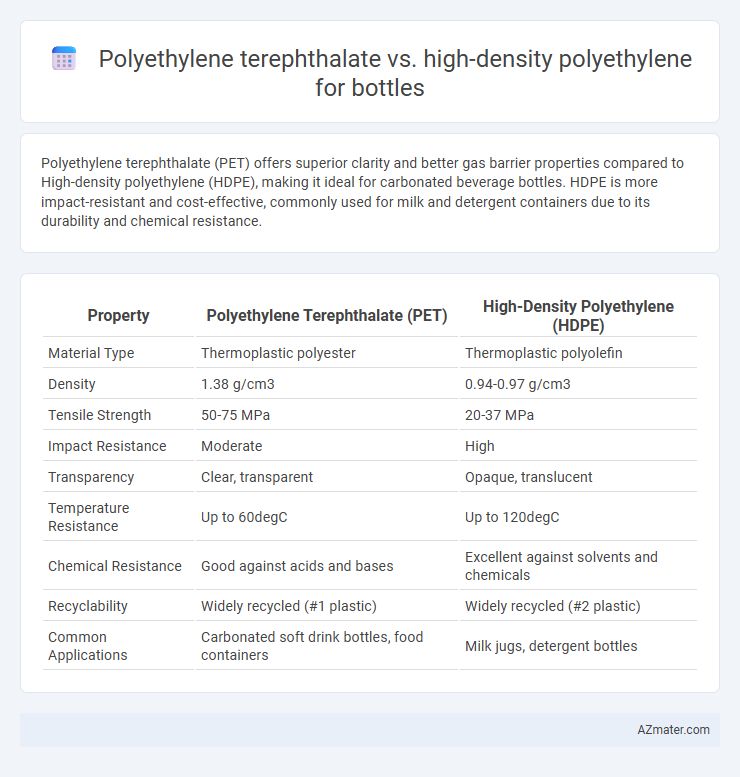
Polyethylene terephthalate (PET) offers superior clarity and better gas barrier properties compared to High-density polyethylene (HDPE), making it ideal for carbonated beverage bottles. HDPE is more impact-resistant and cost-effective, commonly used for milk and detergent containers due to its durability and chemical resistance.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Polyethylene Terephthalate (PET) | High-Density Polyethylene (HDPE) |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Thermoplastic polyester | Thermoplastic polyolefin |
| Density | 1.38 g/cm3 | 0.94-0.97 g/cm3 |
| Tensile Strength | 50-75 MPa | 20-37 MPa |
| Impact Resistance | Moderate | High |
| Transparency | Clear, transparent | Opaque, translucent |
| Temperature Resistance | Up to 60degC | Up to 120degC |
| Chemical Resistance | Good against acids and bases | Excellent against solvents and chemicals |
| Recyclability | Widely recycled (#1 plastic) | Widely recycled (#2 plastic) |
| Common Applications | Carbonated soft drink bottles, food containers | Milk jugs, detergent bottles |
Introduction to Polyethylene Terephthalate (PET) and High-Density Polyethylene (HDPE)
Polyethylene terephthalate (PET) is a lightweight, strong, and transparent thermoplastic polymer widely used for beverage bottles due to its excellent gas barrier properties and recyclability. High-density polyethylene (HDPE) is a durable, opaque thermoplastic known for its high strength-to-density ratio and resistance to impact and chemicals, making it ideal for milk jugs and detergent bottles. Both polymers serve critical roles in packaging, with PET favored for clarity and carbonated drinks, while HDPE excels in durability and chemical resistance.
Chemical Structure and Composition Comparison
Polyethylene terephthalate (PET) features a polyester structure composed of repeating units of terephthalic acid and ethylene glycol, resulting in a rigid, transparent material ideal for bottles requiring clarity and strength. High-density polyethylene (HDPE) consists of long chains of ethylene monomers with minimal branching, creating a highly crystalline, opaque, and flexible polymer well-suited for durable, impact-resistant containers. The aromatic rings in PET's backbone contribute to its higher temperature resistance and barrier properties compared to the saturated hydrocarbon chain structure of HDPE.
