Polyethylene terephthalate (PET) foam offers superior durability, chemical resistance, and recyclability compared to polyurethane foam, which excels in softness and flexibility but has lower environmental sustainability. PET foam is ideal for long-lasting, eco-friendly cushioning, while polyurethane foam suits applications requiring enhanced comfort and shock absorption.
Table of Comparison
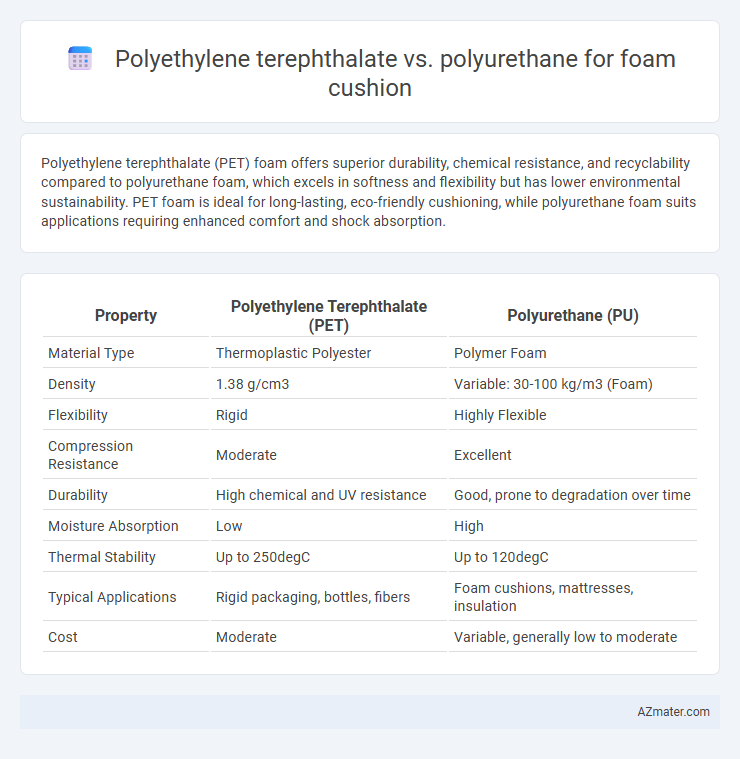
| Property | Polyethylene Terephthalate (PET) | Polyurethane (PU) |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Thermoplastic Polyester | Polymer Foam |
| Density | 1.38 g/cm3 | Variable: 30-100 kg/m3 (Foam) |
| Flexibility | Rigid | Highly Flexible |
| Compression Resistance | Moderate | Excellent |
| Durability | High chemical and UV resistance | Good, prone to degradation over time |
| Moisture Absorption | Low | High |
| Thermal Stability | Up to 250degC | Up to 120degC |
| Typical Applications | Rigid packaging, bottles, fibers | Foam cushions, mattresses, insulation |
| Cost | Moderate | Variable, generally low to moderate |
Overview of Polyethylene Terephthalate (PET) and Polyurethane
Polyethylene terephthalate (PET) is a thermoplastic polymer known for its excellent chemical resistance, durability, and recyclability, commonly used in foam cushions for its lightweight and moisture-wicking properties. Polyurethane foam offers exceptional flexibility, resilience, and superior cushioning support, making it ideal for applications requiring high comfort and impact absorption. Comparing both, PET foam provides a more sustainable and breathable option, whereas polyurethane foam excels in comfort and durability in high-performance cushioning.
Chemical Composition and Structure Comparison
Polyethylene terephthalate (PET) foam is a thermoplastic polymer composed of repeating units of ethylene terephthalate, characterized by its semi-crystalline structure that provides durability and resistance to chemicals and environmental factors. In contrast, polyurethane (PU) foam consists of polymer chains formed through the reaction of polyols and diisocyanates, resulting in a highly flexible and open-cell structure that offers superior cushioning and shock absorption. The chemical composition of PET yields a rigid, water-resistant foam ideal for structural applications, whereas PU's versatile urethane linkages create soft, elastic foam suitable for comfort and impact protection.
