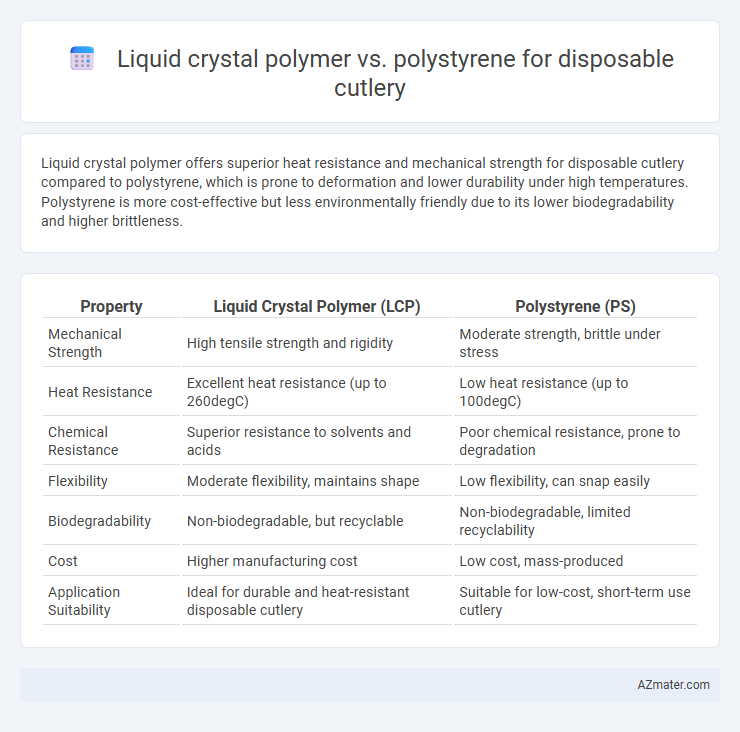
Liquid crystal polymer offers superior heat resistance and mechanical strength for disposable cutlery compared to polystyrene, which is prone to deformation and lower durability under high temperatures. Polystyrene is more cost-effective but less environmentally friendly due to its lower biodegradability and higher brittleness.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Liquid Crystal Polymer (LCP) | Polystyrene (PS) |
|---|---|---|
| Mechanical Strength | High tensile strength and rigidity | Moderate strength, brittle under stress |
| Heat Resistance | Excellent heat resistance (up to 260degC) | Low heat resistance (up to 100degC) |
| Chemical Resistance | Superior resistance to solvents and acids | Poor chemical resistance, prone to degradation |
| Flexibility | Moderate flexibility, maintains shape | Low flexibility, can snap easily |
| Biodegradability | Non-biodegradable, but recyclable | Non-biodegradable, limited recyclability |
| Cost | Higher manufacturing cost | Low cost, mass-produced |
| Application Suitability | Ideal for durable and heat-resistant disposable cutlery | Suitable for low-cost, short-term use cutlery |
Introduction to Disposable Cutlery Materials
Liquid crystal polymer (LCP) offers superior mechanical strength, heat resistance, and chemical stability compared to polystyrene (PS), making it ideal for high-performance disposable cutlery. Polystyrene, widely used for its low cost and ease of molding, lacks durability and heat tolerance, often leading to breakage and deformation with hot foods. Choosing LCP over PS enhances product longevity, safety, and premium user experience in disposable cutlery applications.
Overview of Liquid Crystal Polymer (LCP)
Liquid Crystal Polymer (LCP) is a high-performance thermoplastic known for its exceptional strength, heat resistance, and chemical stability, making it ideal for durable disposable cutlery. Its unique molecular structure provides superior dimensional stability and flexibility compared to Polystyrene, which tends to be more brittle and less heat-resistant. LCP's ability to withstand high temperatures without warping or melting ensures safer use with hot foods and liquids in disposable utensils.
