Polyoxymethylene offers superior stiffness, chemical resistance, and dimensional stability compared to Polyethylene terephthalate, making it ideal for high-strength drink bottle components. Polyethylene terephthalate excels in transparency, impact resistance, and recyclability, making it the preferred material for consumer-facing drink bottles.
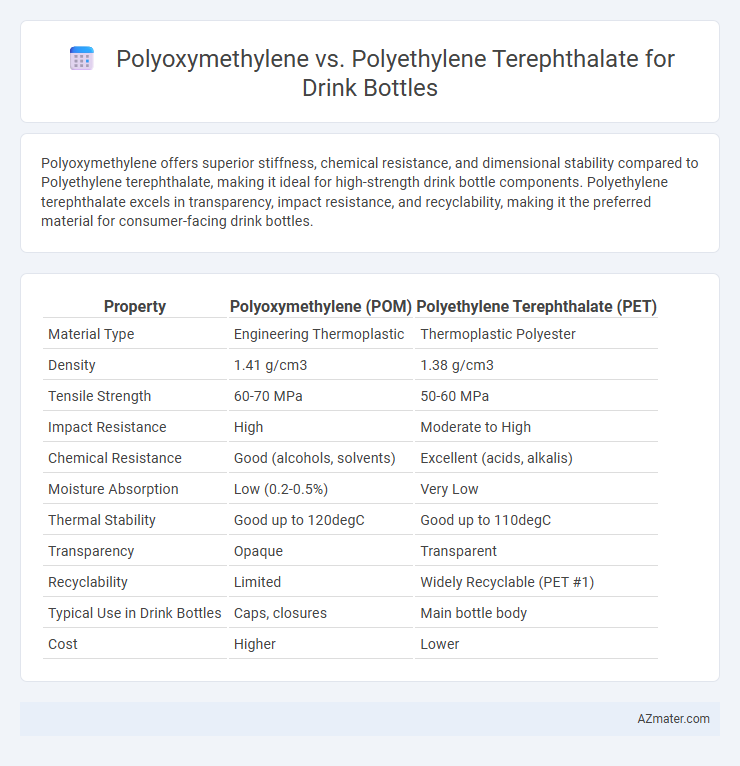
Table of Comparison
| Property | Polyoxymethylene (POM) | Polyethylene Terephthalate (PET) |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Engineering Thermoplastic | Thermoplastic Polyester |
| Density | 1.41 g/cm3 | 1.38 g/cm3 |
| Tensile Strength | 60-70 MPa | 50-60 MPa |
| Impact Resistance | High | Moderate to High |
| Chemical Resistance | Good (alcohols, solvents) | Excellent (acids, alkalis) |
| Moisture Absorption | Low (0.2-0.5%) | Very Low |
| Thermal Stability | Good up to 120degC | Good up to 110degC |
| Transparency | Opaque | Transparent |
| Recyclability | Limited | Widely Recyclable (PET #1) |
| Typical Use in Drink Bottles | Caps, closures | Main bottle body |
| Cost | Higher | Lower |
Introduction to Polyoxymethylene (POM) and Polyethylene Terephthalate (PET)
Polyoxymethylene (POM) is a high-strength engineering thermoplastic known for its stiffness, low friction, and excellent dimensional stability, commonly used in precision parts but less frequent in packaging. Polyethylene terephthalate (PET) is a popular polyester polymer widely utilized in the beverage industry due to its superior clarity, impact resistance, and excellent barrier properties against carbon dioxide and moisture. PET's recyclability and food safety certifications make it highly favored for drink bottles compared to POM, which is more suited for mechanical components than packaging applications.
Chemical Composition and Molecular Structure
Polyoxymethylene (POM) consists of repeating -CH2-O- units, forming a highly crystalline polymer with strong covalent ether bonds that provide excellent rigidity and chemical resistance ideal for structural components in drink bottles. Polyethylene terephthalate (PET) is a polyester composed of repeating units of ethylene glycol and terephthalic acid, characterized by aromatic rings and ester linkages that offer superior barrier properties and clarity crucial for beverage containment. The molecular structure of POM results in high mechanical strength and low moisture absorption, while PET's semi-crystalline arrangement balances durability with flexibility and effective carbonation retention.