Manufacturing Process of PET and Polyurethane Foams
Polyethylene terephthalate (PET) foam is produced through a thermoforming process that involves melting and stretching PET sheets or granules, followed by controlled cooling to create a rigid, lightweight foam structure with high dimensional stability. In contrast, Polyurethane foam manufacturing relies on a chemical reaction between polyols and diisocyanates, which generates a flexible or rigid foam through a foaming process involving gas expansion and curing within molds or continuous conveyors. PET foam offers superior environmental resistance and recyclability due to its polyester base, while polyurethane foams provide greater versatility in density and compression properties, attributed to their polymer formation during manufacturing.
Cushioning Performance and Comfort
Polyurethane foam offers superior cushioning performance with its high resilience and excellent energy absorption, making it ideal for comfort in foam cushions. Polyethylene terephthalate (PET) foams, while durable and resistant to moisture, generally provide firmer support with less bounce and conformability compared to polyurethane. The choice between PET and polyurethane foam cushions depends on desired comfort levels, with polyurethane preferred for enhanced softness and polyethylene terephthalate favored for structural support and longevity.
Durability and Longevity in Foam Cushions
Polyurethane foam cushions offer superior durability due to their high resistance to compression and deformation over time, making them ideal for long-term use. Polyethylene terephthalate (PET) foam cushions provide excellent moisture resistance and dimensional stability, though they may not maintain their shape as effectively under continuous heavy use. When prioritizing longevity in foam cushions, polyurethane typically outperforms PET by retaining cushioning properties and structural integrity for extended periods.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Polyethylene terephthalate (PET) foam cushions offer significant environmental benefits due to their recyclability and lower carbon footprint compared to polyurethane foam, which is derived from non-renewable petroleum sources and difficult to recycle. PET foam is often produced from recycled plastic bottles, contributing to waste reduction and promoting circular economy principles, whereas polyurethane foam generates toxic emissions during production and disposal. Choosing PET foam cushions supports sustainability goals by minimizing landfill waste and reducing greenhouse gas emissions associated with foam manufacturing and end-of-life processing.
Cost Analysis: PET vs Polyurethane Foams
Polyethylene terephthalate (PET) foam generally offers a more cost-effective solution compared to polyurethane foam due to its lower raw material and manufacturing expenses. PET foam provides durability and recyclability, which can lead to long-term savings despite a slightly higher initial investment. Polyurethane foam, while often cheaper upfront, may incur higher costs through shorter lifespan and environmental disposal fees.
Application Suitability for Furniture and Automotive Industry
Polyethylene terephthalate (PET) foam offers superior chemical resistance, dimensional stability, and recyclability, making it ideal for furniture cushions requiring durability and eco-friendly materials. Polyurethane foam provides exceptional elasticity, comfort, and shock absorption, which suits automotive seating and interior components demanding high resilience and ergonomic support. Selection depends on application needs: PET for sustainable, firm cushioning in furniture, and polyurethane for flexible, high-impact comfort in automotive interiors.
Health and Safety Considerations
Polyethylene terephthalate (PET) foam cushions offer low toxicity and excellent resistance to mold and bacteria, making them a safer choice for indoor air quality compared to polyurethane (PU) foams, which may emit volatile organic compounds (VOCs) such as isocyanates during manufacturing and off-gassing. PU foam's chemical composition can pose respiratory risks and skin irritation for sensitive individuals, whereas PET foam is often made from recycled materials and is inherently hypoallergenic and more fire-resistant. Choosing PET foam cushions enhances health safety by reducing exposure to harmful chemicals and supporting eco-friendly, sustainable product use.
Future Trends in Foam Cushion Materials
Future trends in foam cushion materials highlight a growing preference for polyurethane due to its superior elasticity, durability, and customizable density suited for diverse applications. Innovations in bio-based polyurethane foams are advancing sustainability, positioning them as eco-friendly alternatives to traditional petroleum-based polyethylene terephthalate (PET) foams. Enhanced recycling technologies for PET foams persist, but the market shift favors polyurethane's adaptability and performance in next-generation cushioning solutions.
Infographic: Polyethylene terephthalate vs Polyurethane for Foam Cushion
 azmater.com
azmater.com