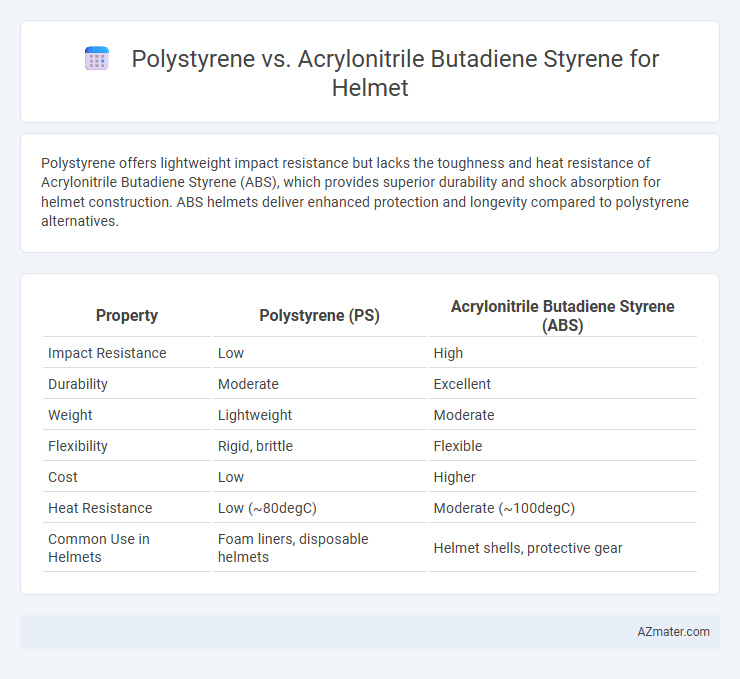
Polystyrene offers lightweight impact resistance but lacks the toughness and heat resistance of Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS), which provides superior durability and shock absorption for helmet construction. ABS helmets deliver enhanced protection and longevity compared to polystyrene alternatives.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Polystyrene (PS) | Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS) |
|---|---|---|
| Impact Resistance | Low | High |
| Durability | Moderate | Excellent |
| Weight | Lightweight | Moderate |
| Flexibility | Rigid, brittle | Flexible |
| Cost | Low | Higher |
| Heat Resistance | Low (~80degC) | Moderate (~100degC) |
| Common Use in Helmets | Foam liners, disposable helmets | Helmet shells, protective gear |
Introduction to Helmet Materials
Polystyrene and Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS) are common materials in helmet manufacturing due to their distinct properties. Polystyrene offers lightweight impact absorption, making it ideal for inner helmet liners, while ABS provides high durability and resistance to impact, perfect for outer shells. Choosing between these materials depends on balancing protection, weight, and cost in helmet design.
Overview of Polystyrene (PS)
Polystyrene (PS) is a lightweight, rigid thermoplastic commonly used in helmet applications due to its excellent impact resistance and shock absorption capabilities. Its low cost and ease of molding make PS a popular choice for producing helmet shells and inner liners that provide essential protection without adding excessive weight. Although less durable than Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS), PS offers sufficient strength for many safety helmet designs, especially in cost-sensitive markets.
Overview of Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS)
Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS) is a thermoplastic polymer known for its high impact resistance, toughness, and excellent strength-to-weight ratio, making it an ideal material for helmet manufacturing. ABS provides superior durability and shock absorption compared to polystyrene, ensuring enhanced protection during impacts. Its ability to undergo extensive molding allows for precise helmet shapes and consistent thickness, optimizing user safety and comfort.
Impact Resistance: PS vs ABS
Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS) offers significantly higher impact resistance compared to Polystyrene (PS), making ABS a preferred material in helmet manufacturing. ABS combines strength and flexibility, effectively absorbing and dispersing impact forces, while Polystyrene tends to be more brittle and prone to cracking under high stress. This superior durability of ABS enhances wearer safety by providing better protection in collision and fall scenarios.
Weight and Comfort Comparison
Polystyrene helmets are lightweight but offer less impact resistance and comfort due to their rigid structure, making them suitable for short-term use. Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS) helmets provide better durability and enhanced comfort with a slightly higher weight, offering improved shock absorption and a more secure fit. The balance between weight and comfort favors ABS for extended wear, especially in high-impact activities.
Durability and Longevity
Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS) helmets offer superior impact resistance and toughness compared to Polystyrene, making them more durable under repeated stress. Polystyrene helmets, often used as foam liners, provide excellent energy absorption but lack the structural strength for long-term use. ABS outer shells maintain longevity in harsh conditions, ensuring better protection and extended helmet lifespan.
Cost Differences
Polystyrene helmets typically cost less due to their lower material and manufacturing expenses, making them a budget-friendly option for basic head protection. Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS) helmets, though higher in price, offer enhanced durability and impact resistance, justifying the increased investment for improved safety. The cost difference between Polystyrene and ABS helmets can range from 15% to 40%, influenced by factors like helmet design, brand, and production scale.
Safety Standards and Certifications
Polystyrene and Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS) differ significantly in helmet safety standards and certifications; ABS helmets typically meet rigorous certifications such as DOT, ECE, and Snell due to their superior impact resistance and durability. Polystyrene, primarily used as a foam liner rather than a helmet shell, contributes to shock absorption but is not certified as a standalone helmet material. ABS's structural strength and compliance with international safety standards make it the preferred choice for certified protective headgear.
Environmental Impact and Recyclability
Polystyrene helmets offer lightweight protection but contribute significantly to environmental pollution due to their poor biodegradability and limited recycling options, often ending up in landfills or oceans. Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS) helmets provide durable impact resistance with better recyclability through established thermoplastic recycling processes, reducing environmental footprint. The choice of ABS supports more sustainable helmet production by enabling material recovery and reuse, whereas polystyrene poses greater challenges for waste management and environmental sustainability.
Choosing the Right Material for Your Helmet
Polystyrene offers lightweight and cost-effective properties but lacks the impact resistance and durability of Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS), making ABS the preferred choice for helmet shells due to its superior toughness and ability to absorb shocks. ABS also provides excellent thermal resistance and surface finish, enhancing helmet comfort and wearability in diverse conditions. For safety-critical applications, selecting ABS ensures better protection and longer-lasting performance compared to polystyrene.
Infographic: Polystyrene vs Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene for Helmet
 azmater.com
azmater.com