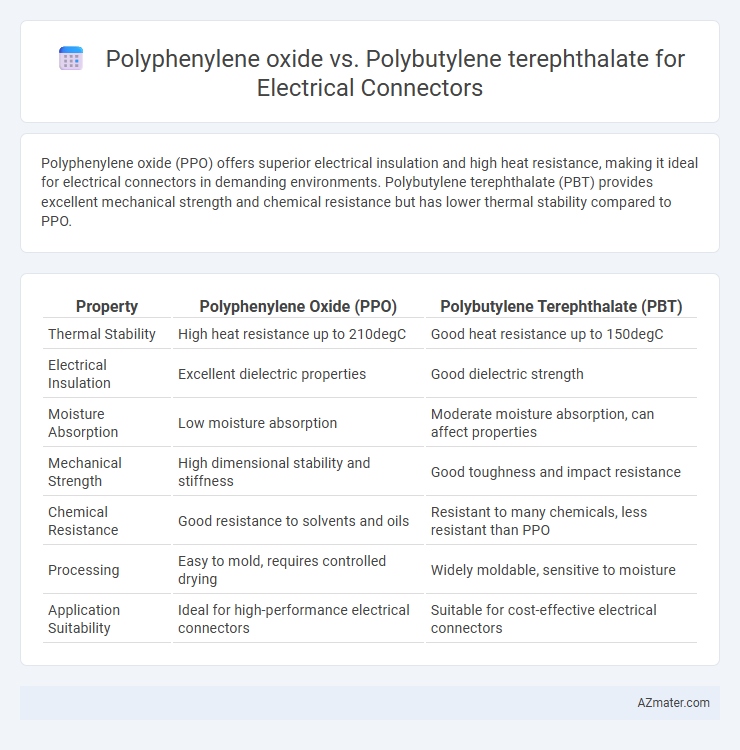
Polyphenylene oxide (PPO) offers superior electrical insulation and high heat resistance, making it ideal for electrical connectors in demanding environments. Polybutylene terephthalate (PBT) provides excellent mechanical strength and chemical resistance but has lower thermal stability compared to PPO.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Polyphenylene Oxide (PPO) | Polybutylene Terephthalate (PBT) |
|---|---|---|
| Thermal Stability | High heat resistance up to 210degC | Good heat resistance up to 150degC |
| Electrical Insulation | Excellent dielectric properties | Good dielectric strength |
| Moisture Absorption | Low moisture absorption | Moderate moisture absorption, can affect properties |
| Mechanical Strength | High dimensional stability and stiffness | Good toughness and impact resistance |
| Chemical Resistance | Good resistance to solvents and oils | Resistant to many chemicals, less resistant than PPO |
| Processing | Easy to mold, requires controlled drying | Widely moldable, sensitive to moisture |
| Application Suitability | Ideal for high-performance electrical connectors | Suitable for cost-effective electrical connectors |
Introduction to PPO and PBT in Electrical Connectors
Polyphenylene oxide (PPO) offers excellent electrical insulation, high heat resistance, and dimensional stability, making it ideal for electrical connector housings in demanding applications. Polybutylene terephthalate (PBT) provides superior chemical resistance, mechanical strength, and low moisture absorption, which enhances the durability and reliability of connectors in harsh environments. Both materials play crucial roles in electrical connectors, with PPO favored for thermal and electrical performance, while PBT is chosen for structural integrity and resistance to environmental stress.
Chemical Structure Comparison: PPO vs PBT
Polyphenylene oxide (PPO) features an aromatic backbone with ether linkages, providing high thermal stability and excellent electrical insulation properties critical for electrical connectors. Polybutylene terephthalate (PBT) consists of a semi-crystalline polyester structure with ester functional groups, offering superior chemical resistance and mechanical strength. The ether linkages in PPO contribute to greater dimensional stability and resistance to moisture absorption, whereas PBT's polyester chains deliver enhanced toughness and ease of processing in connector applications.