Mechanical Strength and Durability
Polyethylene terephthalate (PET) offers superior mechanical strength and rigidity compared to high-density polyethylene (HDPE), making it ideal for bottles requiring high impact resistance and clarity. PET's tensile strength typically ranges from 50 to 100 MPa, while HDPE's tensile strength is around 20 to 37 MPa, reflecting PET's enhanced load-bearing capabilities. In terms of durability, PET exhibits better resistance to environmental stress cracking and chemical degradation, ensuring longer shelf life and maintaining bottle integrity under varying conditions.
Barrier Properties: Gas and Moisture Resistance
Polyethylene terephthalate (PET) exhibits superior gas barrier properties compared to high-density polyethylene (HDPE), making it highly effective in preserving carbonation and preventing oxygen ingress in bottles. PET also offers enhanced moisture resistance, maintaining product integrity and extending shelf life, whereas HDPE tends to be more permeable to gases and water vapor. These attributes make PET the preferred material for beverages requiring longer preservation with minimal flavor and aroma loss.
Transparency and Visual Appeal
Polyethylene terephthalate (PET) offers superior transparency and clarity compared to high-density polyethylene (HDPE), making it the preferred choice for bottles requiring high visual appeal and product visibility. PET bottles exhibit a glass-like appearance that enhances the presentation of beverages and cosmetics, while HDPE bottles are typically opaque or translucent with a matte finish, limiting their usage where clear visibility is critical. The enhanced optical properties of PET improve consumer perception and product attractiveness on retail shelves.
Common Applications in Bottle Manufacturing
Polyethylene terephthalate (PET) is widely used in beverage bottles due to its excellent clarity, strength, and gas barrier properties, making it ideal for carbonated drinks and water containers. High-density polyethylene (HDPE) is favored for milk jugs, detergent bottles, and opaque containers because of its superior chemical resistance, impact strength, and flexibility. Both materials dominate bottle manufacturing with PET preferred for transparent packaging and HDPE for durable, opaque applications.
Environmental Impact and Recyclability
Polyethylene terephthalate (PET) bottles offer superior recyclability due to their well-established recycling infrastructure, yielding high-quality recycled material ideal for beverage containers. High-density polyethylene (HDPE) bottles also provide strong recyclability with lower energy consumption during production, but recycled HDPE is often downcycled into lower-grade products, limiting circularity. PET's clarity and barrier properties support widespread reuse and recycling in the bottled beverage industry, while HDPE's chemical resistance and durability favor applications where recyclability is secondary to environmental persistence and product lifespan.
Safety and Food Contact Regulations
Polyethylene terephthalate (PET) is widely approved for food contact by regulatory agencies like the FDA and EFSA due to its excellent chemical resistance and low migration risk, making it safe for bottled beverages. High-density polyethylene (HDPE) also meets food safety standards and is favored for its robustness and resistance to contamination but may allow higher oxygen permeability compared to PET, potentially affecting shelf life. Both materials comply with global food contact regulations, but PET is generally preferred for transparent, single-use bottles, while HDPE is common in opaque, reusable packaging.
Cost-Effectiveness and Market Availability
Polyethylene terephthalate (PET) offers superior clarity and strength, making it ideal for beverage bottles but typically comes at a higher cost compared to high-density polyethylene (HDPE). HDPE provides enhanced chemical resistance and lower production expenses, resulting in greater cost-effectiveness for bulk packaging and household products. Market availability favors PET in the beverage sector due to strong recycling infrastructures, while HDPE dominates in non-beverage containers because of its wide application and lower manufacturing costs.
Choosing the Right Material: PET vs. HDPE for Bottles
Polyethylene terephthalate (PET) offers superior clarity, impact resistance, and gas barrier properties, making it ideal for carbonated beverage bottles and packaging requiring high transparency. High-density polyethylene (HDPE) provides excellent chemical resistance, durability, and is more cost-effective, often preferred for milk jugs, detergent containers, and opaque bottles. Selecting PET or HDPE depends on the bottle's functional requirements, such as visibility, shelf-life, and recyclability goals.
Infographic: Polyethylene terephthalate vs High-density polyethylene for Bottle
 azmater.com
azmater.com