Polyphenylene oxide offers superior thermal resistance and chemical stability compared to Polyvinyl chloride, making it ideal for high-temperature pipe applications. Polyvinyl chloride pipes provide cost-effective durability and corrosion resistance, suitable for standard plumbing and drainage systems.
Table of Comparison
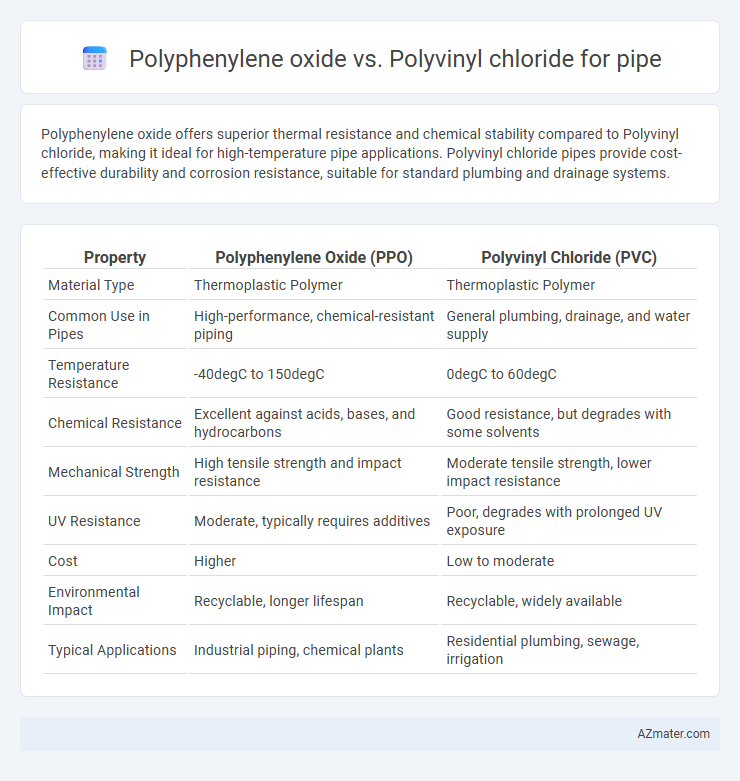
| Property | Polyphenylene Oxide (PPO) | Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC) |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Thermoplastic Polymer | Thermoplastic Polymer |
| Common Use in Pipes | High-performance, chemical-resistant piping | General plumbing, drainage, and water supply |
| Temperature Resistance | -40degC to 150degC | 0degC to 60degC |
| Chemical Resistance | Excellent against acids, bases, and hydrocarbons | Good resistance, but degrades with some solvents |
| Mechanical Strength | High tensile strength and impact resistance | Moderate tensile strength, lower impact resistance |
| UV Resistance | Moderate, typically requires additives | Poor, degrades with prolonged UV exposure |
| Cost | Higher | Low to moderate |
| Environmental Impact | Recyclable, longer lifespan | Recyclable, widely available |
| Typical Applications | Industrial piping, chemical plants | Residential plumbing, sewage, irrigation |
Introduction to Polyphenylene Oxide and Polyvinyl Chloride
Polyphenylene oxide (PPO) is a high-performance thermoplastic known for its excellent dimensional stability, chemical resistance, and thermal stability, making it suitable for specialized piping applications requiring durability and resistance to harsh environments. Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) is a widely used thermoplastic polymer characterized by its affordability, ease of fabrication, corrosion resistance, and widespread use in plumbing, irrigation, and industrial piping. Both materials serve distinct purposes in pipe manufacturing, with PPO favored for high-temperature and chemically aggressive conditions, while PVC dominates in cost-sensitive, general-purpose piping systems.
Chemical Structure and Composition Comparison
Polyphenylene oxide (PPO) features a rigid aromatic polymer backbone composed of phenylene rings linked by oxygen atoms, providing high thermal stability and chemical resistance. In contrast, Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) consists of a vinyl polymer chain with repeating vinyl chloride monomers, characterized by chlorine atoms that contribute to its durability and resistance to corrosion. The distinct chemical structures dictate PPO's superior heat tolerance and electrical insulation properties, while PVC offers cost-effective corrosion resistance and ease of processing for pipe applications.
