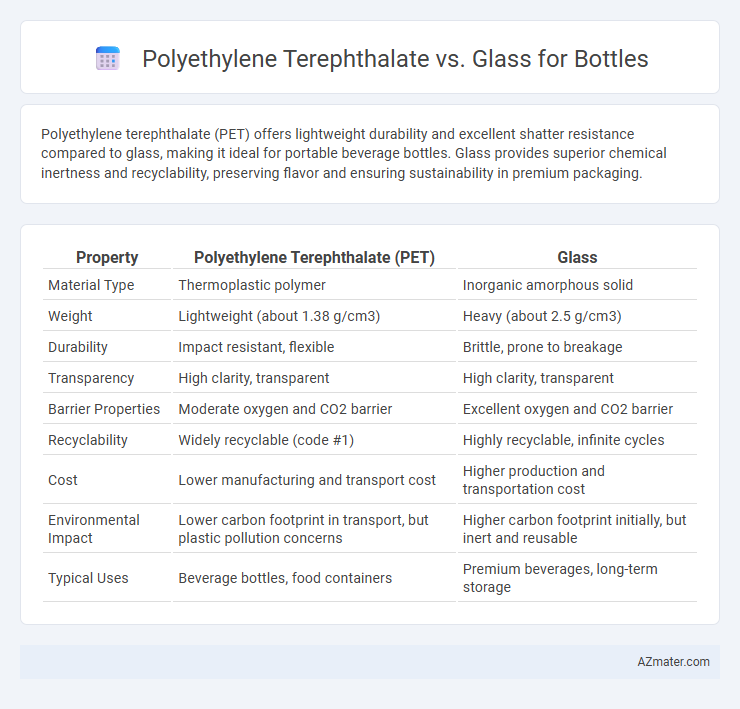
Polyethylene terephthalate (PET) offers lightweight durability and excellent shatter resistance compared to glass, making it ideal for portable beverage bottles. Glass provides superior chemical inertness and recyclability, preserving flavor and ensuring sustainability in premium packaging.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Polyethylene Terephthalate (PET) | Glass |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Thermoplastic polymer | Inorganic amorphous solid |
| Weight | Lightweight (about 1.38 g/cm3) | Heavy (about 2.5 g/cm3) |
| Durability | Impact resistant, flexible | Brittle, prone to breakage |
| Transparency | High clarity, transparent | High clarity, transparent |
| Barrier Properties | Moderate oxygen and CO2 barrier | Excellent oxygen and CO2 barrier |
| Recyclability | Widely recyclable (code #1) | Highly recyclable, infinite cycles |
| Cost | Lower manufacturing and transport cost | Higher production and transportation cost |
| Environmental Impact | Lower carbon footprint in transport, but plastic pollution concerns | Higher carbon footprint initially, but inert and reusable |
| Typical Uses | Beverage bottles, food containers | Premium beverages, long-term storage |
Introduction to Polyethylene Terephthalate (PET) and Glass Bottles
Polyethylene terephthalate (PET) is a lightweight, durable thermoplastic polymer widely used for beverage containers due to its excellent strength-to-weight ratio and recyclability. Glass bottles, made primarily from silica sand, offer superior chemical inertness and impermeability, ensuring no flavor alteration in stored liquids. Both materials serve distinct purposes in packaging, with PET favored for its impact resistance and glass valued for its premium aesthetic and environmental neutrality.