Physical Properties Comparison
Polyoxymethylene (POM) offers higher tensile strength and stiffness compared to Polyethylene terephthalate (PET), making it more resistant to deformation under mechanical stress. PET excels in impact resistance and clarity, which is crucial for transparent drink bottles, while POM tends to have lower transparency and higher crystallinity. In terms of chemical resistance, PET withstands acidic and alcoholic beverages better, whereas POM is more suitable for applications requiring enhanced dimensional stability and low moisture absorption.
Mechanical Strength and Durability
Polyoxymethylene (POM) exhibits superior mechanical strength and rigidity compared to Polyethylene terephthalate (PET), making it highly resistant to deformation under stress in drink bottle applications. PET, while less rigid, offers excellent impact resistance and maintains durability under repeated use and exposure to liquids without significant degradation. The choice between POM and PET depends on specific requirements for stiffness versus impact toughness and chemical resistance in beverage container manufacturing.
Thermal Stability and Temperature Resistance
Polyoxymethylene (POM) offers superior thermal stability and maintains structural integrity at higher temperatures compared to Polyethylene Terephthalate (PET), making it more suitable for applications involving heat exposure. PET, while commonly used for drink bottles due to its clarity and lightweight properties, exhibits lower temperature resistance and can deform or degrade when exposed to temperatures above 70-80degC. The high melting point of POM, around 175degC, enables better performance in hot-filling processes, whereas PET's melting point near 250degC is often compromised by its lower glass transition temperature (~80degC), limiting thermal endurance in elevated temperature scenarios.
Chemical Resistance in Beverage Applications
Polyoxymethylene (POM) offers superior chemical resistance to strong acids and alkalis, making it suitable for beverages with varying pH levels, while Polyethylene Terephthalate (PET) excels in resisting mild acids and alcohols commonly found in soft drinks and juices. PET's excellent barrier properties against gases enhance beverage shelf life, but it is more susceptible to degradation by strong solvents compared to POM. For drink bottles, chemical resistance needs align more with beverage composition, where PET's balance of durability and resistance is widely preferred, though POM may be used in specific applications requiring enhanced solvent resistance.
Manufacturing Processes: Injection Molding and Blow Molding
Polyoxymethylene (POM) offers high stiffness and dimensional stability, making it suitable for precision injection molding in drink bottle components requiring intricate details and tight tolerances. Polyethylene terephthalate (PET) excels in blow molding processes due to its superior stretchability and clarity, enabling the production of lightweight, transparent bottles with excellent gas barrier properties. Manufacturing efficiency hinges on POM's ease of injection molding for rigid parts versus PET's dominance in blow molding for flexible, large-volume drink containers.
Environmental Impact and Recyclability
Polyoxymethylene (POM) offers high strength and chemical resistance but poses challenges in recycling due to limited facilities and its complex polymer structure, leading to environmental concerns when discarded. Polyethylene terephthalate (PET) is widely recycled globally, with established infrastructure that significantly reduces landfill waste and energy consumption; its recyclability promotes a circular economy in drink bottle production. PET's biodegradability and recyclability make it a more environmentally sustainable choice compared to POM for drink bottles.
Cost Efficiency and Market Availability
Polyethylene terephthalate (PET) dominates the drink bottle market due to its superior cost efficiency and widespread availability, making it the preferred choice for mass production. Polyoxymethylene (POM), while offering excellent mechanical strength and chemical resistance, is less cost-effective and less commonly used in beverage containers, limiting its market presence. PET's recyclability and established supply chains further enhance its economic advantage over POM in drink bottle applications.
Conclusion: Best Material Choice for Drink Bottles
Polyethylene terephthalate (PET) is the superior choice for drink bottles due to its excellent clarity, strong barrier properties against moisture and gases, and high impact resistance, ensuring product safety and shelf life. Polyoxymethylene (POM), while offering superior mechanical strength and chemical resistance, lacks the transparency and lightweight nature essential for consumer beverage packaging. PET's recyclability and widespread industry acceptance further solidify it as the optimal material for sustainable and practical drink bottle production.
Infographic: Polyoxymethylene vs Polyethylene terephthalate for Drink bottle
 azmater.com
azmater.com