Overview of Polystyrene (PS)
Polystyrene (PS) is a widely used thermoplastic polymer known for its rigidity, clarity, and cost-effectiveness, making it a common choice in disposable cutlery production. Its low melting point allows for easy molding into various shapes, but it is prone to brittleness and has limited heat resistance compared to liquid crystal polymers (LCP). PS offers excellent insulation properties but is less durable and less chemically resistant than LCP, which impacts its suitability for heavy-duty or heat-exposed applications.
Mechanical Strength Comparison
Liquid crystal polymer (LCP) exhibits significantly higher mechanical strength and heat resistance compared to polystyrene, making it ideal for disposable cutlery requiring durability under stress. LCP's tensile strength ranges between 200-300 MPa, whereas polystyrene typically measures around 40-60 MPa, reflecting LCP's superior stiffness and impact resistance. The enhanced mechanical properties of LCP ensure better performance in hot and heavy-use scenarios, reducing breakage and deformation during use.
Thermal Resistance and Performance
Liquid crystal polymer (LCP) exhibits superior thermal resistance compared to polystyrene, withstanding temperatures up to 300degC without deformation, making it ideal for disposable cutlery exposed to hot foods and liquids. Polystyrene, while cost-effective and lightweight, typically melts around 100degC, limiting its use to cold or room-temperature applications. The high-performance characteristics of LCP, including excellent dimensional stability and durability at elevated temperatures, significantly enhance the functionality and safety of disposable cutlery.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Liquid crystal polymer (LCP) offers superior recyclability and biodegradability compared to polystyrene, significantly reducing environmental footprints associated with disposable cutlery. Polystyrene, predominantly non-biodegradable and challenging to recycle, contributes heavily to landfill waste and marine pollution, raising sustainability concerns. Choosing LCP-based cutlery enhances circular economy initiatives by promoting resource efficiency and lowering ecological impacts in single-use plastic alternatives.
Food Safety and Chemical Resistance
Liquid crystal polymer (LCP) exhibits superior food safety properties compared to polystyrene (PS) due to its high chemical stability and resistance to leaching harmful substances under heat exposure. LCP's exceptional chemical resistance prevents interaction with acidic and oily foods, ensuring no transfer of contaminants, whereas polystyrene is prone to degradation and migration of styrene monomers when in contact with hot or fatty foods. The enhanced thermal stability of LCP also reduces the risk of toxic compound release, making it a safer material choice for disposable cutlery in diverse food service applications.
Cost Analysis and Manufacturing Efficiency
Liquid crystal polymer (LCP) offers superior mechanical strength and thermal stability compared to polystyrene (PS), but comes with higher raw material costs, impacting overall production expenses for disposable cutlery. Polystyrene remains cost-effective due to its low material price and established manufacturing processes like injection molding, which enable faster cycle times and higher throughput. While LCP can reduce waste and improve product durability, its processing complexity may increase energy consumption and equipment wear, potentially offsetting benefits in manufacturing efficiency.
User Experience: Comfort and Aesthetics
Liquid crystal polymer (LCP) offers superior rigidity and smooth surface finish, enhancing comfort and a premium feel in disposable cutlery compared to polystyrene (PS), which often feels brittle and less ergonomic. The inherent high gloss and consistent texture of LCP improve aesthetic appeal, making utensils appear more upscale and visually pleasing. Polystyrene cutlery may suffer from surface imperfections and a lower-quality appearance, negatively impacting the overall user experience in terms of both comfort and style.
Future Trends in Disposable Cutlery Materials
Liquid crystal polymer (LCP) offers exceptional heat resistance and mechanical strength, making it a promising material for durable disposable cutlery, compared to polystyrene (PS), which is more commonly used but less environmentally sustainable. Future trends indicate a significant shift towards biodegradable and high-performance polymers like LCP, driven by increasing regulatory pressure and consumer demand for eco-friendly alternatives. Innovations in LCP composites aim to balance functionality with sustainability, positioning it as a key contender in next-generation disposable cutlery materials.
Infographic: Liquid crystal polymer vs Polystyrene for Disposable Cutlery
 azmater.com
azmater.com