Material Composition and Manufacturing Process
Polyethylene terephthalate (PET) is a lightweight, thermoplastic polymer derived from ethylene glycol and terephthalic acid, produced through a condensation polymerization process that yields high molecular weight chains ideal for blow molding into bottles. Glass bottles, composed primarily of silica sand, soda ash, and limestone, undergo melting at temperatures around 1700degC followed by shaping through blowing or pressing techniques, resulting in an inert, recyclable material with high durability. The manufacturing processes highlight PET's energy-efficient production and recyclability versus glass's higher thermal demands but superior barrier properties and chemical stability.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Polyethylene terephthalate (PET) bottles have a lower carbon footprint during production compared to glass due to less energy-intensive manufacturing processes and lighter weight, which reduces transportation emissions. Glass bottles, while heavier and energy-intensive to produce, are 100% recyclable without quality loss, enabling infinite reuse cycles that enhance sustainability. Both materials present trade-offs: PET contributes to microplastic pollution if not properly recycled, whereas glass demands higher energy consumption but offers superior recyclability and inertness, making resource-efficient recycling and reuse key factors in minimizing environmental impact.
Durability and Strength Comparison
Polyethylene terephthalate (PET) bottles offer high impact resistance and flexibility, making them less prone to shattering compared to glass bottles, which are rigid but brittle. Glass bottles exhibit superior compressive strength and can withstand higher temperatures without deformation, while PET bottles are more susceptible to heat-induced deformation but excel in drop impact durability. The durability of PET makes it ideal for portable and lightweight applications, whereas glass provides long-term strength and chemical inertness in more static environments.
Weight and Transportation Efficiency
Polyethylene terephthalate (PET) bottles weigh significantly less than glass bottles, reducing transportation costs and carbon emissions due to lower fuel consumption. PET's lightweight nature enables more units per shipment, enhancing logistical efficiency and decreasing the overall environmental footprint. Glass bottles, while heavier and more fragile, require more energy for transport, making PET the preferred choice for cost-effective and sustainable distribution.
Health and Safety Considerations
Polyethylene terephthalate (PET) bottles are lightweight, shatter-resistant, and FDA-approved for food contact, reducing injury risks during handling compared to glass. Glass bottles, while chemically inert and impermeable, pose breakage hazards leading to potential cuts and contamination. Health concerns with PET include minimal leaching of antimony and microplastics under prolonged heat exposure, whereas glass remains free from chemical migration but can cause injury from shards if broken.
Cost Analysis: PET vs Glass Bottles
Polyethylene terephthalate (PET) bottles offer significant cost advantages over glass bottles due to lower raw material expenses and reduced transportation costs resulting from lighter weight. Manufacturing PET bottles involves less energy consumption compared to glass, further decreasing production costs. Although glass bottles provide superior reusability and recyclability, the initial higher expenses and fragility increase overall lifecycle costs relative to PET alternatives.
Recyclability and Waste Management
Polyethylene terephthalate (PET) bottles offer high recyclability with established curbside collection systems and a strong market demand for recycled PET (rPET), enabling efficient waste management and closed-loop recycling. Glass bottles, while fully recyclable and infinitely reusable without degradation in quality, face challenges such as higher collection and transportation costs due to weight and breakage risk, which can hinder recycling rates. Effective waste management strategies must consider these factors, promoting PET for lightweight recyclability and glass for sustainable reuse and high-quality recycling.
Applications in the Beverage Industry
Polyethylene terephthalate (PET) bottles dominate the beverage industry due to their lightweight nature, shatter resistance, and excellent barrier properties for carbonated drinks, water, and juices. Glass bottles are preferred for premium beverages like wine, beer, and specialty sodas because of their superior inertness, recyclability, and ability to preserve flavor integrity. The choice between PET and glass depends heavily on factors like cost-efficiency, shelf life, and consumer perception within different beverage market segments.
Consumer Preferences and Market Trends
Polyethylene terephthalate (PET) bottles dominate consumer preferences due to their lightweight, shatter-resistant properties and cost-effectiveness, making them ideal for on-the-go lifestyles. Glass bottles appeal to environmentally conscious consumers by offering recyclability and perceived premium quality, which sustains their niche market presence. Market trends indicate a growing demand for sustainable packaging, driving innovations in biodegradable PET and increased investments in glass recycling systems.
Infographic: Polyethylene terephthalate vs Glass for Bottle
 azmater.com
azmater.com