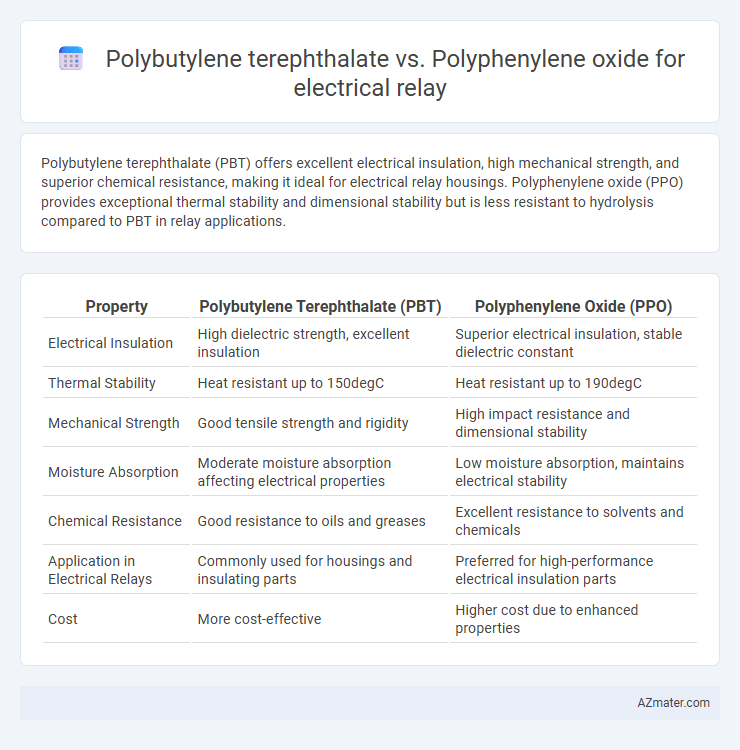
Polybutylene terephthalate (PBT) offers excellent electrical insulation, high mechanical strength, and superior chemical resistance, making it ideal for electrical relay housings. Polyphenylene oxide (PPO) provides exceptional thermal stability and dimensional stability but is less resistant to hydrolysis compared to PBT in relay applications.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Polybutylene Terephthalate (PBT) | Polyphenylene Oxide (PPO) |
|---|---|---|
| Electrical Insulation | High dielectric strength, excellent insulation | Superior electrical insulation, stable dielectric constant |
| Thermal Stability | Heat resistant up to 150degC | Heat resistant up to 190degC |
| Mechanical Strength | Good tensile strength and rigidity | High impact resistance and dimensional stability |
| Moisture Absorption | Moderate moisture absorption affecting electrical properties | Low moisture absorption, maintains electrical stability |
| Chemical Resistance | Good resistance to oils and greases | Excellent resistance to solvents and chemicals |
| Application in Electrical Relays | Commonly used for housings and insulating parts | Preferred for high-performance electrical insulation parts |
| Cost | More cost-effective | Higher cost due to enhanced properties |
Introduction to Electrical Relays: Material Significance
Polybutylene terephthalate (PBT) and Polyphenylene oxide (PPO) are critical thermoplastics for electrical relay components due to their exceptional electrical insulation and thermal stability. PBT offers superior chemical resistance and dimensional stability, making it ideal for relay housings exposed to harsh environments. PPO provides excellent dielectric properties and heat resistance, ensuring reliable performance in high-voltage relay applications.
Overview of Polybutylene Terephthalate (PBT)
Polybutylene terephthalate (PBT) is a thermoplastic polyester known for its excellent electrical insulation properties, high mechanical strength, and resistance to moisture and chemicals, making it ideal for electrical relay components. PBT offers superior dimensional stability and heat resistance up to 150degC, ensuring reliable performance in demanding electrical environments. Compared to polyphenylene oxide (PPO), PBT provides better impact strength and easier processing, contributing to cost-effective manufacturing of durable relays.
Overview of Polyphenylene Oxide (PPO)
Polyphenylene oxide (PPO) is a high-performance thermoplastic known for its excellent electrical insulating properties, dimensional stability, and resistance to heat and moisture, making it ideal for electrical relay components. Its superior dielectric strength and low moisture absorption enhance relay reliability under varying environmental conditions compared to polybutylene terephthalate (PBT). PPO also offers better mechanical toughness and thermal endurance, contributing to longer service life and improved performance in demanding electrical applications.
