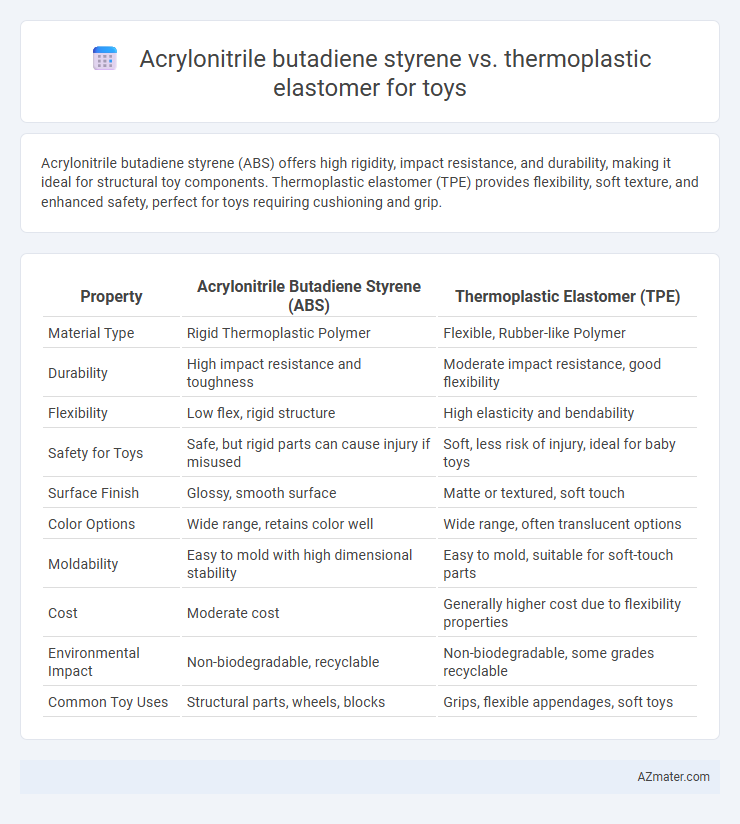
Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS) offers high rigidity, impact resistance, and durability, making it ideal for structural toy components. Thermoplastic elastomer (TPE) provides flexibility, soft texture, and enhanced safety, perfect for toys requiring cushioning and grip.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS) | Thermoplastic Elastomer (TPE) |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Rigid Thermoplastic Polymer | Flexible, Rubber-like Polymer |
| Durability | High impact resistance and toughness | Moderate impact resistance, good flexibility |
| Flexibility | Low flex, rigid structure | High elasticity and bendability |
| Safety for Toys | Safe, but rigid parts can cause injury if misused | Soft, less risk of injury, ideal for baby toys |
| Surface Finish | Glossy, smooth surface | Matte or textured, soft touch |
| Color Options | Wide range, retains color well | Wide range, often translucent options |
| Moldability | Easy to mold with high dimensional stability | Easy to mold, suitable for soft-touch parts |
| Cost | Moderate cost | Generally higher cost due to flexibility properties |
| Environmental Impact | Non-biodegradable, recyclable | Non-biodegradable, some grades recyclable |
| Common Toy Uses | Structural parts, wheels, blocks | Grips, flexible appendages, soft toys |
Introduction to Toy Materials: ABS vs TPE
Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS) and thermoplastic elastomer (TPE) are two popular materials in toy manufacturing due to their distinct properties and safety profiles. ABS offers rigidity, excellent impact resistance, and vibrant color retention, making it ideal for structural components and hard toys with complex shapes. TPE provides softness, flexibility, and a rubber-like feel, enhancing toy safety and tactile comfort, especially in products designed for infants and toddlers.
Composition and Structure: ABS and TPE Explained
Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS) is a rigid thermoplastic composed of acrylonitrile, butadiene, and styrene polymers that provide high impact resistance, toughness, and dimensional stability ideal for durable toy components. Thermoplastic elastomers (TPE) consist of a blend of rubber and plastic materials, offering flexibility, elasticity, and soft-touch properties that enhance safety and comfort in toy design. The structural rigidity of ABS supports detailed molding and strength, whereas TPE's elastomeric microphase-separated structure delivers superior flexibility and resilience for interactive and squeezable toy elements.
