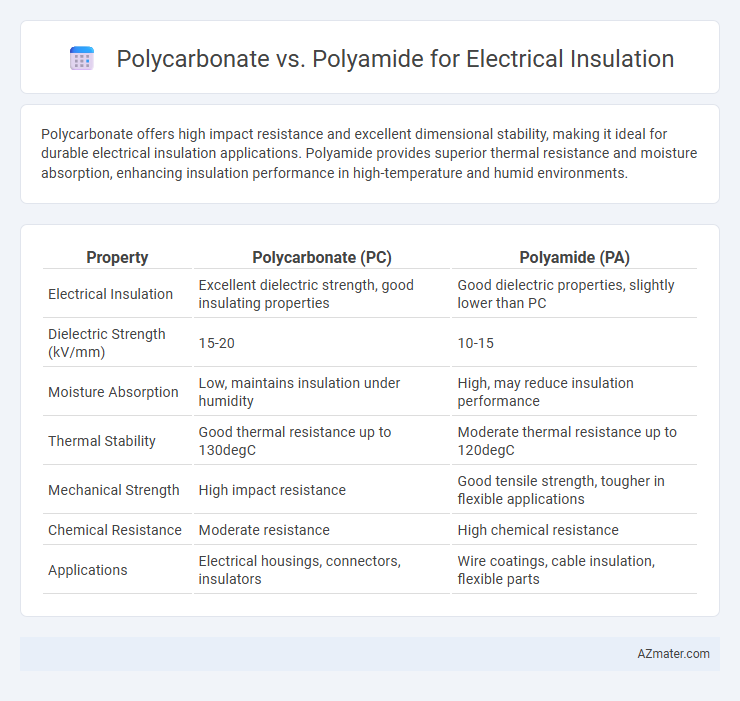
Polycarbonate offers high impact resistance and excellent dimensional stability, making it ideal for durable electrical insulation applications. Polyamide provides superior thermal resistance and moisture absorption, enhancing insulation performance in high-temperature and humid environments.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Polycarbonate (PC) | Polyamide (PA) |
|---|---|---|
| Electrical Insulation | Excellent dielectric strength, good insulating properties | Good dielectric properties, slightly lower than PC |
| Dielectric Strength (kV/mm) | 15-20 | 10-15 |
| Moisture Absorption | Low, maintains insulation under humidity | High, may reduce insulation performance |
| Thermal Stability | Good thermal resistance up to 130degC | Moderate thermal resistance up to 120degC |
| Mechanical Strength | High impact resistance | Good tensile strength, tougher in flexible applications |
| Chemical Resistance | Moderate resistance | High chemical resistance |
| Applications | Electrical housings, connectors, insulators | Wire coatings, cable insulation, flexible parts |
Introduction to Electrical Insulation Materials
Polycarbonate and polyamide are widely used electrical insulation materials distinguished by their unique properties. Polycarbonate offers excellent dielectric strength, high impact resistance, and dimensional stability, making it suitable for components requiring robust insulation under mechanical stress. Polyamide provides superior thermal resistance, good electrical insulating properties, and chemical durability, ideal for applications exposed to high temperatures and harsh environments.
Overview of Polycarbonate and Polyamide
Polycarbonate is a durable thermoplastic known for high impact resistance and excellent electrical insulation properties, making it suitable for electrical housings and components that require toughness and dimensional stability. Polyamide, or nylon, offers superior mechanical strength, chemical resistance, and excellent dielectric properties, which are critical in electrical insulation applications exposed to harsh environments or varying temperatures. Both materials provide reliable insulation, but polycarbonate excels in rigidity and optical clarity, while polyamide delivers enhanced thermal resistance and flexibility for electrical components.
Key Properties of Polycarbonate for Insulation
Polycarbonate offers excellent electrical insulation properties due to its high dielectric strength, typically around 16-18 kV/mm, which prevents electrical breakdown in high-voltage environments. Its low moisture absorption below 0.15% ensures consistent insulating performance even in humid conditions, maintaining dimensional stability and electrical resistance. The material also features superior thermal resistance, with a glass transition temperature near 147degC, allowing it to perform reliably in applications where temperature fluctuations are common.
Key Properties of Polyamide for Insulation
Polyamide exhibits excellent thermal resistance up to 150degC, making it ideal for electrical insulation in high-temperature environments. Its superior dielectric strength, often exceeding 20 kV/mm, ensures effective insulation and minimizes electrical leakage. The inherent moisture resistance and mechanical toughness of polyamide contribute to long-term durability and reliability in demanding electrical applications.
Thermal Stability: Polycarbonate vs Polyamide
Polycarbonate offers superior thermal stability with a high glass transition temperature around 147degC, making it ideal for electrical insulation applications requiring resistance to heat and flame. Polyamide, commonly known as nylon, exhibits good thermal stability but typically has a lower melting point near 220degC and glass transition temperature around 50degC, which can limit its performance under prolonged high-temperature exposure. Both materials provide electrical insulation properties, but polycarbonate's enhanced thermal stability ensures better durability and safety in high-heat environments.
Electrical Insulation Performance Comparison
Polycarbonate exhibits superior electrical insulation properties compared to polyamide, with higher dielectric strength typically around 15-20 kV/mm versus 10-15 kV/mm for polyamide. Polycarbonate's lower dielectric constant and dissipation factor contribute to reduced energy loss and better insulation efficiency in high-voltage applications. Conversely, polyamide offers enhanced moisture resistance but lower electrical performance, making polycarbonate the preferred choice for critical electrical insulation components.
Durability and Mechanical Strength Analysis
Polycarbonate exhibits superior impact resistance and high tensile strength, making it highly durable for electrical insulation in demanding environments. Polyamide offers excellent flexibility and abrasion resistance but may degrade faster under continuous mechanical stress. For applications requiring long-term mechanical strength and resistance to physical damage, polycarbonate is often the preferred material.
Chemical Resistance in Electrical Applications
Polycarbonate offers moderate chemical resistance in electrical insulation, particularly against acids and alcohols, while being susceptible to strong solvents and alkalis, impacting its long-term durability in harsh environments. Polyamide (nylon) exhibits superior chemical resistance, especially to oils, fuels, and greases, making it ideal for electrical components exposed to automotive and industrial chemicals. Selecting polyamide over polycarbonate enhances reliability in electrical insulation where chemical exposure is frequent, ensuring stable dielectric properties and mechanical integrity.
Cost Effectiveness and Material Availability
Polycarbonate offers moderate cost effectiveness with widespread availability in electrical insulation, making it a popular choice for budget-conscious projects. Polyamide (nylon) typically incurs higher costs due to its superior mechanical strength and thermal resistance but is less readily available in specialized electrical grades. Choosing between the two depends on balancing initial material expenses against performance requirements and supply chain accessibility.
Best Choice: Polycarbonate or Polyamide for Electrical Insulation
Polycarbonate offers excellent electrical insulation properties with high dielectric strength and thermal stability, making it suitable for applications requiring robust performance under heat. Polyamide provides superior mechanical strength and moisture resistance but tends to absorb more water, which can reduce its electrical insulation efficiency over time. For electrical insulation purposes, polycarbonate is generally the best choice due to its consistent insulating properties and durability in varying environmental conditions.
Infographic: Polycarbonate vs Polyamide for Electrical Insulation
 azmater.com
azmater.com