Mechanical Properties Comparison: PBT vs PPO
Polybutylene terephthalate (PBT) exhibits higher tensile strength and improved impact resistance compared to polyphenylene oxide (PPO), making it more suitable for electrical relay components requiring mechanical durability. PBT also offers superior dimensional stability under thermal stress, ensuring consistent performance in fluctuating electrical environments. Conversely, PPO provides excellent rigidity and heat resistance but with lower impact toughness, often necessitating reinforcement for mechanical-intensive relay applications.
Thermal Resistance in Electrical Relay Applications
Polybutylene terephthalate (PBT) offers excellent thermal resistance with a melting point around 223degC and a continuous service temperature up to 150degC, making it suitable for electrical relay components exposed to moderate heat. Polyphenylene oxide (PPO), with a higher glass transition temperature near 215degC and inherent thermal stability, outperforms PBT in applications requiring prolonged exposure to elevated temperatures without deformation. Thermal resistance directly impacts the longevity and reliability of electrical relays, positioning PPO as a better choice for high-temperature environments, while PBT is preferred for cost-effective solutions with adequate thermal endurance.
Electrical Insulation Capabilities
Polybutylene terephthalate (PBT) offers excellent electrical insulation properties with high dielectric strength and resistance to tracking, making it ideal for electrical relay applications requiring reliable insulation under varying voltage stresses. Polyphenylene oxide (PPO) provides superior dimensional stability and thermal resistance alongside good electrical insulation, but its dielectric properties are generally lower compared to PBT. For electrical relays, PBT tends to outperform PPO in preventing electrical breakdown and ensuring long-term insulation reliability under high-frequency and high-voltage conditions.
Chemical Resistance and Environmental Stability
Polybutylene terephthalate (PBT) exhibits superior chemical resistance to solvents, oils, and acids compared to polyphenylene oxide (PPO), making it highly suitable for electrical relays exposed to harsh chemical environments. PBT also demonstrates better environmental stability with strong resistance to heat and moisture, ensuring consistent performance in varying temperature and humidity conditions. PPO, while offering good dimensional stability and electrical insulation properties, tends to have lower chemical resistance and can degrade faster under prolonged exposure to aggressive chemicals and UV radiation.
Processing and Manufacturability
Polybutylene terephthalate (PBT) offers excellent moldability and shorter cycle times due to its lower melting point of approximately 223degC, making it ideal for high-volume electrical relay components. Polyphenylene oxide (PPO), with a higher glass transition temperature around 210degC and no true melting point, requires specialized processing techniques like extrusion or injection molding at elevated temperatures, resulting in longer cycle times and potential need for drying. The superior dimensional stability and electrical insulation properties of PPO come with increased complexity in manufacturability compared to the more easily processed and cost-effective PBT for relay housings.
Cost Considerations: PBT vs PPO
Polybutylene terephthalate (PBT) typically offers a lower material cost compared to polyphenylene oxide (PPO), making it a more economical choice for electrical relay housings. PBT's cost advantage is attributed to its widespread availability and simpler processing requirements, which reduce manufacturing expenses. While PPO provides superior thermal stability and dimensional stability, its higher price may impact overall production budgets in volume applications where cost-sensitive solutions are prioritized.
Application Suitability and Final Recommendations
Polybutylene terephthalate (PBT) offers excellent electrical insulation properties, high impact resistance, and superior dimensional stability, making it highly suitable for electrical relay housings and components requiring long-term durability under thermal and mechanical stress. Polyphenylene oxide (PPO) provides outstanding thermal stability, excellent dielectric properties, and superior resistance to thermal aging, ideal for relay parts exposed to higher operating temperatures and demanding electrical environments. For electrical relays, PBT is recommended for general applications requiring toughness and electrical insulation, while PPO is preferred for high-temperature, high-performance scenarios where enhanced thermal and dielectric stability are critical.
Infographic: Polybutylene terephthalate vs Polyphenylene oxide for Electrical relay
 azmater.com
azmater.com