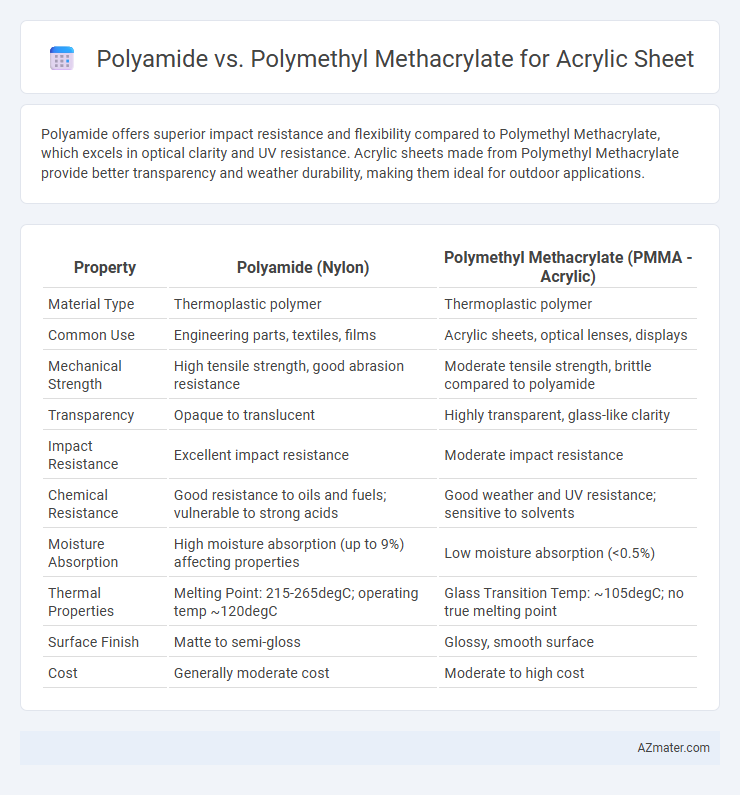
Polyamide offers superior impact resistance and flexibility compared to Polymethyl Methacrylate, which excels in optical clarity and UV resistance. Acrylic sheets made from Polymethyl Methacrylate provide better transparency and weather durability, making them ideal for outdoor applications.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Polyamide (Nylon) | Polymethyl Methacrylate (PMMA - Acrylic) |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Thermoplastic polymer | Thermoplastic polymer |
| Common Use | Engineering parts, textiles, films | Acrylic sheets, optical lenses, displays |
| Mechanical Strength | High tensile strength, good abrasion resistance | Moderate tensile strength, brittle compared to polyamide |
| Transparency | Opaque to translucent | Highly transparent, glass-like clarity |
| Impact Resistance | Excellent impact resistance | Moderate impact resistance |
| Chemical Resistance | Good resistance to oils and fuels; vulnerable to strong acids | Good weather and UV resistance; sensitive to solvents |
| Moisture Absorption | High moisture absorption (up to 9%) affecting properties | Low moisture absorption (<0.5%) |
| Thermal Properties | Melting Point: 215-265degC; operating temp ~120degC | Glass Transition Temp: ~105degC; no true melting point |
| Surface Finish | Matte to semi-gloss | Glossy, smooth surface |
| Cost | Generally moderate cost | Moderate to high cost |
Introduction to Acrylic Sheets
Acrylic sheets are commonly manufactured from materials such as polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA) and polyamide, each offering distinct properties for various applications. Polymethyl methacrylate is prized for its exceptional clarity, UV resistance, and weather durability, making it a preferred choice for transparent and outdoor uses. Polyamide acrylic sheets provide superior impact resistance and flexibility but typically have lower transparency compared to PMMA, influencing their selection based on mechanical demands versus optical performance.
Overview of Polyamide Materials
Polyamide materials, commonly known as nylons, are synthetic polymers characterized by high strength, excellent abrasion resistance, and outstanding chemical stability, making them suitable for demanding applications. Unlike polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA), polyamides offer superior impact resistance and flexibility, which enhances durability in mechanical environments. Their inherent moisture absorption can influence dimensional stability, requiring careful consideration in environments with high humidity or water exposure.