Mechanical Properties: Strength and Flexibility
Polyphenylene oxide (PPO) exhibits high tensile strength and excellent dimensional stability, making it ideal for electrical connectors requiring durability under mechanical stress. Polybutylene terephthalate (PBT) offers superior flexibility and impact resistance, enabling connectors to withstand repeated mechanical deformation without cracking. Selecting between PPO and PBT depends on the specific balance of rigidity and flexibility needed for optimal connector performance.
Thermal Stability and Heat Resistance
Polyphenylene oxide (PPO) exhibits superior thermal stability with a continuous use temperature around 150-170degC, making it highly suitable for electrical connectors exposed to elevated heat. Polybutylene terephthalate (PBT) offers good heat resistance but generally withstands continuous exposure up to 120-140degC, which is lower than PPO. The higher glass transition temperature and inherent flame retardancy of PPO enhance its performance in demanding electrical connector applications requiring robust thermal management.
Electrical Insulation Performance
Polyphenylene oxide (PPO) offers superior electrical insulation performance compared to Polybutylene terephthalate (PBT) due to its higher dielectric strength and lower dissipation factor, making it ideal for high-frequency electrical connector applications. PPO's excellent thermal stability also ensures consistent insulation properties under elevated temperatures, reducing the risk of electrical failure. In contrast, PBT, while mechanically robust, exhibits higher moisture absorption that can degrade its electrical insulation effectiveness over time.
Moisture Absorption and Dimensional Stability
Polyphenylene oxide (PPO) exhibits significantly lower moisture absorption compared to Polybutylene terephthalate (PBT), making it more suitable for electrical connectors exposed to high humidity or wet environments. PPO maintains superior dimensional stability due to its amorphous structure and low water uptake, which minimizes swelling and deformation under moisture exposure. In contrast, PBT's higher moisture absorption often leads to dimensional changes and reduced mechanical performance in humid conditions, potentially compromising connector reliability.
Processability: Molding and Manufacturing
Polyphenylene oxide (PPO) offers superior dimensional stability and excellent electrical insulation, making it highly suitable for complex electrical connector molds that demand precision and heat resistance. Polybutylene terephthalate (PBT) provides easier flow characteristics during injection molding, allowing faster cycle times and improved manufacturability for high-volume production runs. The choice between PPO and PBT hinges on balancing PPO's superior thermal and dielectric performance with PBT's enhanced moldability and cost-effective manufacturing throughput.
Flame Retardancy and Safety
Polyphenylene oxide (PPO) offers superior flame retardancy compared to polybutylene terephthalate (PBT), making it a preferred choice for electrical connectors requiring high safety standards. PPO's inherent thermal stability and self-extinguishing properties reduce the risk of fire hazards in electrical applications. PBT, while also flame retardant, typically requires additional additives to meet stringent safety certifications, which can affect its mechanical and electrical performance.
Cost Considerations and Economic Impact
Polyphenylene oxide (PPO) offers moderate material costs with excellent thermal stability and dimensional stability, making it suitable for high-performance electrical connectors. Polybutylene terephthalate (PBT) tends to be more cost-effective due to lower raw material prices and easier processing, which can reduce manufacturing expenses and improve economic efficiency in large-scale production. When evaluating cost considerations, PBT provides a better balance of affordability and durability, while PPO may increase upfront expenses but enhance long-term reliability, influencing the overall economic impact based on application requirements.
Application Suitability: Selecting the Right Material
Polyphenylene oxide (PPO) provides excellent electrical insulation and high thermal stability, making it ideal for high-performance electrical connectors operating in elevated temperature environments. Polybutylene terephthalate (PBT) offers superior mechanical strength, chemical resistance, and dimensional stability, which suits connectors exposed to mechanical stress and harsh chemicals. Selecting between PPO and PBT depends on application-specific requirements such as thermal endurance, electrical insulation, and environmental exposure to optimize connector reliability and performance.
Infographic: Polyphenylene oxide vs Polybutylene terephthalate for Electrical Connector
 azmater.com
azmater.com