials, reducing landfill waste and energy consumption, but it can release harmful chemicals if overheated. Polypropylene offers better heat resistance and durability with lower carbon emissions during production, yet it is less commonly recycled compared to PET, leading to increased environmental persistence.
Common Applications in Microwave Safe Dishes
Polyethylene terephthalate (PET) is widely used in microwave-safe dishes due to its excellent heat resistance and clarity, making it ideal for packaging ready-to-eat meals and microwaveable containers. Polypropylene (PP) is favored for microwave-safe dishes because of its high melting point, durability, and resistance to chemical leaching, commonly found in reusable containers and microwaveable storage boxes. Both materials serve critical roles in food safety and convenience, with PET preferred for single-use applications and PP for multiple-use purposes in microwave environments.
Final Comparison: Which is Safer for Microwave Use?
Polyethylene terephthalate (PET) and polypropylene (PP) differ significantly in microwave safety, with polypropylene being the safer choice due to its higher heat resistance and lower chemical leaching risk when exposed to microwave temperatures. PET can release harmful substances like antimony and acetaldehyde under prolonged microwave heating, making it less suitable for repeated microwave use. Polypropylene's durability and stability at microwave temperatures ensure minimal degradation, making it ideal for microwave-safe dishes.
Infographic: Polyethylene terephthalate vs Polypropylene for Microwave Safe Dish
 azmater.com
azmater.com