Mechanical Properties: Strength and Flexibility Comparison
Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS) exhibits high tensile strength and impact resistance, making it ideal for durable toy components subject to rough handling. Thermoplastic elastomers (TPE) offer superior flexibility and elasticity, providing enhanced shock absorption and safer, softer toy parts. ABS excels in rigidity and structural integrity, while TPE prioritizes pliability and comfort, influencing toy design based on required mechanical performance.
Safety and Toxicity: Child-Friendly Considerations
Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS) exhibits strong mechanical properties but can release potentially harmful chemicals like styrene and acrylonitrile, raising safety concerns for children. Thermoplastic elastomers (TPE) offer increased flexibility and lower toxicity levels, making them more suitable for child-friendly toys due to their non-toxic and hypoallergenic nature. Regulatory compliance and thorough safety testing are essential for both materials to ensure non-toxic, BPA-free, and phthalate-free formulations safe for prolonged child contact.
Manufacturing Processes for ABS and TPE Toys
Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS) toys are primarily manufactured using injection molding, which allows for high precision, durability, and ease of mass production with complex shapes. Thermoplastic elastomer (TPE) toys utilize injection molding or extrusion processes, offering flexibility and softness while maintaining durability and recyclability. The manufacturing of ABS emphasizes rigidity and structural integrity, whereas TPE processes focus on elasticity and comfort, influencing tool design and cycle times within production lines.
Durability and Longevity in Toy Applications
Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS) offers superior impact resistance and structural strength, making it highly durable for rigid toy components that undergo frequent stress and drops. Thermoplastic elastomers (TPE) provide excellent flexibility and resilience, ideal for parts requiring repeated bending or squeezing without cracking but may wear faster under constant mechanical abrasion. ABS generally ensures longer longevity in toys with hard, load-bearing parts, while TPE excels in soft, flexible components prone to deformation.
Design Versatility: Moldability and Surface Finish
Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS) offers superior moldability with high impact resistance and a smooth, glossy surface finish ideal for detailed toy designs. Thermoplastic elastomers (TPE) provide enhanced flexibility and soft-touch textures but may lack the rigid structural integrity and sharp surface detail achievable with ABS. Both materials allow for customized surface finishes, but ABS excels in precision molding and durability for intricate toy components.
Cost Analysis: Production and Material Expenses
Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS) generally incurs higher production costs due to its rigid structure and complex molding process, whereas thermoplastic elastomers (TPE) offer lower material expenses because of their flexible properties reducing machining requirements. ABS raw material prices average around $1.80 to $2.20 per pound, while TPE costs vary between $1.50 and $2.00 per pound, influencing overall budget allocation for mass toy production. Manufacturers must weigh ABS's durability benefits against TPE's cost-efficiency in materials and streamlined manufacturing to optimize toy production budgets.
Environmental Impact and Recyclability
Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS) offers durable, rigid properties for toys but poses environmental challenges due to its non-biodegradable nature and limited recyclability, often ending up in landfills. Thermoplastic elastomers (TPE) provide enhanced environmental benefits with greater recyclability and lower ecological toxicity, supporting more sustainable lifecycle management. Choosing TPE for toy manufacturing reduces plastic waste and facilitates circular economy practices compared to traditional ABS materials.
Choosing the Right Material: ABS or TPE for Toys
Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS) is prized for its high impact resistance, rigidity, and glossy finish, making it ideal for durable, structured toy parts like building blocks and action figures. Thermoplastic elastomer (TPE) offers superior flexibility, softness, and safer tactile feel, suitable for squeezable or wearable toys that require a gentle touch and enhanced grip. Selecting between ABS and TPE depends on the toy's functional demands--ABS for hard, impact-resistant components and TPE for elastic, safe, and comfortable play elements.
Infographic: Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene vs Thermoplastic elastomer for Toy
 azmater.com
azmater.com