Mechanical Properties: Strength and Durability
Polyphenylene oxide (PPO) exhibits higher tensile strength and superior impact resistance compared to polyvinyl chloride (PVC), making it more suitable for high-stress pipe applications requiring enhanced mechanical durability. PPO pipes demonstrate excellent thermal stability and resistance to cracking under mechanical loads, whereas PVC pipes, while cost-effective, have lower resistance to UV degradation and tend to become brittle over time. The superior mechanical properties of PPO result in a longer lifespan and better performance in demanding environments, emphasizing its advantage in structural integrity and durability for pipe systems.
Thermal Resistance and Operating Temperatures
Polyphenylene oxide (PPO) offers superior thermal resistance with a continuous operating temperature up to 190degC, outperforming polyvinyl chloride (PVC), which typically withstands temperatures only up to 60-70degC. PPO maintains mechanical integrity and dimensional stability under higher thermal stress, making it ideal for applications requiring sustained heat exposure. PVC pipes are more prone to deformation and chemical degradation at elevated temperatures, limiting their use in hot water or industrial fluid transport where temperature resilience is crucial.
Chemical Resistance to Corrosive Substances
Polyphenylene oxide (PPO) exhibits superior chemical resistance to a wide range of corrosive substances, including acids, bases, and organic solvents, making it highly suitable for demanding industrial pipe applications. In contrast, polyvinyl chloride (PVC) offers moderate chemical resistance but is vulnerable to degradation when exposed to strong solvents, ketones, and aromatic hydrocarbons. PPO's enhanced thermal stability and corrosion resistance ensure longer service life in aggressive chemical environments compared to PVC pipes.
Ease of Fabrication and Installation
Polyphenylene oxide (PPO) pipes offer superior ease of fabrication due to their higher thermal stability and excellent dimensional stability, allowing for precise cutting, welding, and bending without warping. Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) pipes are widely favored in installation for their low cost and compatibility with solvent cement joining methods, but they can become brittle under UV exposure and extreme temperatures, complicating handling. PPO pipes generally enable faster installation times with fewer fittings due to their ability to withstand higher pressures and temperatures, reducing the need for additional support or frequent replacement.
Cost Analysis and Market Availability
Polyphenylene oxide (PPO) pipes generally exhibit higher initial material costs compared to polyvinyl chloride (PVC) pipes due to their superior thermal stability and chemical resistance, making them suitable for specialized applications. PVC pipes dominate market availability with extensive production facilities and established supply chains, resulting in lower prices and widespread accessibility for standard plumbing and irrigation uses. Cost efficiency and market penetration heavily favor PVC, while PPO offers performance benefits justified by higher investment in niche industrial sectors.
Environmental Impact and Recyclability
Polyphenylene oxide (PPO) pipes exhibit superior environmental benefits due to their higher thermal stability and resistance to chemical degradation, leading to longer service life and reduced waste generation compared to polyvinyl chloride (PVC) pipes. PVC pipes contribute significantly to environmental pollution during production and disposal, releasing harmful dioxins and chlorinated compounds, whereas PPO is more eco-friendly with fewer toxic emissions. Regarding recyclability, PPO can be more efficiently recycled into high-quality products through thermal and mechanical processes, contrasting with PVC's limited recyclability hindered by its chlorine content and plasticizers.
Common Applications in Piping Systems
Polyphenylene oxide (PPO) pipes are commonly used in industrial applications requiring high-temperature resistance, chemical stability, and excellent dimensional stability, such as in chemical processing and automotive coolant systems. Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) pipes are widely utilized in residential and commercial plumbing, irrigation, and drainage systems due to their cost-effectiveness, corrosion resistance, and ease of installation. PPO offers superior mechanical strength and thermal performance, making it suitable for specialized environments, whereas PVC remains the preferred choice for general-purpose water and waste piping systems.
Summary: Choosing the Right Material for Your Pipes
Polyphenylene oxide (PPO) pipes offer superior heat resistance, chemical stability, and dimensional strength, making them ideal for high-temperature and corrosive environments. Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) pipes are cost-effective, lightweight, and provide excellent corrosion resistance for general water supply and drainage applications. Selecting between PPO and PVC depends on application-specific factors such as temperature tolerance, chemical exposure, budget constraints, and mechanical durability requirements.
Infographic: Polyphenylene oxide vs Polyvinyl chloride for Pipe
 azmater.com
azmater.com