Overview of Polymethyl Methacrylate (PMMA)
Polymethyl Methacrylate (PMMA), a transparent thermoplastic often used as a lightweight and shatter-resistant alternative to glass, is prized for its excellent optical clarity and UV resistance. PMMA sheets exhibit superior weatherability, good chemical resistance, and high surface hardness, making them ideal for applications like signage, glazing, and automotive components. Compared to polyamide, PMMA offers better transparency and rigidity but has lower impact resistance and flexibility.
Mechanical Properties Comparison
Polyamide exhibits superior impact resistance and tensile strength compared to polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA), making it more suitable for applications requiring durability and flexibility. PMMA offers higher stiffness and better scratch resistance, but it is more brittle and prone to cracking under stress. Both materials have distinct mechanical property profiles, with polyamide excelling in toughness and PMMA in rigidity and surface hardness.
Optical Characteristics and Clarity
Polyamide exhibits lower optical clarity and higher light scattering compared to Polymethyl Methacrylate (PMMA), which offers superior transparency and enhanced optical clarity for acrylic sheets. PMMA, commonly known as acrylic glass, transmits up to 92% of visible light with minimal haze, making it ideal for applications demanding excellent clarity and UV resistance. In contrast, polyamide's semi-crystalline structure reduces its transparency, resulting in lower light transmission and its suitability primarily for mechanical rather than optical applications.
Durability and Weather Resistance
Polyamide offers superior impact resistance and flexibility, making it highly durable for applications requiring mechanical strength. Polymethyl Methacrylate (PMMA) acrylic sheets excel in weather resistance with excellent UV stability and clarity retention under prolonged sun exposure. PMMA's resistance to yellowing and surface degradation outperforms polyamide, making it ideal for outdoor use and long-term aesthetics.
Chemical Resistance and Stability
Polyamide exhibits moderate chemical resistance but can degrade when exposed to strong acids and bases, limiting its use in harsh environments for acrylic sheets. Polymethyl Methacrylate (PMMA) offers superior chemical stability and resistance to many solvents, acids, and alkalis, making it more suitable for applications requiring long-term clarity and durability. The enhanced UV resistance and lower moisture absorption of PMMA further contribute to its stability, outperforming polyamide in maintaining physical and optical properties over time.
Processing and Fabrication Differences
Polyamide sheets offer superior flexibility and impact resistance, making them well-suited for applications requiring durability during processing, such as thermoforming and extrusion. Polymethyl Methacrylate (PMMA) acrylic sheets excel in clarity and surface hardness but require careful temperature control during fabrication to avoid cracking or crazing under thermal stress. Unlike polyamide, PMMA is more prone to stress fractures during laser cutting or machining, necessitating slower feed rates and optimized cooling techniques to maintain optical quality.
Cost Analysis and Market Availability
Polyamide sheets generally offer a lower cost compared to Polymethyl Methacrylate (PMMA) acrylic sheets, making them a budget-friendly option for applications requiring durability and flexibility. PMMA acrylic sheets, while more expensive, provide superior optical clarity and UV resistance, justifying their higher price in markets demanding premium aesthetics and weather resistance. Market availability for PMMA acrylic sheets is broader globally due to their widespread use in signage and glazing, whereas polyamide sheets are more niche, often found in industrial and automotive sectors with moderate supply chains.
Best Applications for Polyamide vs PMMA Sheets
Polyamide sheets offer superior impact resistance, chemical stability, and flexibility, making them ideal for industrial applications such as automotive components, mechanical parts, and protective gear. Polymethyl Methacrylate (PMMA) sheets provide excellent optical clarity, UV resistance, and weatherability, which suits them perfectly for signage, display cases, and architectural glazing. Choosing between polyamide and PMMA depends on whether mechanical durability or visual transparency is the primary requirement.
Infographic: Polyamide vs Polymethyl Methacrylate for Acrylic Sheet
 azmater.com
azmater.com