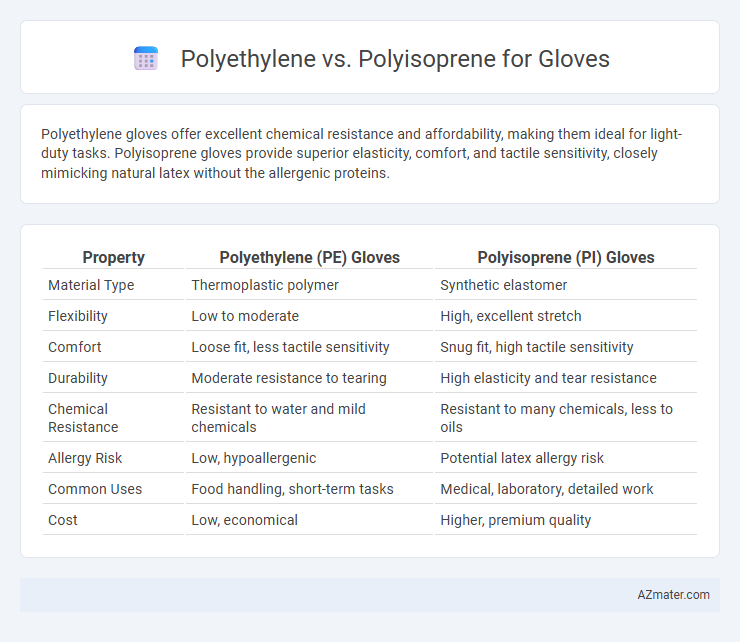
Polyethylene gloves offer excellent chemical resistance and affordability, making them ideal for light-duty tasks. Polyisoprene gloves provide superior elasticity, comfort, and tactile sensitivity, closely mimicking natural latex without the allergenic proteins.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Polyethylene (PE) Gloves | Polyisoprene (PI) Gloves |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Thermoplastic polymer | Synthetic elastomer |
| Flexibility | Low to moderate | High, excellent stretch |
| Comfort | Loose fit, less tactile sensitivity | Snug fit, high tactile sensitivity |
| Durability | Moderate resistance to tearing | High elasticity and tear resistance |
| Chemical Resistance | Resistant to water and mild chemicals | Resistant to many chemicals, less to oils |
| Allergy Risk | Low, hypoallergenic | Potential latex allergy risk |
| Common Uses | Food handling, short-term tasks | Medical, laboratory, detailed work |
| Cost | Low, economical | Higher, premium quality |
Introduction to Glove Materials
Polyethylene gloves offer cost-effective, low-barrier protection ideal for light-duty tasks, providing excellent resistance to water-based substances and flexibility. Polyisoprene gloves deliver superior elasticity and comfort with higher tactile sensitivity, making them suitable for medical and high-precision applications due to their natural rubber-like properties. Material choice depends on required durability, sensitivity, and chemical resistance specific to industry standards.
Overview of Polyethylene Gloves
Polyethylene gloves are lightweight, disposable gloves made from a thermoplastic polymer derived from ethylene gas, commonly used in food handling and light-duty tasks due to their cost-effectiveness and chemical resistance. These gloves offer excellent moisture resistance and provide a loose fit, enhancing comfort for short-term use but lack the elasticity and durability found in polyisoprene gloves. Polyethylene gloves serve as an economical alternative for environments where minimal protection is required, contrasting with the higher tactile sensitivity and flexibility of polyisoprene gloves used in medical and laboratory settings.
Overview of Polyisoprene Gloves
Polyisoprene gloves offer superior elasticity, comfort, and tactile sensitivity compared to polyethylene gloves, making them ideal for medical and surgical applications. They provide excellent puncture resistance and biocompatibility while maintaining a latex-free composition to minimize allergic reactions. Polyisoprene gloves deliver a natural rubber feel combined with enhanced durability, ensuring reliable protection and precision during detailed tasks.
Material Composition and Properties
Polyethylene gloves are made from high-density polyethylene (HDPE) or low-density polyethylene (LDPE), offering excellent chemical resistance, water impermeability, and affordability, but limited elasticity and durability. Polyisoprene gloves, derived from synthetic natural rubber, provide superior elasticity, tensile strength, and tactile sensitivity, closely mimicking natural latex without causing allergic reactions. The material composition of polyethylene results in stiffer, less flexible gloves, while polyisoprene's polymer chains enable enhanced stretchability and comfort for prolonged use.
Comfort and Fit Comparison
Polyisoprene gloves provide superior comfort and a snug fit due to their elasticity and ability to conform closely to hand contours, reducing hand fatigue during prolonged use. Polyethylene gloves offer a looser fit and less tactile sensitivity, often leading to diminished comfort in tasks requiring precision. For applications prioritizing dexterity and prolonged wear, polyisoprene outperforms polyethylene in delivering enhanced user comfort and fit.
Barrier Protection and Safety
Polyethylene gloves provide basic barrier protection against water-based fluids and contaminants but offer limited chemical resistance and durability, making them suitable for low-risk tasks. Polyisoprene gloves, known for their superior elasticity and puncture resistance, deliver enhanced barrier protection against a wide range of chemicals and biological hazards, ensuring higher safety in medical and industrial environments. The choice between polyethylene and polyisoprene gloves depends on the required level of chemical resistance, flexibility, and protection against pathogens.
Chemical Resistance Differences
Polyethylene gloves offer excellent resistance to water-based chemicals, acids, and bases, making them suitable for light-duty tasks involving mild substances. Polyisoprene gloves provide superior protection against organic solvents, oils, and fats due to their natural rubber composition and elasticity. Chemical resistance in polyethylene is limited against hydrocarbons and oils, while polyisoprene resists a wider range of chemicals but may degrade with certain solvents.
Cost and Availability
Polyethylene gloves are significantly more affordable and widely available due to their simple manufacturing process and use of low-cost raw materials. Polyisoprene gloves, favored for superior elasticity and comfort, are generally more expensive and less readily available as they require synthetic rubber production and more complex processing. Cost-efficiency and large-scale accessibility make polyethylene gloves the preferred choice for low-risk, disposable applications.
Environmental Impact and Disposal
Polyethylene gloves exhibit lower environmental impact due to their simpler chemical composition and higher recyclability compared to polyisoprene, which is derived from natural rubber and requires more complex processing. Polyisoprene gloves contribute to biodegradability but often incorporate additives that hinder complete breakdown, complicating disposal. Both materials present challenges in waste management, yet polyethylene's compatibility with existing plastic recycling streams offers a more efficient pathway for reducing landfill accumulation.
Choosing the Right Glove for Your Needs
Polyethylene gloves offer cost-effective, lightweight protection suitable for short-term, low-risk tasks, while polyisoprene gloves provide superior elasticity, strength, and tactile sensitivity, making them ideal for medical or high-precision applications. Understanding the material properties, such as chemical resistance and allergen potential, helps select gloves that match specific environmental and safety requirements. Prioritizing glove characteristics like durability, comfort, and barrier performance ensures optimal protection tailored to your operational needs.
Infographic: Polyethylene vs Polyisoprene for Glove
 azmater.com
azmater.com