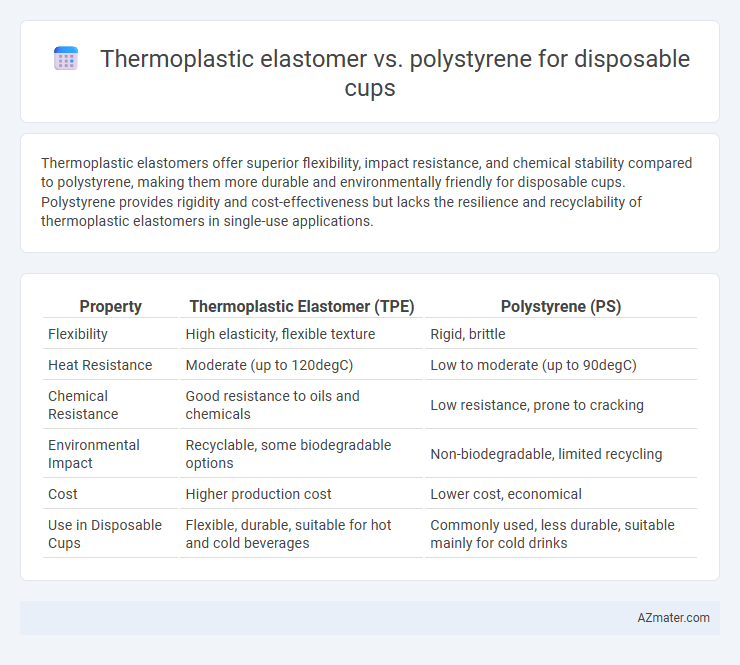
Thermoplastic elastomers offer superior flexibility, impact resistance, and chemical stability compared to polystyrene, making them more durable and environmentally friendly for disposable cups. Polystyrene provides rigidity and cost-effectiveness but lacks the resilience and recyclability of thermoplastic elastomers in single-use applications.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Thermoplastic Elastomer (TPE) | Polystyrene (PS) |
|---|---|---|
| Flexibility | High elasticity, flexible texture | Rigid, brittle |
| Heat Resistance | Moderate (up to 120degC) | Low to moderate (up to 90degC) |
| Chemical Resistance | Good resistance to oils and chemicals | Low resistance, prone to cracking |
| Environmental Impact | Recyclable, some biodegradable options | Non-biodegradable, limited recycling |
| Cost | Higher production cost | Lower cost, economical |
| Use in Disposable Cups | Flexible, durable, suitable for hot and cold beverages | Commonly used, less durable, suitable mainly for cold drinks |
Introduction: Comparing Thermoplastic Elastomers and Polystyrene
Thermoplastic elastomers (TPEs) offer flexibility and durability, making them suitable for disposable cups requiring resistance to heat and deformation. Polystyrene, a rigid and lightweight polymer, provides excellent insulation but tends to be brittle under stress and less environmentally friendly. Evaluating these materials highlights TPEs' elasticity and reusability against polystyrene's cost-effectiveness and ease of molding in disposable cup manufacturing.
Material Composition and Properties
Thermoplastic elastomers (TPE) are composed of a blend of polymers that combine the elastic properties of rubber with the processing advantages of plastics, offering superior flexibility, softness, and impact resistance ideal for disposable cups requiring durability. Polystyrene (PS) is a rigid, brittle thermoplastic derived from styrene monomers, known for its clarity, ease of molding, and lower cost but limited in flexibility and resistance to heat or impact. Material properties such as TPE's higher elongation at break and better thermal stability contrast with polystyrene's stiffness and lower thermal resistance, influencing their suitability for disposable cup applications based on desired user experience and thermal performance.
Manufacturing Process Differences
Thermoplastic elastomer (TPE) for disposable cups undergoes a flexible molding process, allowing for easy reheating and reshaping without significant degradation, which enhances recyclability and production efficiency. Polystyrene (PS) manufacturing utilizes injection molding or thermoforming, requiring precise temperature control to maintain rigidity and clarity but often generates more waste due to brittleness and limited recyclability. The TPE process supports faster cycle times and reduced material waste compared to the more energy-intensive and brittle-dependent PS molding techniques.
Thermal Performance and Hot Liquid Resistance
Thermoplastic elastomers (TPE) offer superior thermal performance and hot liquid resistance compared to polystyrene (PS) in disposable cups, as TPE materials maintain structural integrity at higher temperatures without deformation. While polystyrene tends to soften and lose rigidity when exposed to hot liquids above 70degC, TPE-based cups withstand temperatures exceeding 100degC, reducing the risk of leaks and spills. The enhanced heat resistance and flexibility of thermoplastic elastomers make them more suitable for hot beverage applications, ensuring safety and durability during use.
Durability and Flexibility Comparison
Thermoplastic elastomers (TPE) offer superior flexibility and impact resistance for disposable cups compared to polystyrene (PS), which tends to be more rigid and brittle. TPE's elasticity allows it to withstand bending and compression without cracking, enhancing cup durability during handling and transport. Polystyrene, while cost-effective and lightweight, often exhibits lower resistance to stress and can easily crack under pressure, reducing its overall lifespan in practical use.
Environmental Impact and Recyclability
Thermoplastic elastomers (TPE) offer superior environmental benefits compared to polystyrene (PS) for disposable cups due to their recyclability and reduced ecological footprint. TPEs can be reprocessed multiple times without significant degradation, promoting circular economy practices, whereas polystyrene often ends up in landfills or as marine debris, taking hundreds of years to degrade and releasing harmful styrene monomers. The lower carbon footprint and enhanced recyclability of thermoplastic elastomers make them a more sustainable choice for single-use beverage containers.
Cost Effectiveness for Mass Production
Thermoplastic elastomers (TPE) offer reusable flexibility and impact resistance but are generally more expensive than polystyrene (PS), which is favored for disposable cups due to its low cost and efficient mass production capabilities. Polystyrene's ease of molding and rapid cooling times reduce manufacturing expenses, making it highly cost-effective for large-scale disposable cup production. While TPE provides superior durability, polystyrene dominates in affordability and scalability for single-use applications.
Consumer Safety and Chemical Leaching
Thermoplastic elastomers (TPE) offer superior consumer safety in disposable cups due to their low chemical leaching properties and resistance to harmful additives compared to polystyrene, which can release styrene monomers linked to potential health risks. TPE materials minimize exposure to endocrine disruptors and carcinogens, making them a safer choice for hot and cold beverages. Polystyrene's brittleness and propensity to degrade under heat increase the likelihood of toxic substances migrating into liquids, raising concerns over long-term consumer health.
Market Availability and Customization Options
Thermoplastic elastomers (TPE) offer superior flexibility and durability for disposable cups, with wide market availability due to their growing use in eco-friendly packaging. Polystyrene (PS), commonly found in disposable cups, remains widely accessible but faces increasing regulatory restrictions impacting supply longevity. Customization options for TPE include enhanced elasticity, varied textures, and color integrations, while polystyrene cups primarily offer limited color and print variations.
Final Verdict: Best Choice for Disposable Cups
Thermoplastic elastomers (TPE) offer superior flexibility, heat resistance, and recyclability compared to polystyrene, making them a more sustainable choice for disposable cups. Polystyrene, while cost-effective and rigid, tends to crack under heat and poses greater environmental concerns due to poor biodegradability. For disposable cups, TPE stands out as the best choice, balancing durability with eco-friendly properties.
Infographic: Thermoplastic elastomer vs Polystyrene for Disposable cup
 azmater.com
azmater.com